The Boeing 787 is a wide-body aircraft designed to transport passengers, the Dreamliner or “Dream Airplane,” created by specialists from The Boeing Company. Today this airliner is very popular among air carriers around the world. The reason for this is the excellent technical characteristics and pleasant design of the aircraft.
Short story
The life of the project begins in 2004. On April 26 of that year, Boeing’s new creation, a project codenamed 7E7, was highlighted in the media as an improved prototype of the Sonic Cruiser. Already in January 2005, the official name of the 7E7 was announced - for the Boeing 787 .
A year later, one could see a model of a finished aircraft with a specific design. 4 years later, after a series of lawsuits related to the delay in the delivery of life support parts for the aircraft due to the fault of manufacturers, on December 15, 2009, the Boeing 787 Dreamliner took off.
The aircraft participated in exhibitions, for example, at Farnborough, one of the world's largest air shows. Visitors to MAKS 2011 could get acquainted with the interesting design of the Dreamliner.
The first delivery of the Dreamler was made on September 25, 2011. Test piloting was carried out on July 2, 2011 on the route Seattle - Haneda. The aircraft was tested with the participation of All Nippon Airways (ANA). The Boeing 787 was awarded an official certificate confirming the Dreamliner's ability to carry passengers on August 26, 2011. The aircraft entered mass production and already made its first flight on October 26, 2011.
The Boeing 787 is the world's first aircraft with a monolithic main section fuselage. Conventional prefabricated aircraft use more than 45 thousand rivets: the new model made it possible to save money due to the solidity of the body.
Total development costs for the Dreamliner exceeded $32 billion.
Unrealized project
Interestingly, the history of the Dreamliner dates back to the late 1990s. At this time, leading Boeing engineers and designers came to the conclusion that the Boeing 767 model was hopelessly outdated, and that a new competitive solution was required - the Sonic Cruiser.
Unfortunately, due to the tragic events of the Twin Towers on September 11, 2001, the expensive project was postponed indefinitely. In addition, the Boeing 787-3 – for 295 passengers with a flight range of over 6.5 thousand km – was not put into production. The aircraft was to be used for short-distance transport. Considered as an alternative to the Airbus A300 and Boeing 767 in Japanese domestic airlines. But fate decreed otherwise, and the project was closed on 12.2010 in favor of the 787/8 model.
Economy class
Reclining comfortable seats with a standard distance between them provide an acceptable level of comfort.
Many people consider the best seats in economy class to be the 7th row and 26th row, where there is more space in front of the seats. But some people don’t like the fact that the eating tables are located in the armrests. The rows may not match in different versions of the interior. For passengers in the 25th and 37th rows, the noise from the kitchen and toilet may seem unacceptable. The 38th row is also closed by partitions with limited visibility. However, there are no completely uncomfortable seats on the plane; everyone chooses according to their preferences.
Design
The design of the long-haul airliner includes lightweight composite materials, modern communication systems, and highly efficient engines. According to the manufacturer, this model is 20% more fuel efficient compared to the previous version. The Dreamliner's fuselage parts are manufactured in Washington.
The body contains:
- 50% - composite materials - body;
- 20% - aluminum - in the wings, engine and tail;
- 15% - titanium alloy - in fastenings;
- 10% - steel - strength elements;
- 5% - other materials.
At the end of 2022, over 599 aircraft had been produced. The cost of one Boeing varies from 225 to 306 million US dollars.
The average piloting speed of this aircraft model is 900 km per hour. Flight altitude varies from 12 to 13 km. – standard indicator for passenger transportation.
Motors are used with low noise levels from:
- General Electric;
- Rolls Royce.
The luggage compartment capacity is 2 times higher than that of the previous model.
Cockpit
The cockpit of the “Dream Liner” involves the use of wide-format screens for flight control: they, like military airliners, have a head-up display (HUD), recording any information.
The cabin is strikingly different from all previous designs by Rockwell Collins:
- 5 liquid crystal displays are connected to the interface;
- 2 HUD displays;
- Ethernet Internet standard – ARINC/664, protected by multi-stage security protocols that exclude access by ordinary users.
The same cockpit is used in the MS-21 and Comac C919, on the Orion space models.
Pilots note that the cockpit is easy to use and intuitive. The energy system is a consolidation of 7 powerful energy generators:
- emergency – 2 pcs.;
- in a jet engine - 2 pcs.;
- in the emergency turbine - 1 pc.
Lithium-ion batteries are the most effective solution for aircraft, produced by GS Yuasa - 2 pcs. weighing 29 kg each. The first provides Boeing with an uninterrupted supply of energy while on the ground and is capable of operating in emergency mode in the event of generator failure. The second is used to start engines in the event of an auxiliary power unit shutdown. Used to maintain the functioning of auxiliary aviation systems. Despite the many advantages, the new battery system has a drawback associated with a higher fire hazard compared to the nickel-silicon system.
Cabin
The cabin of the Boeing 787 aircraft is equipped with the latest technology: the extensive dimensions of the interior are 5.5 m, which makes it an ideal option for customization to suit the needs of different categories of passengers: from economy class to super VIP and business clients.
The gap between the seating arrangements is:
- 45-60 inches or 115-145 cm for 1st grade;
- 90-100 cm or 35-40 inches for the “Business” class;
- 85 cm or 33 inches for Economy class.
The most common combination is 3+3+3 for Economy class passengers. For tall and large passengers, this seating arrangement is not comfortable during a long flight.
The size of the porthole, which, by the way, does not have curtains, is 25 x 45 cm - this is the highest figure of all standard liners. The glass is capable of automatically adjusting the absorption of light in the cabin. In addition, buttons have been developed for passengers that allow them to quickly change the transparency by simply pressing. They left the curtain in the toilet.
There are no light bulbs in the cabin of a Boeing 787! Instead, LED lighting is used, the color and brightness of which can be adjusted.
The cabin has a new system for regulating atmospheric pressure at a level of 1.8 thousand m. For comparison, in earlier models the pressure was maintained at a level of 2-2.5 thousand m. Now, thanks to innovations, harmful exhaust gases do not enter the cabin, and the moisture level in the cabin tends to 15%. Previously, at Boeing it was at around 4%.
Another distinctive feature of Boeing is the increased size of the toilets, which allows even people in wheelchairs to travel. The upper shelves in the cabin can safely store 4 huge suitcases, and the Smoother Ride Technology flight system allows passengers to feel comfortable even after entering a pocket of air and turbulence.
Sensors in the aircraft cabin allow you to track the slightest changes in air pressure, and the flaperon system is adjusted automatically using the latest computer technology.
Interior layout
The following factors were taken into account when creating:
- spaciousness;
- comfortable light;
- big windows;
- wide shelves for luggage;
- availability of displays for each passenger.
Business Class
In the privileged compartment there are comfortable chairs with the ability to fold out into a bed. Each seat is a half-cabin, and they are arranged in a herringbone shape.
Seats in rows 1, 3 and 6 may be considered inconvenient, as they are located next to utility rooms and a toilet, and row 6 is in economy class. The noise of the toilet flush is reduced, but frequent movement of passengers and staff, turning on the lights, and the sound when opening and closing doors can interfere with proper rest.
Production
Since 2016, the number of aircraft produced per year has been increased to 168. This is 14 Boeing 787s per month. As of May 2022, 691 units have been produced.
Manufacturing facilities are located in Everett, USA. Moreover, for the most part, finished parts are assembled at the factory. 1.2 thousand people are involved in the process.
The company's contractors are based in different areas of the world. Thus, the wings are produced by Japanese Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, the doors by the French Latecoere, the tail by the Italian Alenia Aermacchi and the Korean Industries Aerospace, and the chassis by the joint British-French corporation Messier-Bugatti-Dowty.
Aircraft parts are delivered from the manufacturer to the customer on a specially created Boeing 747 LCF DreamLifter production aircraft, of which Boeing has 4.
Japanese engineers played a key role in the project: 35% of all components of the airliner in 2022 were manufactured in Japan. In addition, it was the Japanese who took an active part in the design and development of the Dreamliner.
Partnerships
As noted above, one of the hallmarks of the 787 program was massive outsourcing.
Partners
| Partners | Element |
| Dassault Systems | Design software |
| Metrology group | Metrology software |
| ZAE – Zodiac Aerospace | Electrical conductors, primary and secondary distribution |
| Labial | Electrical cables and optical fibers |
| Latécoère | Passenger doors |
| Safran Landing Systems (Messier-Bugatti) | Electric braking system |
| Safran Landing Systems (Messier-Doughty) | Chassis |
| Michelin | Chassis tires |
| Suryau | Circular connectors, approximately 2500 per aircraft |
| Thales | Electrical conversion system and emergency display (cab) |
| Zodiac | Evacuation slides, water and waste management systems, pilot oxygen system |
| Kawasaki Heavy Industries | Central box. |
| Fuji Heavy Industries | Reinforced structure design in the lower half of the central fuselage. |
| Mitsubishi Heavy Industries | Wing design |
| Alenia Aeronautica | Design of the horizontal stabilizer (wingspan 19.50 m) and the upper part of the central fuselage. |
| Vought | Rear fuselage of the aircraft |
| Saab | Cargo and entrance doors |
| SMAC | Aircraft cabin acoustic protection |
The table shows that many French equipment manufacturers were selected by Boeing to build this aircraft. This is largely due to the fact that they were the first suppliers to Airbus for decades and were therefore closely associated with many of the innovations made by European aircraft manufacturers, and that they were able to solve the problems listed by Boeing's purchasing director about 20 years ago.
This is also likely a consequence of the appointment of Yves Gallande, former Minister (notably of Industry and Delegate for Finance and Foreign Trade from 1995 to 1997), as then President of Boeing France in May 2003.
Aircraft modifications and their costs
The Boeing 787 today has 3 main modifications:
- Boeing 787-8 worth $224.6 million;
- Boeing 787-9 worth $264.6 million;
- Boeing 787-10 worth $306.1 million.
Original
This group is the smallest, it includes only 2 modifications: 737-100 and 737-200. These aircraft were produced from 1967 to 1988. Today, the first model is not in use due to fuel inefficiency, expensive maintenance, and its technical characteristics are very outdated. The second modification is quite rare for the same reasons. The specific fuel consumption of the Boeing 737-200 is about 33 g/pass-km. For example, it is worth noting that the next model required approximately 26 g/pass-km of fuel.
According to Boeing, after 2007 there were not a single 737-100 aircraft left in airworthy condition, so the aircraft of this model can only be seen in aviation museums or in photographs. The 737-200 modification is mainly found on either low-cost carriers or airlines owned by developing countries.
Airplane Boeing 737-100
Specifications
Specifications vary by model. Summary information on the models is presented in the table:
| Model | 787-8 | 787-9 | 787-10 |
| Date of issue | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 |
| Price (millions of dollars) | 225 | 265 | 306 |
| Type | base | extended | the longest |
| Length (meters) | 56 | 63 | 69 |
| Height (meters) | 17 | ||
| Fuel capacity (thousand liters) | 124,7 | 139 | 145,6 |
| Power point | Gen. Electric - GEnx/1B Rolls Royce Trent 1k | ||
| Ultimate thrust (in tf) | 2X-28.6 | 2X-32.6 | 2X-34.7 |
| Limit number of passengers | 210 (2 classes) 250 | 250 (2 classes) 490 | 300 (2 classes) 350 |
| Flow limit | 13 thousand m | ||
| Distance (in thousand km.) | 13,6 | 14,1 | 11,9 |
| Maximum weight (tons) | 217 | 245 | 245 |
| Cruising speed | 903 km/h at an altitude of 12 thousand m | ||
| Wingspan (meters) | 58,8 | 60 | |
Boeing 787-8
This is the most popular and inexpensive model of the Boeing 787. Its capacity is 250 people, and its flight length is 13.5 thousand km. Such a plane costs 225 million dollars. Date of creation: 2011
Boeing 787-9
Longer version of the 787-8. Depending on the modification, it can accommodate about 300 passengers. The distance over which this liner can transport passengers is 14 thousand km. It costs $265 million and was put into operation in 2014. It is a direct competitor to the Airbus A330, 340/200, Lockheed L-1011 and Douglas MD 11.
Boeing 787-10
The longest modification of the Dreamliner. Accommodates up to 330 passengers. The transportation range is over 11.9 thousand km. The first deliveries were planned for 2022. This is the main competitor of the Airbus A350-1000 for short-haul flights and an improved version of the Boeing 777 series (200 and 200ER).
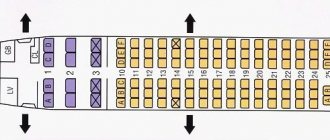
Passenger cabin plan
How many seats are inside the cabin depends on the Boeing modification. The cabin layout of the basic version of the 787-8 includes:
- 36 business class seats;
- 206 economy class seats.
Arrangement of seats in rows:
- in business class - 2-2-2;
- in economy class - 3-3-3.
Different airlines may change the cabin layout as desired. For example, make a 1-2-1 layout for business class, 2-4-2 for economy class, or use a single-class cabin.
Advantages of the Boeing 787 Dreamliner
The main features that make it possible to advantageously differentiate the Boeing 787 Dreamliner from all similar aircraft:
- huge capacity;
- economical fuel consumption;
- high load capacity;
- reduction in operating engine noise by as much as 20%;
- low aircraft weight due to lighter materials;
- ease of operation for pilots;
- the ability to quickly monitor all aircraft parameters on the windshield.
The above factors can save carriers huge amounts of money. As for passengers, the latest equipment, a spacious cabin, ample luggage space, pleasant lighting and stylish design guarantee a comfortable flight to anywhere in the world.
We recommend watching an interesting video about the Boeing 787 Dreamliner. History and description of the dream liner.
Classic
Over time (by 1979), the need to design new aircraft became extremely urgent, since in addition to high fuel costs, as well as expensive and labor-intensive maintenance, the “original” aircraft had another problem - increased noise levels on board. Already in 1980, based on the 737-200 Advanced model, engineers presented to the world a then modern airliner with 150 passenger seats - the 737-300. It received new engines and an improved interior. The main differences of this aircraft, due to which it could no longer be considered “original,” were changes in aerodynamics and the appearance of a forklift. The length of the Boening 737-300 aircraft has increased by 3 meters compared to its predecessor and amounted to 33.18 meters. Flight range is 4,400 km.
The Boeing 737-400 was developed primarily in response to numerous requests from charter carriers to increase the cabin, which required a complete redesign of the air conditioning system.
The latter feature was later carried over to other stretchliners (-800 and -900). The fuselage length of the 400th model is about 36 meters, and the cabin capacity is 168 people. The maximum flight range is 5,000 km.
Boeing 737-400. Missing portholes and 2 emergency exits are clearly visible
The Boeing 737-500 is the smallest representative of the classic series (2 meters smaller than its predecessor), but at the same time it can cover distances of up to 5,200 km and is still operated by many airlines. Serial production ceased in 1999, as the company introduced a more modern alternative - the Boeing 737-600, which already belongs to the “new generation”.
Which airlines operate Boeing 737
Today, Boeing 737 airliners of various modifications are operated on medium- and short-haul flights by many airlines in 115 countries around the world. This model is in great demand among Russian air carriers.
Aeroflot
A large Russian carrier entered into a contract for the supply of Boeing aircraft to the aviation fleet with a well-known American aircraft manufacturer in 2011. As of 2022, the most popular domestic air carrier operates 42 Boeing 737-800 aircraft, with 5 more units expected to be delivered.
The aircraft are equipped with two-class passenger cabins for 158 people. For those traveling on a business tariff, there are 20 seats in a separate comfortable cabin.
S7 Airlines
The Russian airline S7 Airlines, which carries out passenger transportation on domestic and international routes, operates 21 Boeing 737-800 and 2 airliners of the MAX8 modification. There are 9 more aircraft on order.
The cabins of passenger airliners have a two-class layout. The total number of seats is 176 (8 seats - business class).
Nordwind Airlines
The Russian charter airline Nordwind has 5 Boeing 737-800 modifications in its fleet. A single economy class cabin accommodates 189 passengers.
Victory
The Russian budget company Pobeda, a subsidiary of Aeroflot, operates 23 Boeing 737-800 on its routes with a capacity of 189 passengers. These are all aircraft available in the fleet of a given carrier. The air fleet will soon be replenished with 7 more aircraft of this modification. Also on order are 20 Boeing 737MAX8 versions.
Flydubai
The UAE state budget airline has 51 Boeing 737-800 aircraft, 10 737 MAX 8 aircraft and 2 737 MAX 9 aircraft.
The cabin of the base model is configured for one class of service with a capacity for 189 people. There are also two-class aircraft designed to carry 174 passengers.
The fourth generation Boeings are equipped with comfortable two-class cabins with 166 and 172 seats.
The carrier Flydubai has 121 Boeing 737 MAX 8, 68 - MAX 9 and 50 MAX 10 units on order.
UTair
The Russian carrier UTair operates 9 Boeing 737-800. The salons are arranged in one and two classes of service. Passenger capacity – 159/186 people.
Royal Flight
The Russian charter airline Royal Flight has 2 Boeing 737-800 in its fleet. The cabins are arranged in one economy class of service with a capacity of 189 seats.
Azur Air
The domestic air carrier Azur Air operates 6 aircraft of the 737-800 modification on its airlines. The 1st class cabin accommodates 189 passengers.
Belavia
The Belarusian airline Belavia maintains in its aviation fleet 7 Boeing 737-300 (single-class for 189 people), 6 airliners 737-500 (two-class cabins for 120/123 and 148 people) and 5 aircraft 737-800 (single-class cabin for 189 people) . The order includes 4 Boeing MAX8 modifications.
Russia
Rossiya Airlines operates 16 737-800 aircraft. The salons are configured for 1st and 2nd class service. The total number of seats is 168/189.
Nordavia
The Russian carrier Nordavia, based in Arkhangelsk, operates 9 Boeing 737-500 (single-class cabins for 132/135 passengers) and 2 airliners 737-700 (1 class of service, accommodating 148 people). There are 2 B737-800 aircraft on order.
NordStar
The Russian airline NordStar (Taimyr) maintains 9 Boeing 737-800 aircraft in its fleet. Two-class cabin layout for 180 people. One Boeing 737-300 modification with an economy class passenger cabin for 148 people will also be used.
Pegasus Fly
The Russian carrier Pegas Fly has 4 Boeing 737-800 modifications in its fleet. Single-class cabin for 189 passengers.
Turkish Airlines
Turkey's major flag carrier operates 105 Boeing 737-800s on its routes. The cabin is arranged into 2 classes of service. The total number of seats is 165.
The aviation fleet also includes Boeing 737-700 (1 aircraft with a capacity of 149 people in an economy class cabin) and a modification of the 737-900ER (15 aircraft, two-class cabins for 159 people).
Turkish Airlines has an order for 65 Boeing 737 MAX 8 aircraft and 10 737 MAX 9 aircraft.
The popularity of the Boeing 737 line is fully justified by the high level of reliability, efficiency, safety and maximum comfort for passengers. B737s of various modifications occupy the vast majority of the aircraft fleets of many global carriers.
Family 737
The 737 family airliner has been in production since 1967. It was a very successful project - both from the point of view of aircraft design and from a commercial point of view. It remains one of the most common passenger aircraft in the world.
Image caption
The Boeing 737 airframe was designed for completely different engines. This photo was taken in 1968
The 737 used what would become a classic design for passenger aircraft - a low-wing design (its wing is located at the bottom of the fuselage) with the engines located under the wing.
The first Boeing 737-100 was designed to carry from 85 to 215 passengers. The original series included models 100 and 200. The airframe of this aircraft was designed to use Pratt & Whitney JT8D-1 turbojet engines, which were shaped like an elongated cigar and occupied the entire space under the aircraft's wing.
At the same time, the height of the landing gear was designed in such a way that the aircraft was as close as possible to the surface of the earth and was easier to maintain.
In the 1980s, the first generation of 737s, which remained in history under the name Original, was replaced by a new one, called Classic. It was then that the Boeing 737 received its familiar appearance, which was determined by a new type of engine - turbofan. They were less noisy, more economical, but had a noticeably larger diameter.
The designers of the American corporation had to solve the problem of how to place them under the wing. They had to be carried far forward.
Image caption
Boeing 737-400 – representative of the Classic generation
In addition, the engine parts located in the lower part had to be moved to the side walls - the 737 received the characteristic outlines of non-circular engines.
MCAS system
Already after the first disaster, reports appeared online about some kind of automatic system on the plane, about which the pilots were allegedly not informed.
We are talking about a program that helped pilots “taxi” the plane, adjusting its position in the air and pointing it slightly downward. This system is called “Maneuvering Characteristics Augmentation System” (MCAS).
The introduction of such a system was necessary due to the design features of the new Boeing.
The 737 Max received new engines, which turned out to be slightly larger in diameter and more powerful than those on the predecessor 737-800 NG. They had to be brought forward and raised a little, which changed the behavior of the aircraft in the air, and it had a tendency to “pitch up” - it began to “turn up its nose” a little.
This behavior of the aircraft in the air had to be corrected somehow, because uncontrolled pitching up can lead to a loss of speed, and this is fraught with stalling.
That’s why the MCAS system appeared on the new Boeings. It worked when the autopilot was turned off (the autopilot does not need help, it monitors everything itself), when the flaps and slats were removed (they create additional lift, which prevents the plane from falling even at a relatively low speed) and, most importantly, when the speed increased. attack angle. This is the name of the angle between the direction of movement of the aircraft and its longitudinal axis - that is, if the nose of the aircraft is raised up, and it flies forward.
Each time, during manual control, the angle of attack increased above a certain level, the system was activated, slightly deflecting the elevators, pointing the nose of the aircraft slightly downward.
Already after the first disaster, rumors appeared on the network that this system allegedly could not have worked correctly due to a faulty sensor that transmitted incorrect information about the angle of attack to it.
After the second disaster, despite the almost complete absence of information in open sources about the progress of the investigation, they began to talk about the possible similarity of the causes.
Image caption
Flight data from an Ethiopian Airlines Boeing 737 MAX 8 indicates the aircraft made several abrupt altitude changes.
At the same time, the investigation into the first crash has not yet been completed; it is not yet possible to say unequivocally about malfunctions of any aircraft system as the cause of the disaster.
Moreover, Boeing issued an official statement in which it explained exactly how this system works and emphasized that it was certified by the American Aviation Administration, which still does not consider the 737 Max unsafe.
The US Aviation Administration initially said it considered the 737 Max a safe aircraft and had no intention of banning it.
However, on Wednesday evening, US President Donald Trump announced that he had ordered the grounding of Boeing 737 Max 8 and Max 9 passenger aircraft until further notice. The United States is the latest on the list of countries to suspend operation of these aircraft. And on Thursday the ban was announced in Russia.
The decision to lift the ban will be based on an analysis of messages that will come from US aviation authorities, the head of the Federal Air Transport Agency said. There are only two Boeing 737 Max 8 in Russia so far - S7 Airlines, which suspended flights of these aircraft on Tuesday.
“Neither yesterday nor the day before yesterday did aircraft of this type fly over the territory of the Russian Federation,” Neradko recalled.