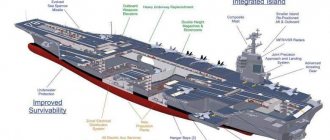
The French aircraft carrier Charles de Gaulle represents the combat core of an operational naval formation: an aircraft carrier strike, multi-purpose or anti-submarine group.
This is the main ship that directly carries out combat missions and at the same time provides cover for the auxiliary ships that are part of the group. In addition, Charles de Gaulle is able to carry out independent military campaigns, support the population and refugees in hot spots and disaster areas.
Story
Apart from the Soviet Union (now the Russian Federation) and the United States, only France can currently afford to build and maintain a nuclear-powered aircraft carrier.
The nuclear-powered aircraft carrier Charles de Gaulle is the flagship of the fleet of the French Republic.
There are many superlatives that can be used in relation to Charles de Gaulle. She became the most powerful ship of the Navy of the French Republic, its flagship, as well as the first French nuclear-powered surface combatant and the first nuclear-powered aircraft carrier not built in the United States. Today, Charles de Gaulle is the only modern French aircraft carrier class ship commissioned into service, as well as the largest warship ever built in France.
Charles de Gaulle replaced the obsolete aircraft carriers Klemanso and Fosh in the fleet, which were put into service back in the 1960s. The decision to replace these ships in the early 1980s. adopted by the highest military authority in France - the Defense Council. Since 1986, the construction of the new aircraft carrier has been carried out by the DCN shipbuilding enterprise (Brest). Due to financial reasons, the deadlines were delayed. The official transfer of the ship to the French Navy took place only in September 2000. The creation of a second ship of this type with a planned commissioning in 2015 was canceled for financial reasons.
Initially, the French military proposed to name the aircraft carrier after the French commander and political leader Charles de Gaulle, but the then President of the French Republic F. Mitterrand, for political reasons, just before the presidential elections of 1988, decided to name the ship after the name of another historical figure - Cardinal Richelieu. However, in 1989, the Prime Minister of France and concurrently the leader of the Gaullist party, J. Chirac (future President of France), convinced F. Mitterrand, and the ship received its modern name.
The only combat episode with the participation of Charles de Gaulle was Operation Clear Sky with the participation of the forces of the international coalition of the NATO bloc during the civil war in Libya in 2011. In addition to Charles de Gaulle, the French group included air defense frigates Forbin and Jean Bart, frigates Dupleix and Aconit, as well as the tanker Meuse.
The first French aircraft carriers
The first steps in equipping the navy with aircraft carriers were taken by the French back in the first quarter of the 20th century. Following the British, they turned the battleship Béarn into an aircraft carrier, equipping it with a deck for take-off and landing of aircraft, the length of which was 182 m, width 31 m. In the 30s of the last century, the ship was modernized. But this did not allow the aircraft carrier to prove itself during the war. As soon as Paris surrendered to the Nazis, he went to the Antilles, where he remained until 1944.
Military operations at sea during the war of 1939 - 1945. showed that it is aircraft carriers that are capable of effectively performing combat missions in new conditions. Almost the entire French fleet was unable to resist and was destroyed. The country's leadership understood the need to equip the fleet with ships of this type, first of all, in order to strengthen its presence in the French colonies. "Bearn" is already obsolete, it was used for some time as a floating base, and then withdrawn from the armed forces.
Aircraft carrier "Béarn"
France did not have its own capabilities; its former leading positions in the field of shipbuilding were irretrievably lost. Considering that to solve military-political problems it needed 6 aircraft-carrying ships, France counted on the help of its allies. But the USA and England were in no hurry to share technology, but they were ready to give not new aircraft carrier ships. As a result, France's first post-war aircraft carriers were foreign-made. Great Britain transferred 2 vessels:
- 1945 convoy aircraft carrier "Biter" (12,150 tons, 20 aircraft). It was created in the USA under Lend-Lease for England. In France it was called "Dixmud". Until 1960, the French actively used the ship during the colonial wars in Vietnam and Algeria. After 6 years he was returned to the USA.
- In 1946, the aircraft carrier Colossus (19,600 tons, 24 aircraft) was leased from the British, and 5 years later the aircraft carrier Colossus was purchased. In France he served under the name "Arromanches". It was part of the Navy until 1974. During this time it was modernized several times, and participated in the war against Egypt in 1956.
The United States also transferred 2 light aircraft carriers of the Independent class, displacement 15,800 tons, 26 aircraft:
- 1951 "Langley" (the Americans no longer used it, transferring it to reserve), in France it received the name "Lafayette", served until 1964.
- 1953 Bello Wood, renamed Bois Bleu, was needed for the Indochina War in 1954. Upon return, it was modernized and used as an air transport until 1960.
| The first aircraft carriers in the service of the French Navy | ||
| Name | Commissioned | Removed from the fleet |
| Bearn | May 1927(France) | 1949 |
| Biter/Dixmude | May 1, 1942 (UK) April 9, 1945 (France) | 1966 |
| Colossus/Arromanches | 16 December 1944 (UK) 1946 (France) | 1974 |
| "Bello Wood"/"Bois Bleu" Belleau Wood/Bois Belleau | March 31, 1943 (USA) December 23, 1953 (France) | 1964 |
| Langley/La Fayette Langley/La Fayette | August 31, 1943 (USA) June 2, 1951 (France) | 1963 |
Design
The design of the aircraft carrier is based on a traditional design: the superstructure is shifted to the starboard side, and there is an angled runway on the deck. The ship's hull is welded and made of steel. Even after any three adjacent compartments are flooded, the aircraft carrier remains afloat due to their waterproofness. The nuclear reactor, ammunition magazines and fuel tanks are protected by armor plates. To take off aircraft weighing up to 25 tons with an intensity of one aircraft per minute, two steam catapults are used. Lifting aircraft from the hangar to the flight deck is provided by two lifts.
To reduce the level of acoustic signature, the ship's design includes special low-noise propellers and mechanisms for shock absorption. It is possible to accommodate a marine unit of up to 800 soldiers and officers on the aircraft carrier.
The power plant includes two nuclear reactors of the K15 type from the French company GEC-Alsthom with a total capacity of 76,200 hp. With. Autonomy for nuclear fuel is 5 years, for fuel and food reserves - 45 days.
electronics
Countermeasures and combat system
They consist of Sagaie and LAD anti-aircraft decoys, SLAT anti-submarine installations.
Its combat system includes three major codified functions such as: AIDCOMER, SDC and SYTEX, as well as two minor functions called AVIATION and SCEB. Normal fire control is carried out by two Sagem VIGY 105 optical-electronic devices located on the island on the starboard side.
Radars
The air detection radar is a 3D DRBJ11B located in the aft igloo, plus a forward-facing DRBV26D ground-based DRBV15C and a fire control radar, a 3D Eurosam Arabel located in another smaller igloo, both on the top. Regiment and Thompson, respectively.
As for navigation, it consists of two DRBN34 from Racal. He also has a Tacan NRBP20, all located on the island.
Armament
Charles de Gaulle is the 12th largest nuclear-powered aircraft carrier (after the 10 American Nimitz-class aircraft carriers and the Russian cruiser Admiral Kuznetsov). It is almost three times smaller in size than American aircraft carriers and carries a correspondingly reduced air group, which includes up to 36 attack carrier-based aircraft, 2-3 early warning aircraft and 2-3 helicopters. However, the composition of carrier-based aircraft may change depending on the combat mission. For example, the aviation group during the Libyan operation in 2011 consisted of eight Dassault Rafale fighter-bombers, six Super Etendard attack aircraft from Dassault-Breguet, two E-2 Haw keye AWACS aircraft from Grum man, two medium multi-purpose helicopters AS.365 Dauphin from Aerospatiale, two light multi-purpose Alouette III helicopters from Sud-Aviation, two heavy transport and landing helicopters EC.725 Cougar from Eurocopter and one medium transport and landing helicopter SA.330 Puma from Sud-Aviation.
A Grumman E-2 Hawkeye AWACS aircraft, part of the air wing of the aircraft carrier Charles de Gaulle, takes off from the deck of an aircraft carrier
Air defense systems include two Aster 15 air defense systems (each as part of an eight-container vertical launch system), two Sadral air defense systems (each as a six-container launcher) and eight single-barrel 20 mm Giat 20F2 automatic gun mounts (rate of fire - 720 rounds per minute).
Notes[ | ]
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Shunkov V.N.
Aircraft carriers and naval aviation. - Minsk: Potpourri, 2003. - P. 576. - ISBN 985-438-979-0.. - Défense - Dassault Aviation (unspecified)
(unavailable link). Access date: January 14, 2016. Archived November 2, 2014. - The formation also includes the destroyer Chevalier Paul, the frigate La Motte-Pique, the support vessel Marne and the Ruby-class nuclear submarine. The British Royal Navy destroyer Defender and the Belgian frigate Leopold I are also operating together with the French formation. [1]
- The aircraft carrier Charles De Gaulle attacked IS positions in Syria and Iraq for the first time // TVC, November 23, 2015
- Hollande sent the Charles de Gaulle to the Persian Gulf // Lenta.ru, December 4, 2015
- French aircraft carrier Charles de Gaulle headed for the Persian Gulf // RIA Novosti
- Russian submarines scared the NATO squadron // December 12, 2016
- Two French Navy fighters fell into the Mediterranean Sea // RBC, 2009
- The number of people infected with coronavirus on the aircraft carrier Charles de Gaulle exceeded 1 thousand // NG, 04/18/2020
possibilities
This new type of aircraft carrier is prepared for multi-role use in both peacetime and wartime, being able to launch its aircraft in sea conditions of 5/6. Its maximum combat capacity is 100 sorties per day, using an average of 20 to 24 aircraft or several waves of four or eight aircraft, mainly in two types of missions: the main one, dedicated to attacking military, industrial or naval targets, more control and protection of marine areas; secondary - to support ground operations, cooperation with other branches of the military in helicopter operations and humanitarian assistance in disaster areas.
As the flagship of a battle group, it can launch five waves of aircraft consisting of 20-24 aircraft in 24 hours at a range of 400 miles from the target and at a range of 150-200 miles, successive waves of four or eight aircraft. every hour and a half.
The crew has an interesting living space, with cabins of variable capacity, from 9 to 21 people, two multi-purpose kitchens capable of serving 4,000 meals a day, three dining rooms, four separate rooms for chiefs, officers, non-commissioned officers and sailors, a large recreation room, an autonomous hospital with 60 beds, equipped with two operating theatres, a sports ward, a post office, two hairdressers and a supermarket, everything is designed to be able to spend a year at sea without the need to stock up.