The term “Cold War” refers to the geopolitical confrontation between two world powers, the USA and the USSR, which occurred immediately after the end of the Second World War. Globally, it was not so much a confrontation between these states as a struggle between two ideas, two ways of life, two economic and political systems. On the one hand, the USA and Western Europe, personifying capitalism and democracy, on the other hand, the Soviet Union and its allies, actively building communism and at the same time a totalitarian system. What were the reasons, main stages and results of the Cold War, read on.
It is believed that the term “Cold War” was first used by the famous English science fiction writer George Orwell, the author of several dystopian novels (“1984”, “Animal Farm”). In his article written on October 19, 1945, “You and the Atomic Bomb,” he put forward the idea that there would be a constant “cold war” between countries possessing atomic weapons, that is, a confrontation without active hostilities. For, as Albert Einstein also once said, “If the third world war will take place with atomic bombs, then the fourth will take place with stones and sticks.”
Background and causes of the conflict
After the end of the Second World War, it was only a matter of time before contradictions emerged between the countries of the anti-Hitler coalition. After all, in the eyes of Western countries, the USSR until recently was the same aggressor as Nazi Germany: here we can recall the Finnish War of 1940 and the partition of Poland together with the Nazis in 1939. And after the war, the “country of the Soviets” also captured large territories in Eastern Europe; many Eastern European countries: Poland, Hungary, Romania, Yugoslavia and others found themselves in the sphere of Soviet influence. Therefore, it is not surprising that after the victory over Germany, relations within the Allied camp began to rapidly deteriorate.
Churchill's Fulton speech
On March 5, 1946, the legendary British Prime Minister Sir Winston Churchill gave a speech at Westminster College in Fulton (USA) in the presence of American President Harry Truman. In his speech, Churchill called on Western countries to unite against the “Red threat” approaching from the east in the name of protecting the rights and freedoms of a democratic society. “Soviet Russia wants...the unlimited spread of its power and its doctrines,” Churchill said. And yes, he was right, even the first Russian revolutionaries sought to kindle the “flame of revolution” throughout the world.
One way or another, Churchill's Fulton speech became the official beginning of the Cold War, not just between two states, but between two ideologies.
So, speaking about the causes of the Cold War, we can highlight several main ones:
First détente of the war
The first détente of the Cold War occurred immediately after Stalin's death in 1953. Khrushchev announces that the Soviet Union is ready to discuss a policy of peaceful coexistence with the West. His ideas found a positive response in Western countries.
History of the Cold War
At the same time, the Korean War ends. Diplomatic relations are being established between Israel and the USSR. In exchange for a promise to maintain a neutral position, Khrushchev withdraws the Red Army from Austria. There were no similar gestures from America.
Main stages
Truman Doctrine and Marshall Plan
In the spring of 1947, American President Harry Truman adopted a foreign policy doctrine, also known as the “doctrine to contain communism,” according to which the United States would fight against any claims of the Soviet Union in the world.
In addition to possible military actions, it was also planned to use economic instruments. Thus, US Secretary of State J. Marshall developed measures to provide economic assistance to war-ravaged European countries - the Marshall Plan. US economic assistance was especially useful to Western Germany, which was in ruins (West Germany), which within 20 years was on par with other leading European countries in terms of GDP. But economic affairs in eastern Germany (GDR), which found itself in the sphere of Soviet influence, were not so rosy. In fact, the Marshall Plan showed the higher efficiency of a market and competitive economy compared to a planned socialist one.
Korean War
Unfortunately, the Cold War was not always so cold. Since in some places there were real military conflicts between two military-political blocs. The first of these conflicts was the Korean Civil War, which led to its division into South Korea and North Korea. Unfortunately, this division continues to this day. As we know, North Korea is communist, it was supported by the USSR and China (which also took the path of communism), while the USA, Japan and the UN stood up for South Korea. The war in Korea ended in what is called a draw, both sides concluded a truce (note, not peace). This truce officially lasts to this day and the situation between the two Koreas is still very tense.
But here the economic results of these two countries are more telling. Today there is simply a huge economic gap between North and South Korea, of course, not in favor of North Korea. The example of Korea emphasizes even more clearly the higher efficiency of a market economy compared to a planned socialist one. As someone wittily remarked: “The US gets South Korea, and the USSR gets North Korea.”
Berlin crisis
After the Second World War, Germany was divided into zones of occupation. The capital Berlin, despite the fact that it was in the Soviet zone of occupation, was also divided into West Berlin and East Berlin. In an attempt to drive the former allies out of the city entirely, the Soviets began a blockade of West Berlin. However, the parties soon came to an agreement, the blockade of West Berlin was lifted, and Germany itself was officially divided into two states:
- pro-Western Federal Republic of Germany (FRG)
- pro-Soviet German Democratic Republic (GDR).
The city of Berlin also retained its division. In the post-war years, many Germans who found themselves in the Soviet zone of occupation, subsequently on the territory of the GDR and who did not want to “build communism” quickly fled to Western Germany. And one of the places where this could be done was Berlin. To prevent this flight, the Soviets built the Berlin Wall along the demarcation line, which for decades became an architectural symbol of the Cold War and the division of the world.
Berlin Wall.
The arms race and the space program
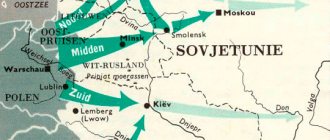
Both sides, despite the absence of global military action (there were still local conflicts), were actively building up their weapons. So already in 1949, the Soviet Union created its own atomic bomb, and the prospect of a nuclear apocalypse loomed before the whole world in the event of an escalation of the conflict.
The United States and NATO countries, a military bloc created in opposition to the USSR and its Warsaw Pact countries, also actively developed weapons, which had some positive aspects. So, with the arms race, science developed rapidly, both in the Soviet Union and Western countries. By the way, many inventions made for military purposes later found their peaceful application.
Another positive aspect in the confrontation between the USA and the USSR was the rapid development of space programs; both countries wanted to conquer space and actively competed with each other to see who could do it faster. And in 1961, the Soviet Union sent a man into outer space for the first time. The flight of Yuri Gagarin, the first cosmonaut in history, became a significant global event, designed at the same time to show the whole world how progressive the Soviet Union is (though at the same time, in the same Soviet Union, mass production of toilet paper began only 2 years after the first human flight into space ).
The Americans also took a thorough approach to space research, creating a special scientific organization - NASA, which in 1969, during the Apollo program, sent astronauts Buzz Aldrin and Neil Armstrong to the Moon. “A small step for a man, a big leap for humanity,” said then American President John F. Kennedy about this flight.
Unfortunately, with the end of the Cold War and the confrontation between the two superpowers, many scientific programs for space exploration were reduced; we hope that in our time they will resume with renewed vigor.
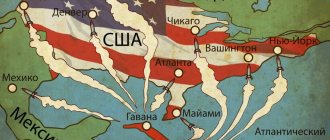
Caribbean crisis
The Cuban missile crisis can be considered the hottest stage of the confrontation between the USA and the USSR, since at that time the whole world was literally on the verge of a nuclear war. On our website there is a separate detailed article about
The Cuban missile crisis, its causes and main events, follow the link.
Hungarian Uprising and Prague Spring
At times, some countries that found themselves in the communist pro-Soviet bloc sought to leave it. The first sign was the Hungarian Uprising of 1956, when the Hungarians sought to overthrow their pro-communist government and almost succeeded. But, unfortunately, the uprising was suppressed by Soviet troops who entered the country, effectively violating its sovereignty.
Soviet tanks on the streets of Budapest.
12 years later, in 1968, another country that found itself under the heel of the Soviet regime, Czechoslovakia, tried to get rid of it. The Czechoslovak government carried out liberal reforms known as the "Prague Spring", which did not sit well with Soviet leaders, resulting in the Soviet invasion of Czechoslovakia and the suppression of the "Prague Spring"
Separate large articles could be written on each of these topics in recent history.
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War, like the Korean War, also became one of the hottest stages of the Cold War. The Soviet Union supported northern communist Vietnam, while the United States stood up for southern pro-Western Vietnam. The Vietnam War was very difficult and bloody, and ended in defeat for South Vietnam and the United States, which was forced to withdraw its troops.
War in Afghanistan
The Soviet Union, in turn, also found itself drawn into a long and difficult war in Afghanistan, from which it wanted to make another satellite country. But both the communist and pro-Western democratic systems were equally alien to the Afghan mujahideen and Islamic fundamentalists. After a long and protracted war, the Soviet Union was forced to withdraw its troops from Afghanistan.
In addition to these wars, there were many other smaller conflicts, for example in African countries: the USA and the USSR actively competed for the attention of certain African countries, supplied them with weapons and money, were friends with their leaders, among whom were very odious personalities, for example the president of the Central African republics, as well as the cannibal (the real one) Jean Bedel Bokassa.
The same Bokassa in the Artek pioneer camp, Crimea.
Why is it called “cold”?
The Cold War is called because the US and USSR troops did not conduct military operations with each other.
Initially, the concept of “Cold War” was invented and used by the English writer George Orwell in the article “You and the atomic bomb” (1945).
Orwell wrote that the creation of the atomic bomb would lead to a permanent “cold war” between neighbors. That is, there will be no full-scale wars and peace will seem to reign, which, due to the presence of atomic weapons, will not feel like peace.
Officially, the conflict between the USSR and the USA was called the “Cold War” by US Presidential Advisor Bernard Baruch in 1947.
Since there was no military action, countries used other means to achieve victory:
- Arms race (development, production and accumulation of nuclear and other weapons and military equipment at an accelerated pace).
- Formation of military blocs of countries (NATO, Council for Mutual Economic Assistance, Warsaw Pact Organization).
- Support for communist and, conversely, anti-communist regimes in other countries.
End of the conflict, perestroika and collapse of the USSR
Throughout the Cold War, there were both hot conflicts and moments of relaxation and thaw between the two sides. Gradually, in the confrontation in the economic sphere, the inefficiency of the Soviet economic system became clear; the lag in the economy between pro-Soviet countries and pro-Western ones was increasingly clear. In an effort to bridge the growing economic gap, the new leader of the Soviet Union, Mikhail Sergeevich Gorbachev, began a series of global reforms in 1985 aimed at liberalizing the Soviet system. These reforms were called “Perestroika”, as they implied significant changes in the political and economic system of the country. For the first time in many years, the shoots of legitimate entrepreneurship began to sprout in the Soviet Union. Illegal entrepreneurs (aka speculators), of course, existed before, but the Soviet system persecuted them in every possible way.
The same processes were taking place in other countries of the socialist bloc. Previously, communist countries were actively transitioning from communism to democracy and market economies. In some places this happened peacefully and naturally, and in others with mass popular protests.
In 1989, the Berlin Wall, this symbol of the Cold War, was destroyed, eastern and western Germany were reunited into one state, the Polish democratic Solidarity movement replaced the communist government in power, and in Romania the pro-communist dictator Nicolae Ceausesco, who did not want to give up power, was shot. Across eastern Europe, countries were awakening from their “communist slumber.”
The fall of the Berlin Wall.
The culmination of these events was the collapse of the USSR in 1991. Many states that were once part of it gained independence. With the collapse of the Soviet Union, the Cold War also ended.
Historical meaning
Thanks to the military race, space technology emerged. Progress received constant financial support. Modern gadgets, the Internet and space flights are all a unique legacy of that period of time.
But both America and the Soviet Union lost much more. Both sides spent huge amounts of money on the arms race. Soviet and American soldiers died in numerous conflicts.
Due to constant interference in the affairs of other countries, the political map of the world was redrawn, which also led to numerous casualties
Echoes of propaganda are preserved in documentaries and feature films, and ideological literature.
Results
The main result of the Cold War was the failure of the alternative communist system and the ineffectiveness of the planned economy. Yes, of course, capitalism, a market economy, and democracy also have their many disadvantages. But despite them, this is “the best thing that has been invented by mankind.” Since the alternative is much worse, which is shown today by the example of the same North Korea, which has turned into a rogue state, a country where in the 90s there was a real famine that killed thousands of people. While neighboring South Korea is one of the most economically developed and successful countries in the Eastern region.
As for neighboring China, which is nominally still communist, but capitalism and market relations have been actively developing there since the 90s, which has allowed China to become the “global forge of goods.” In fact, China now represents “efficient capitalism under the nominal leadership of the Communist Party.”
Near East
Another point of contact between the two powers was the Middle East. Since the establishment of the State of Israel, this region has become a hotbed of constant tension. Since 1947, when Israel was formed, the region has seen a series of Arab-Israeli wars, in which the United States supported the Jews and the Soviet Union supported the Arabs. I would like to note that the very formation of the Jewish state became possible thanks to military supplies from the USSR. However, later groups closely associated with the United States came to power in the country, and, accordingly, the USSR had to support the Arab countries. Moreover, they had large reserves of oil and gas.
Literature and useful links
- J. Arnold, J. Burt, W. Dudley. Flame of the Cold War: Victories that never happened = Cold War Hot: Alternative Decisions of the Cold War / ed. Peter Tsouros (English)Russian, trans. Yu. Yablokova. - M.: AST, Lux, 2004. - 480 p. - (Great Controversies). — 5000 copies. — ISBN 5-17-024051-1.
- Creder A.A. Recent history of foreign countries. 1914 - 1997: Textbook for 9th grade of primary school. — 2nd ed., add. and correction. - M.: "Center for Humanitarian Education", 2005. - 432 p. — ISBN 5-7662-0062-5.
- Cold War / Egorova N. I. // Khvoyka - Shervinsky. - M.: Great Russian Encyclopedia, 2022. - P. 132. - (Big Russian Encyclopedia: [in 35 volumes] / chief editor Yu. S. Osipov; 2004-2017, vol. 34). — ISBN 978-5-85270-372-9.
- V. Manjola. “Cold War” // Ukrainian Diplomatic Encyclopedia: 2 volumes / ed. number: L.V. Gubersky (head) and in. - K.: Zannanya Ukrainy, 2004. - T. 2: M - Y. - 812 p. — ISBN 966-316-045-4.
Author: Pavel Chaika, editor-in-chief of the historical site Time Travel
When writing the article, I tried to make it as interesting, useful and high-quality as possible. I would be grateful for any feedback and constructive criticism in the form of comments on the article. You can also write your wish/question/suggestion to my email [email protected] or Facebook, with respect, the author.
Historical site Time Travel
Worsening relations
In 1960, relations between the USSR and the USA again experienced a crisis: a Soviet missile shot down an American reconnaissance aircraft flying at altitudes inaccessible to fighters. Khrushchev demanded an apology from Eisenhower for this outrageous incident, but never heard it.
On November 8, 1960, the United States changes its president, now John Kennedy. He attempts to overthrow the communist regime in Cuba. The leader of the Cuban communists, Fidel Castro, was planned to be overthrown by the Cubans themselves, but the counter-revolution on the island failed.
In 1961, at a meeting with the US President, Khrushchev demanded a change in the status of West Berlin. The city was used by Western intelligence for campaigning and for the escape of people from the territories of the GDR to the Federal Republic of Germany. As a result of these unsuccessful negotiations, the Berlin Crisis broke out. In August of the same year, the GDR authorities separated from West Berlin by a wall. Entire families were separated.
The deterioration of relations continues. America is purposefully surrounding the Soviet Union with its own military bases with missile silos. Nuclear weapons are spreading everywhere. Realizing that the entire territory of the country is under threat, Khrushchev decides to put the same pressure on America. For this purpose, it is planned to install medium-range missiles in Cuba. If war breaks out, all of America could be destroyed from the Cuban base. This leads to the Cuban Missile Crisis of 1962, which brings the world to the brink of nuclear disaster.
However, during difficult negotiations, the countries still come to a compromise: the USSR removes its missiles from Cuba, and the United States abandons its plans for the island and closes bases in Turkey.
The Cuban missile crisis became a valuable lesson for the leadership of both countries: for the first time it became clear that the insatiable desire to dominate the world stage could lead to the destruction of humanity. Having approached this dangerous point, the Cold War began to subside. On August 15, 1963, an agreement was concluded between the USSR and the USA banning nuclear tests in the atmosphere, space and water.