What's inside the Armata tank
≡ November 14, 2015
← Ukrainian pensions
Why were manuscripts encrypted →
The promising T-14 Armata tank was first shown to the general public at the Victory Parade on Red Square in Moscow on May 9, 2015 and was highly appreciated by Russian and foreign experts.
The main difference between the T-14 "Armata" and existing analogues is that it has an isolated armored capsule in which the crew is located. A shell from the tank's 125mm cannon is capable of burning through a meter of steel. Designed to conduct maneuverable combat operations against any enemy as part of tank and motorized rifle units as the main multi-purpose combat weapon in conditions of the use of nuclear weapons and other types of weapons of mass destruction.
Performance characteristics:
Crew…………………………………………..3 people Combat weight……………………………48 t Weight with kit for urban combat…… …………..53 t Length with gun forward …………………10.8 m Width ………………………………………………………3.5 m Width across screens……… ………………….3.9m Height………………………………………………………..3.3m
Weapons:
1x125mm smoothbore gun-launcher 2A82-1M. Ammunition 40 rounds (of which 32 in the automatic loader)
1x7.62mm PKTM machine gun in a remote-controlled installation. Ammunition 2000 rounds in a continuous belt
Power point:
X-shaped turbocharged multi-fuel diesel 2V-12-3A. Power 1200…1500hp
Transmission: mechanical, “robotic”
Fan type cooling system (2 fans)
Suspension - controlled vane shock absorbers, hydraulic shock absorbers
Tracks with parallel track with steel treadmill and the ability to install asphalt shoes, 93 links
Maximum speed………………………………….75-80km/h
Average speed over rough terrain…..45-50km/h
Power reserve (without barrels)……………………………………..500 km
Combined, modular protection, universal dynamic protection complex, Afganit KAZ, system for setting up multispectral curtains, upper hemisphere protection system, electromagnetic protection system, radio fuses suppression complex.
Mine protection of the bottom in the crew area
Fire control system:
Day-night multi-channel gunner's sight
Commander's sight panoramic day-night multi-channel
Target detection and recognition ranges are at the level of the world's best analogues. Complete duplication of the work of the commander and gunner has been implemented.
Backup low-level television sight with autonomous power supply.
Automatic target tracking. Device for automatically accounting for thermal bending of the barrel. Full all-round visibility for all crew members thanks to self-powered TV cameras.
Integration into automated control systems with the ability to fire according to external target designations.
Ergonomics ensure that the crew remains continuously inside the tank for 72 hours.
Warranty life…………14000km
Tags: weapons • interesting • educational • Russia • tank • what's inside
Comments:
Comments for the site Cackl e
T-14 "Armata"
History of the issue
The development of a new (third post-war) generation tank began in the USSR a little later than the creation of the new main tank T-64A in the 70s. Leningrad, Chelyabinsk and, later, Kharkov designers participated in the work called “Topic 101”.
A number of projects were implemented, both with traditional and new layouts, most of which remained on drawings or in the form of mock-ups.
Tanks with traditional solutions, such as the Object 255 and Object 480, did not provide a significant advantage over the modernized versions of the T-64A, T-72 and the tank with a gas turbine engine. Tanks with a new layout (Object 450) required a long search for both layout solutions and the creation of fundamentally new components.
These works are described in detail in the material TANKS AND PEOPLE. Diary of the chief designer Alexander Alexandrovich Morozov. Part 2.
At the end of the 70s and throughout the 80s, the Kharkov design bureau was chosen as the lead design bureau on the topic of creating a promising tank of the 90s. These events are considered from the point of view of one of the developers of the tank, responsible for its electronic component - The last breakthrough of Soviet tank builders (diary of a participant in the development of the Boxer tank). Variants of the configurations considered in the 80s are discussed in the material - Tanks “Rebel”, “Boxer”, “Hammer” (object 490, object 490A, object 477).
The development of the promising tank was never completed before the collapse of the USSR.
The design bureaus remaining in Russia began to create a promising tank based on the existing groundwork. Among the most advanced, we can mention the Leningrad Object 299 (JSC Spetsmash), which had a very bold layout. Which, along with objective reasons characteristic of the 90s, prevented its implementation.
Omsk Object 640 “Black Eagle” was also a project with very controversial advantages, which is why it was chosen for demonstration (VTTV 1997) and was even promoted abroad.
Nizhny Tagil (UKBTM) had a project for the evolutionary development of the T-72, which did not provide significant reasons for replacing the T-72 in production, since the solutions contained in it could be implemented during modernization.
As the economic situation improved, work intensified. Here, as in the 70s, two projects were implemented, one of them with high technical risk, the other with traditional and less risky solutions. The first is Nizhny Tagil Object 195 “T-95” (JSC UKBTM) and the second Omsk project Development of a unified combat compartment, theme “Burlak” (JSC KBTM).
In 2009, the closure of these projects was announced.
One gets the feeling that a promising tank will never be created in the post-Soviet space.
But in 2015, at the Victory Parade, products based on the Armata platform were presented to the general public - the new generation T-14 tank and the T-15 heavy infantry fighting vehicle with front-mounted MTO.
With the advent of the first shots of the Armata, a lot of speculation about this tank appeared. Some gave it embellished qualities, others called it veneer and invented non-existent shortcomings.
Layout
The scheme with the concentration of the crew in the front part of the hull requires maximum automation of the control of weapons installed in the fighting compartment, creating a number of technical difficulties. This scheme is of interest due to the great potential for enhancing crew protection, including from weapons of mass destruction, as well as improving the conditions for interaction between personnel.
When placing 3 crew members shoulder to shoulder, as is done, the crew is accommodated in fairly comfortable conditions. But at the same time, it is not possible to provide sufficient protection for the onboard part of the crew compartment. Even with a reduction in the width of the space allocated for each crew member from 70 to 60 cm, the ability to provide protection when fired into the side areas is minimal. At the same time, railway dimensions do not allow increasing the width of the hull.
In addition, such a scheme does not provide a good all-round view to the tank commander, which in a number of countries, despite the development of technical vision equipment, is considered an important quality. More details - Development of a promising tank in the USA.
This scheme has been considered more than once since the 70s in different countries, but has not found application in tank building with the exception of experimental models, such as the American FTTB.
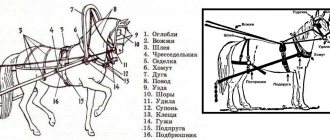
Crew capsule. The driver's seat is located on the left side of the tank.
The driver's display complex (DKMV) installed on the tank is designed to replace pointer instrumentation and provide solutions to control problems, monitoring functioning, operational technical diagnostics of chassis systems and assemblies and issuing recommendations for the operation of the facility.
Gear shifting is carried out using buttons on the steering wheel. The most important information about the movement parameters is displayed directly on the remote display on the control wheel. The monitor displays an image from a forward-looking thermal imaging device located on the upper part of the bow assembly of the hull.
video viewing device and control button block
View of the driver's seat from the gunner's seat located in the center of the crew capsule
PMF-5.0 monitors with high-resolution LCD panels from the “5” series of multifunctional panels.
On the left in the photo is the gunner's control panel.
PMF-5.0 (5.1) products have an expanded set of interfaces, including a touch panel with multi-touch function, etc. Developed by the Instrument Engineering Design Bureau (UKBP), which is part of the Radioelectronic Technologies Concern.
The information control system displays information on the status of weapon systems, security, mobility, etc. Information messages are displayed on the screen below, critical messages are shown in red, important ones in yellow, and regular ones in white.
View of the commander's and gunner's positions. Commander panels (3) right side of the photo.
They display video information from external sources, synthesized video information from devices (TV cameras, sighting systems), exchange of information, output of navigational cartographic information, as well as input and transmission of information to control the main systems of the tank. Control panels are installed under the panels, the gunner and commander have similar devices
The devices are manufactured in the Russian Federation and are unified for the entire line of promising ground vehicles (Armata, Kurganets, Boomerang).
The production and assembly of devices is still done by hand, but their reliability is increasing.
It is on these devices that the tank control is based.
Commander's place. A visual overview of the area is carried out through three viewing devices. The main information is supposed to be obtained through TV cameras located around the perimeter of the tank and a multi-channel panoramic sight-surveillance device.
This decision can be called very bold, especially for ground-based equipment, where the conditions are much more stringent than in aviation. On the right is the AVSKU-E control panel (intercom, switching and control equipment). Under the remote control is an optical sensor of the fire-fighting equipment system (OD1-1S). Installation of optical sensors and high-speed cylinders in the fighting compartment ensures fire detection and release of fire extinguishing agent in a time of no more than 150 ms. Such sensors are installed along the entire perimeter of the capsule
View of the back of the crew capsule. HVAC systems visible
Despite the many digital innovations, some traditions in post-Soviet tank building are unshakable, for example, not very neat welding seams.
Comfortable seats – a big step forward compared to previous generation tanks
View of the side of the crew capsule from the gunner's position. Crew seats have a wide range of adjustments, ensuring crew comfort
Protection
The layout of the "Armata" is similar to that used on the "Object 195". Increased crew protection is achieved by transferring the crew workstations located in the turret to a highly protected bow module of the hull, the protection weight of which can be increased by the amount of reduction in the weight of the turret protection, due to a reduction in its dimensions and the internal volume intended for crew workstations.
Increased protection and survivability of the crew in the module is achieved by reducing the total area of the internal surfaces of the control module (compared to the habitable compartment of tanks of a classical layout).
The weapons module is separated from the control module by a transverse partition, which reduces the likelihood of injury to the crew in the module.
Fire and explosion safety of the module and crew survivability are achieved by complete separation of the crew's work stations from the sealed fuel volume and from the ammunition.
Schematic representation of the general layout of the T-14 "Armata" tank (similar to the T-95)
The advantage indicated by the authors of the patent, along with those listed above, also has one more drawback - insufficient protection of the tower. They will come to this question, just as the developers of the promising Soviet-era tanks, “Molot” and “Nota,” came to.
The tank's protection complex includes combined and dynamic protection installed in the front part of the hull with the crew capsule, providing protection.
Also, dynamic protection is installed on the sides of the hull (before the engine and transmission compartment). At the front, the track branches are blocked by remote protection, which is especially important when placing the crew in the hull. In the front part of the hull side, the DZ blocks are made folding for ease of maintenance of the chassis. In general, the solutions for installing the remote sensing system are reminiscent of its installation on the Nota tank (KhKBM).
The turret is covered with dynamic protection on top, and the ERA is also installed to protect the capsule, including the hatches. Part of the hull side in the MTO area is covered with lattice screens.
The DZ covers both the upper and lower parts of the nose assembly of the hull.
Externally, the remote control is similar to that installed on the T-95. the working surface of the thrown plate is significantly increased
The technical requirements for a promising tank, set back in Soviet times, required protection from above from cumulative ammunition with an armor-piercing ability of 250-300 mm. Despite the small size of the roof and hatches, which is clearly visible in the photographs, we can assume that this requirement has been met.
The most important feature of the tank is the use of a complex of means for protection against high-precision weapons. They include an active protection complex that provides cover in the range of 120° in the direction of the tank turret and a complex for setting up multispectral curtains and a complex of laser and UV radiation indicators installed along the perimeter of the turret.
To shoot decoy IR and radar targets quickly and accurately in the direction of the attack vehicle, no matter where it approaches, without rotating the turret, the use of quickly rotating grenade launchers is required.
Thus, protection from ammunition attacking in a horizontal projection is provided by the KAZ and the jamming complex (in two rotating installations on the turret). And from attackers from above - a jamming complex (in two fixed installations directed upward).
An electromagnetic mine protection system is also installed.
Tank protection complex against WTO
Along the perimeter of the tower there are indicators of laser irradiation and ultraviolet radiation (missile launch detection system).
Under the front indicators of irradiation and missile launch there are radars with phased array detection and target designation of the KAZ. On the roof of the tower there is a system for launching multispectral interference in rotary and fixed installations
The irradiation and launch indicators are covered with shutters in photographs and during demonstrations at the parade. Next to the front and side view TV camera indicator block
KAZ launchers are installed under the radar unit. KAZ "Afganit" is a development of the "Drozd" system. This development of TsKIB SOO dates back to the 80s. The difference from the Drozd is the ability to correct the counter-ammunition being fired in azimuth (~0.5 m) and vertically (±4°). The complex has the ability to destroy anti-tank missiles attacking a target while flying, but does not protect against attackers from above
To reduce the visibility of the tank, a lightweight casing with geometric characteristics optimal for reducing visibility in the radar wavelength range is installed on the turret
Side view of the T-14 Armata, in the central third of the hull there are EZ blocks installed, optimized for protection against cumulative warheads at an impact angle close to normal
Part of the hull side in the MTO area is covered with lattice screens. The fastenings of the fuel barrels are visible. At the parade in Moscow, the Armatas were without them. Apparently they think it's not fashionable
Firepower
The tank is equipped with a 125mm high-power 2A82-1M cannon. Judging by the patents, the gun can use both standard shots and newly developed ones with an increased powder charge. Ammunition capacity: 40 rounds (of which 32 are in the automatic loader, 8 are portable). The ideology of the AZ is retained from the “Object 195”, but the small ammunition load of 152 mm is increased to an acceptable value.
7.62mm PKTM machine gun in a remote-controlled installation on a platform combined with a panoramic sight-observation device. Ammunition capacity: 2000 rounds of continuous ammunition.
The absence of a coaxial machine gun is a strange and undoubtedly wrong decision. This will lead to increased consumption of ammunition by the gunner on targets that do not correspond to 125 mm shells, and will distract the commander from monitoring the battlefield when using a single machine gun. Some justification for this may be in the form of an increase in automated ammunition by 10 shots compared to the T-72. The 30 mm automatic cannon, as was on the Molot and T-95, is also missing.
AZ diagram of an uninhabited tower.
Shells and charges are arranged vertically.
The conveyor is raised above the bottom of the hull to prevent jamming when the bottom sag (mine explosion).
The idea of installing such a gun arose a long time ago, back in the late 70s (D-91T) and continued later, including the “Object 187”. Its potential is 30% higher than the standard one.
It is known that high-power shots 3VBM22 with BPS 3BM59 "Svinets-1" and 3VBM23 with BPS 3BM60 "Svinets-2" with L=740 mm have increased armor penetration by 100-150 compared to the standard one (3BM44 "Mango" - 440 mm) mm . Improved BPS developed for the Armata will likely reach a level of more than 800 mm (450/60°). The possibility of using both standard ammunition and newly developed ammunition of increased power is provided.
Whether or not this has been achieved is an open question; all these topics have been ongoing for more than two decades. So the same “Svinets-1” and “Svinets-2” have been formally included in the ammunition load of the modernized T-72BA, T-80UA, T-80UE1 since 2004.
To combat infantry, the 3VOF128 “Telnik”-1 shot was developed (Completion of the development work - 2014). The projectile implements a trajectory explosion on approach to the target (at the lead point) with the target being hit by the axial flow of the GGE; trajectory explosion over the target with the target being hit by a circular field of hull fragments; impact ground burst with instantaneous (fragmentation) action; impact ground explosion with high-explosive fragmentation action (small deceleration); impact ground rupture with a setting for penetrating high-explosive action (large deceleration).
The 2E58 weapon stabilizer is electromechanical with an electric drive for vertical and horizontal guidance. It has reduced energy consumption, increased accuracy and less fire hazard.
The UUI-2 transceiver is installed at the base of the trunk. Provides automatic measurement of barrel bending during shooting. Wind and pressure sensor (WPS). The capacitive type sensor provides measurement of longitudinal, transverse wind and atmospheric pressure.
Mobility
"Armata" is equipped with a 12-cylinder four-stroke X-shaped diesel engine with 2V-12-3A turbocharging. Turning mechanism with GOP
Engine power 1200 horsepower. According to the developers, there are possibilities of boosting up to 1500-1800 hp. in perspective.
The total capacity of the tank's fuel system is 2015 liters with two connected barrels. Of this, 1,615 liters are in the internal and external fuel tanks of the tank, the fuel is partially located inside the hull (816 liters), the rest is in fuel tanks on the fenders in the rear of the hull.
The transmission is mechanical with a planetary central gearbox with automatic shifting. The built-in reverse can provide an equal number of forward and reverse gears, which is important when unifying the chassis with rear and front mounted gearboxes. The cooling fan drive is two-stage controlled.
The stiffness of the suspension is 167...206 kN/m, and the resistance of the hydraulic shock absorber in forward and reverse strokes does not exceed 55 kN and 120 kN, respectively.
the torsion shaft has an operating stress level of more than 147·104 kN/m2 and an allowable twist angle of more than 80°.
The damping characteristic of a hydraulic shock absorber is high-speed, that is, it represents the dependence of the resistance force on the speed on the lever. The kinematic connection of the hydraulic shock absorber with the suspension is designed to provide a gear ratio of the vertical speed of the support roller of the tracked mover of the tracked vehicle to the speed of movement of the hydraulic shock absorber lever of 0.15...3.5 with an increase at the end of the travel of the support roller.
An increase in the progressiveness of the suspension characteristics of the suspension system and the smooth running of tracked vehicles weighing up to 55 tons is achieved.
1 - guide wheel; 2 — caterpillars; 3 – support rollers; 4 — support rollers; 5 — torsion shaft; 6 — balancer; 7 — hydraulic shock absorbers; 8 traction
The progressive characteristics of the suspension are shown, in comparison with the characteristics of the suspension of the Leopard 2 tank
Project evaluation
The positive side of the project is that it was nevertheless implemented, to a greater extent than any of the existing projects of a promising tank in the post-Soviet space after the creation of the T-64 tank.
A positive for the industry in the Russian Federation is the development of new technologies (touch panels), new element base in tank control systems (ICS, control systems, etc.), the development of which can become a serious impetus in the development of the electronics industry.
Sufficient attention has been paid to the complex protection of the tank - KOEP, KAZ, DZ, etc.
Ergonomics meets modern requirements.
Negative features of the tank arise from the choice of its layout, such as the inability to provide sufficient side armor for the capsule due to the placement of the crew shoulder to shoulder, the vulnerability of the turret from the fire of modern automatic guns, the lack of a visual channel for the commander and gunner's sights, and the inability to provide all-round visibility from the commander's seat. The exhaust on both sides increases the IR visibility of the tank.
Among the removable shortcomings, we can note the absence of a machine gun coaxial with the cannon. And a backup gunner sight.
And the main thing that can be added is that the tank is undergoing tests, a small number of them have been produced at the moment. Most of the systems installed in Armata have not yet been sufficiently mastered; it will undoubtedly take a long time to cure “childhood diseases”. So time will tell whether “Armata” will be or not.
Stop kidding! "Armata" was armed with... a toilet
Tank "Armata" at the Victory Parade.
Photo: Vladimir VELENGURIN
Now someone will admire the progress, and someone will clearly make a snide joke, but the fact remains: the newest Russian T-14 Armata tank is equipped not only with state-of-the-art weapon systems, but also with its own... toilet. Yes, yes, Ilya Baranov, Director for Quality and Information Technologies of the Ural Design Bureau of Transport Engineering, said this in all seriousness.
— There is water and packed rations in the tank, but everything else, sorry, is not provided. The problem was solved only in vehicles on the Armata platform. This tank was initially designed to allow the crew to carry out combat missions for a long time, so it has a so-called life support device - a life support device, or, more simply, a toilet,” he said.
WE ARE NOT THE FIRST HERE
It must be said that the Russians are far from Columbus in “opening” toilets for tank crews.
Designers in other countries have also long wondered: what should a tanker do if he’s been inside an armored vehicle for a long time, and suddenly has an urge to relieve himself? And you cannot leave the combat vehicle. Here the tankers had to rely on their ingenuity. For this, they usually used plastic bags or bottles and spent cartridges. Well, as a last resort, you could use the evacuation hatch in the bottom of the tank. In general, no “conveniences” were provided in combat vehicles for a long time. Moreover, in the cramped “internal volume” of the tank it is not so easy to find free space for a toilet.
But nevertheless, they somehow found a place for air conditioners or even coffee makers.
Historians of tank construction say that for the first time, American and German designers began solving the problem of a toilet in a tank back in the 60s of the last century, when they created the MVT-70, a tank for NATO. It had a place under which there were disposable containers. The designers of the British Challenger 2 tank went the furthest. And now the British say that it is supposedly the best tank in the world, because the British tank driver has a kind of bio-toilet under his seat and he can relieve himself with the hatches closed. Although there is something similar in the Israeli Merkava tank, as well as in the German-Dutch infantry fighting vehicle - “Boxer”.
British Challenger 2 tank.
Photo: ru.wikipedia.org
THE BIKE HAS ALREADY APPEARED
Tankers are funny people, they’ve already written a story about this. About the method of disposal of crew waste.
Allegedly, the container with the “incense” was supposed to be removed from the tank using a cannon - with a shot with a weakened charge. But this idea was abandoned. Someone joked that with such a disposal method, the enemy would immediately face accusations of unleashing a bacteriological war...