Tank Grote. USSR
Home » Books on the history of tanks » Tank Grote. USSR
Books on the history of tanks Little-known and unrealized projects of tanks and other armored vehicles Unrealized projects of tanks and other armored vehicles of the USSR
boroda 09/12/2009 511
3
to Favoritesin Favoritesfrom Favorites 2
I have long wanted to post this car in the section “Unrealized projects of tanks and other armored vehicles of the USSR.” And then I came across a suitable text, and I decided to fill this gap. The text of the main article is taken from the magazine “Front-line Illustration - Multi-turret tanks of the Red Army T-35, SMK, T-100” , which is on my website and anyone can download it. In addition to the Grotte Tank, it tells about many more pre-war heavy vehicles that were not accepted for service.
The machine is truly mysterious and little-known, needless to say, if I myself learned about its existence only a few years ago from Svirin’s book “The Armor is Strong. History of the Soviet tank (1919-1937)" . The machine uses technical solutions that have never been used before or since in the USSR. It is also notable for the fact that for the first and last time (here, in my opinion, I can’t say 100%) foreign engineers participated in the design, even engineers from a potential enemy country.
By the way, despite its exotic appearance, the tank turned out to be quite successful, and its only drawback was its high price - it cost as much as 25 BT-2.
In March 1930, a group of engineers led by Edward Grote arrived from Germany to the Soviet Union. This group was entrusted with the development of promising models of tanks for arming the Red Army. Control over the activities of German engineers was carried out by the Technical Department of the EKU O GPU, whose head is Comrade. Already in April 1930, E. Grote issued a technical assignment for the design of a tank weighing 18-20 tons, speed 35-40 km/h and armor thickness 20 mm. The armament was supposed to consist of two guns of 76 and 37 mm caliber and five machine guns. The remaining parameters (placement and installation of weapons, ammunition, power reserve, etc.) were left to the discretion of the designer. To design and build an experimental machine, the AVO-5 design bureau was created in Leningrad. In addition to German specialists, it also included young Soviet engineers (Barykov, Vorobyov, etc.), who later became famous developers of domestic armored vehicles.
The production of the new tank, which received the TG index, was carried out in an atmosphere of deep secrecy. Representatives of the RVS and the USSR government directly observed the work. So, on November 17-18, 1930, K.N. Voroshilov personally visited, about which he reported to I. Stalin: “The readiness of the tank today is 85%. The completion of the engine group, gearbox and a number of additional units remained unfinished. The sample is manufactured in a special workshop, which today employs about 130 workers and technicians. Currently, the construction of the tank is delayed due to the serious illness of E. Grotte himself, but our engineers assume that the prototype will still be completed on December 15-20...” However, over the following months the tank was never completed. The reason for this beer was the unreliable operation of a special air-cooled tank engine designed by E. Grote. Therefore, in April 1931, it was decided to temporarily install an M-6 aircraft engine on the TG tank for the first cycle of tests. This required some modifications to the tank's components, since the dimensions of the .M-6 turned out to be somewhat larger than those of the Grote engine. Only by the beginning of July the tank was ready for testing.
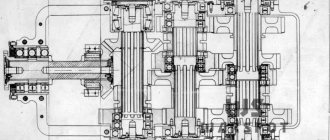
The TG differed from other domestic and foreign cars of that time not only in its general appearance, but also in its manufacturing technology and layout. First of all, the tank had a completely welded hull, which was an undoubted innovation. The weapons were placed in three tiers. A 37-mm cannon designed by Syachentov, with anti-aircraft firing capability, was installed in the upper rotating turret. The lower fixed conning tower housed a 76-mm tank gun designed by Grote-Syachentov and three Maxim machine guns in ball mounts (according to the original design, the conning tower was supposed to have a circular rotation. BUT then this was abandoned).
The sides of the hull housed two DT machine guns, which had limited guidance points (they fired through oval holes in the bulwarks).
The chassis of the TT, applied to one side, consisted of five large-diameter rollers, four medium-diameter support rollers and two small-diameter rollers. And the dependent suspension of the road wheels on spiral springs, together with semi-pneumatic Elastic tires, provided the tank with an extremely soft ride. The caterpillar of the original design, made of stamped parts, had a high tensile strength. It is interesting to note that all the road wheels were equipped with brakes designed to stop the tank in an emergency if the track broke.
An M-6 aircraft engine was openly installed in the rear of the hull (later it was planned to replace it with an E. Grote tank engine and cover it with an armored hood), and directly next to it was a six-speed gearbox. The tank was controlled using servos, and thanks to the presence of a special reverse mechanism, the TT could move forward and backward at the same speed.
The tank crew, consisting of five people, could observe the battlefield through viewing slits and a strobe light mounted on the roof of a small turret.
Testing of the tank began on JUNE 27, 1931 and continued intermittently until October 1. They reached a maximum speed of 34 km/h. The tank demonstrated good cross-country ability and maneuverability. The TG transmission worked well, and the use of pneumatic drives made the process of controlling the machine unusually easy.
At the same time, many design defects were noted: the cramped fighting compartment, inconvenient access to transmission components and assemblies, insufficient adhesion of the track to the ground, and a number of others.
By order of the Soviet government, on October 4, 1931, a special commission was created to thoroughly study the Grote tank. After examining the vehicle and hearing the designer’s report, the commission decided: “To consider that the TG tank in this form is a purely experimental type of tank, on which all mechanisms of practical interest should be tested in operation.” Due to the extremely high cost, amounting to 1.5 million rubles (for comparison: BT-2 cost only 60 thousand rubles), the TG, even with the elimination of all the noted shortcomings, could not be accepted for mass production. By this time, the further services of Grote and other German engineers were refused and they returned to Germany. KB LAN)-5 was reorganized and included designers M.P. Zigel, B.A. Andrykhevich, A.B. Gakkel, Ya.N. Obukhov and others. The design bureau was headed by a young energetic engineer N.V. Barykov, who had previously worked as Grote’s deputy.
How much does the T-34 tank weigh?
T-34 is a real military legend. Production of the first "thirty-fours" began in 1940, and by the beginning of 1941 the USSR had about 1,225 units of equipment in service. The T-34 model tank changed and improved its technical characteristics several times during the war years. Therefore, the mass in different years of production was also unequal:
- Issue 1940 – 26.3 t
- Issue 1941 – 28 t
- Issue 1942 – 28.5 t
- Issue 1943 – 30.9 t
At the same time, in the total mass of the combat vehicle, the weight of the tracks takes up about 1150 kg. When comparing the weight of the combat turret of a tank from 1940 and 1942, there is a noticeable tendency to increase - from 3200 to 3900 kg. The T-34 crew includes a gunner-radio operator, a driver, a loader and a commander.
The Maus tank was created in 1943 and weighed about 188 tons. This is a real “heavyweight” of German tank building, the length of its gun reached 2.5 m. And the total length of the combat “Mouse” was about 11.5 m! The vehicle's ammunition load included two twin cannons (128 mm and 75 mm). The capacity of the Maus fuel tank is 2650 liters. The number of crew members is five people.
This is interesting!
On these pages you can find out: How much a bear weighs How much gold weighs How much a sumo wrestler weighs How much a cloud weighs How much a piano weighs
Despite the impressive size and weight of the Maus tank, almost all the free space inside was occupied by numerous instruments and parts. So the crew of the combat vehicle had to be located “on a residual basis.”
According to the results of field tests, the Maus achieved good performance: a speed of 20 km/h, overcoming a rise, a vertical obstacle 76 cm high at an angle of 30 degrees, crossing a water trench 2 m wide.
True, all the efforts spent on creating and improving the types of this model were in vain. At the end of 1944, by order of Hitler, work on heavy tanks was stopped, and in the spring of 1945, prototypes of the 205 type were prepared for defense of the training ground in the event of capture by the Red Army. After the war, the two surviving Type 205 tanks were transported to Leningrad, and from there to the tank training ground in Kubinka.