Nanotechnology in action
On September 11, Channel One showed Russian tests of the world’s most powerful vacuum bomb, comparable in effectiveness to nuclear weapons. As noted on air, the new aerial bomb will replace a number of previously created nuclear weapons.
“The test results of the created aircraft munition showed that its effectiveness and capabilities are comparable to nuclear munitions. At the same time, I especially want to emphasize this, the effect of this ammunition does not pollute the environment at all,” said Deputy Chief of the General Staff of the RF Armed Forces Alexander Rukshin.
According to Rukshin, the new warhead “will provide us with the opportunity to realize the security of the state and at the same time counter international terrorism in any situation and in any region.”
The explosive contained in this aerial bomb is much more powerful than TNT. This, according to Channel One, was achieved through the use of nanotechnology.
“This, in turn, made it possible to reduce the requirements for accuracy, hence the reduction in cost - the quality that we need in modern conditions. We received relatively cheap ammunition with high destructive properties,” said Yuri Balyko, head of a department at one of the research institutes of the Russian Ministry of Defense.
The Ministry of Defense, meanwhile, declares that the new military development does not violate a single international treaty.
At the same time, Western media view the emergence of reports about powerful Russian weapons as yet another intention of the Kremlin to demonstrate its power to the world.
Modified bombs
The serial version ODAB-500PM with a radio altimeter can be dropped from an aircraft from an altitude of 200 to 12,000 meters and at a speed of 50-1,500 km/h. At an altitude of 30 to 50 m, a braking parachute is released to stabilize the bomb body and slow its fall. At the same time, a radio altimeter is launched, measuring the instantaneous height of the ammunition above the ground. At a height of 7 to 9 m, the bomb body is detonated, and 193 kg of liquid explosive of an unknown recipe is sprayed into the air, after which a gas cloud is formed. With a delay of 100 to 140 milliseconds, this cloud detonates due to the detonation of an additional charge. The explosion creates very high temperatures and pressures of 20 to more than 30 bar for a short time. The force of the explosion is approximately equivalent to 1000 kg of TNT. The effective range against field fortifications is 25 m. For cars and aircraft, as well as for living targets, the radius of the bomb is 30 m.
The ODAB-500PMV version is optimized for use from helicopters at a bombing altitude of 1100-4000 m at a speed of 50-300 km/h, although it can also be dropped from aircraft, i.e. it is all-altitude.
Why is “the father of all bombs” better than “the mother”?
Before this, the most powerful vacuum bomb in the world was in service with the American Air Force. The first tests of the GBU-43/B MOAB (Massive Ordnance Air Burst) bomb took place in 2003: footage was shown by all television companies in the world. Then this weapon was called the “mother of all bombs.” By analogy, Russian developers nicknamed their new ammunition: “the father of all bombs.”
The Russian aerial bomb is superior to its American counterpart in all respects. The explosive mass is smaller, but the bomb is four times more powerful. The temperature at the epicenter of the explosion is twice as high. In terms of total area of destruction, our bomb is 20 times larger than the American one.
Explosive character
The uranium nucleus contains 92 protons. Natural uranium is mainly a mixture of two isotopes: U238 (which has 146 neutrons in its nucleus) and U235 (143 neutrons), with only 0.7% of the latter in natural uranium. The chemical properties of isotopes are absolutely identical, therefore it is impossible to separate them by chemical methods, but the difference in masses (235 and 238 units) allows this to be done by physical methods: a mixture of uranium is converted into gas (uranium hexafluoride), and then pumped through countless porous partitions. Although the isotopes of uranium are indistinguishable either in appearance or chemically, they are separated by a chasm in the properties of their nuclear characters.
The fission process of U238 is a paid process: a neutron arriving from outside must bring with it energy - 1 MeV or more. And U235 is selfless: nothing is required from the incoming neutron for excitation and subsequent decay; its binding energy in the nucleus is quite sufficient.
Chain reaction When hit by neutrons, the uranium-235 nucleus easily splits, producing new neutrons. Under certain conditions, a chain reaction begins.
When a neutron hits a fission-capable nucleus, an unstable compound is formed, but very quickly (after 10−23−10−22 s) such a nucleus falls apart into two fragments that are unequal in mass and “instantly” (within 10−16−10− 14 c) emitting two or three new neutrons, so that over time the number of fissile nuclei can multiply (this reaction is called a chain reaction). This is only possible in U235, because greedy U238 does not want to share from its own neutrons, whose energy is an order of magnitude less than 1 MeV. The kinetic energy of fission product particles is many orders of magnitude higher than the energy released during any chemical reaction in which the composition of the nuclei does not change.
Metallic plutonium exists in six phases, the densities of which range from 14.7 to 19.8 kg/cm3. At temperatures below 119 degrees Celsius, there is a monoclinic alpha phase (19.8 kg/cm3), but such plutonium is very fragile, and in the cubic face-centered delta phase (15.9) it is plastic and well processed (it is this phase that they are trying to preserve using alloying additives). During detonation compression, no phase transitions can occur—plutonium is in a state of quasi-liquid. Phase transitions are dangerous during production: with large parts, even with a slight change in density, a critical state can be reached. Of course, this will happen without an explosion - the workpiece will simply heat up, but a discharge of nickel plating may occur (and plutonium is very toxic).
What is a vacuum bomb?
A vacuum bomb (the old name ODAB - volumetric detonating aircraft bombs or FAE - fuel air explosive) is created based on the effect of a volumetric explosion of dust, gas and dust-air clouds. They use liquid fuels (ethylene oxide) as the main charge.
When such ammunition encounters an obstacle, the explosion of a small charge destroys the bomb body and sprays the fuel, which, turning into a gaseous state, forms an aerosol cloud in the air. As soon as the cloud reaches a certain size, it is undermined by special grenades fired from the bottom of the bomb. The resulting high-pressure zone, even in the absence of a supersonic shock wave, effectively hits enemy personnel, freely penetrating into areas inaccessible to fragmentation ammunition. During the formation period, the cloud flows into trenches and shelters, thereby increasing its destructive ability.
Links
- Volumetric explosion ammunition
- Mixtures contained in Volume Explosion Ammunition
| Types of artillery ammunition | |
| Concrete | Armor-piercing high-explosive | Armor-piercing | Armor-piercing incendiary | Incendiary | Tracer | Impact core | Cumulative | Cumulative-fragmentation | Shrapnel | Buckshot | Shrapnel | High explosive | High Explosive | Thermobaric | Chemical | Nuclear | Propaganda | Smoke | Lighting | Sighting and target designating | Special Purpose Ammunition | Non-lethal ammunition |
Operating principle of a vacuum bomb
A cloud of sprayed flammable material explodes in the air. The main damage is caused by a supersonic air shock wave and high temperature. Because of this, the soil after the explosion is more similar to lunar soil, but there is no chemical or radioactive contamination.
A typical "vacuum bomb" consists of a container of reagent and two independent explosive charges. After the ammunition is dropped or fired, the first charge opens the container at a certain height, spraying the reagent into a cloud that mixes with atmospheric oxygen (the size of the cloud depends on the amount of reagent). This mixture then envelops objects and penetrates into structures. At this moment, the mixture is undermined by a second charge, resulting in the formation of a powerful shock wave. We took an example of such an explosion from the website of the Weapons Division of the US Naval Air Warfare Center, China Lake, California:
Where can you use a vacuum bomb?
In one of the materials of the magazine “Military Knowledge” they wrote that this type of weapon can be effectively used both against personnel outside shelters, and against weapons and military equipment, fortified areas and individual shelters. It can also be used to create passages in minefields, clear landing sites for helicopters, destroy communications centers and neutralize strongholds during street fighting within the city, HRW reports. A vacuum bomb is capable of completely destroying vegetation and agricultural crops in a certain area.
With the simultaneous use of a large number of ammunition, the destruction can be more than significant. The effect of such weapons is also enhanced in enclosed spaces. It is 12-16 times more powerful than conventional explosives when used on objects with a large surface area, such as frame buildings, dugouts and transport hangars.
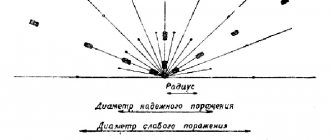
Damaging factors of a vacuum bomb
Nothing is known yet about the new Russian weapon. This aerial bomb does not even have an official name yet, it only has a secret code.
Here's what the 1993 Defense Intelligence Agency report says about a similar bomb of lower power:
— The mechanism of destruction of living objects has no analogues. The damaging factor is the shock wave, or more precisely, the rarefaction (vacuum) that follows it, leading to rupture of the lungs... If the explosive component simply burns out without detonating, the victims receive severe burns and may also inhale the burning substance. Since ethylene oxide or propylene oxide, the most commonly used munitions in such munitions, are highly toxic, an unexploded munition would pose the same danger to personnel caught in its cloud as most chemical agents.
As stated in a separate US CIA study, “the impact of a volume detonating munition explosion in confined spaces is enormous. At the flashpoint, people simply burn to ashes. Those located near the perimeter are highly likely to receive internal, and therefore invisible, damage, including ruptured eardrums and destruction of the organs of the inner ear, severe concussion, rupture of the lungs and other internal organs; loss of vision is also possible.”
Another Defense Intelligence Agency document suggests that because “the shock wave and pressure drop cause minimal damage to brain tissue, victims of a volume detonating munition may remain conscious and suffer for a few seconds or minutes until death from the explosion occurs.” suffocation."
History of creation and application
Volumetric explosion ammunition (like many other weapons) owes its birth to the evil German weapons genius. During the last world war, the Germans paid attention to the power of explosions that occur in coal mines. They tried to use the same physical principles to produce a new type of ammunition.
Nothing real came of it, and after the defeat of Germany, these developments went to the allies. They were forgotten for many decades. The Americans were the first to remember about volumetric explosions during the Vietnam War.
In Vietnam, the US made extensive use of combat helicopters, with which they supplied their troops and evacuated the wounded. The construction of landing sites in the jungle became a rather serious problem. Clearing an area for just one helicopter to land and take off required the hard work of an entire sapper platoon for 12-24 hours. It was not possible to clear the sites using conventional explosions, because they left behind huge craters. That’s when they remembered about volumetric explosion ammunition.
A combat helicopter could carry several similar ammunition on board, the explosion of each of them creating a platform quite suitable for landing.
The combat use of bulk ammunition also turned out to be very effective; they had a strong psychological effect on the Vietnamese. It was very difficult to hide from such an explosion even in a reliable dugout or bunker. The Americans successfully used volumetric explosion bombs to destroy partisans in tunnels. At the same time, the USSR began developing similar ammunition.
The Americans equipped their first bombs with various types of hydrocarbons: ethylene, acetylene, propane, propylene and others. In the USSR they experimented with a variety of metal powders.
However, the first generation volumetric explosion ammunition was quite demanding in terms of bombing accuracy, was highly dependent on weather conditions, and did not work well at subzero temperatures.
To develop second-generation ammunition, the Americans used a computer on which they simulated a volumetric explosion. At the end of the 70s of the last century, the UN adopted a convention banning these weapons, but this did not stop their development in the USA and the USSR.
Today, third-generation volumetric explosion ammunition has already been developed. Work in this direction is actively carried out in the USA, Germany, Israel, China, Japan and Russia.
Known Russian volume-detonating ammunition and high-yield ammunition
According to Human Rights Watch:
- ODAB-500PM, aerial bomb of volumetric detonating action.
- KAB-500Kr-OD, airborne volume-detonating bomb with television guidance.
- ODS-OD BLU container with 8 volumetric detonating cluster bombs.
- 300-mm 12-barrel MLRS 9A52-2 (Smerch), the warhead of a high-power rocket (based on a powder reagent).
- 220-mm 16-barrel MLRS 9P140 (Uragan), the warhead of a high-power rocket (based on a powder reagent).
- ATGM "Sturm", launched from a helicopter, the warhead has a volumetric detonating effect.
- ATGM "Attack", launched from a helicopter, the warhead has a volumetric detonating effect.
- 80-mm aircraft missile S-8D (S-8DM), the warhead of a volumetric detonating effect.
- Long-range anti-tank guided missile system "Kornet-E": the warhead of a thermobaric (volume-detonating) missile.
- RPO-A (Shmel) infantry flamethrower. The fatal impact and destruction inside the structure is reported to be 80 cubic meters. In open areas, the area of effective destruction is 50 square meters.
- AS-11 and AS-12, missile warheads. Most of the information is classified.
Sergey Minenko
The original version of the aerial bomb
It was designated ODAB-500P and had a mechanical proximity fuse. The algorithm of its operation includes the release of a cable bundle with a contact leader device at the end from the nose of a flying bomb. Braking of the leader by the earth's surface (or a ground obstacle) leads to the activation of the contacts of the inertial contactor included in the electrical circuit, detonation of the bomb body and the release of 145 kg of liquid explosives into the air. After a short time delay sufficient for the formation of a gas cloud, the initiating charge installed in the tail section is detonated, and a volumetric explosion begins.
Design
The ODAB-500 bomb (and its modifications) has a cylindrical elongated body shape with a round cross-section and a pointed tip. At its rear there are four flat stabilizers, around which there is an annular wing. In front of the bomb there is an electric cocking mechanism. In the central part there is a cylindrical container with liquid explosives and a dispersing charge. At the rear of the bomb there is a container for a braking parachute and an initiating secondary charge. The length of the ammunition is 2.28-2.6 m, and the weight is from 520 to 525 kg, depending on the version. The diameter of the body is 500 mm, and the span of the stabilizer wings is also about 500 mm.