Even those who are far from the world of weapons know about this legendary rifle. Mosinka has a rich history. It appeared back in 1891 and was used by the army first of the Russian Empire and then of the Soviet Union for more than 50 years. This weapon remains relevant today. For military purposes, sniper rifles based on the Mosin three-line are used. The Mosinka can also be used for hunting. This is a very reliable, inexpensive rifle that is suitable for hunting medium and large game.
History of the Mosin rifle
The Model 1891 three-line rifle, more often referred to simply as the Mosin rifle, "Mosinka" or three-line rifle, was adopted for service in 1891. It was used en masse from 1892 until the end of the 50s of the 20th century. During this time, the rifle underwent modernization several times. It is called three-line because of its caliber, which is equal to three lines. This is a traditional length measure equal to 2.54 mm.
- Russian designer Sergei Ivanovich Mosin presented the first version of his famous three-line design in 1889. It was developed on the basis of his earlier single-shot rifle, from which it borrowed the receiver and bolt group unchanged. But in order to adopt it for service, the Russian army needed to change the design of the bolt group and magazine, which was done. In 1892, production of this version of the rifle began at the Izhevsk, Tula and Sestroretsk arms factories. Since their capacity was not enough, Mosinki at this time were also produced at a plant in the French city of Chatellerault;
- in combat conditions, the three-line gun was first used in 1893 during the battle with the Afghans in the Pamirs. The first stage of rearmament of the Russian army with Mosinka was completed in 1897. Subsequently, rifles adopted by the armies of other countries were quickly modernized, while the three-line rifle lagged behind them in this regard. As a result, by the First World War, the Mosinka was noticeably inferior to them in terms of characteristics;
- In the first years of Soviet power, there was a question about replacing the Mosin rifle with a more advanced one or modernizing it. The second option was chosen because after changes were made to the design, the Mosinka could meet the requirements for this class of weapon. At the same time, the development of a new repeating rifle was pointless, since repeating rifles were an obsolete type of weapon. As a result of the 1924 modernization, the Mosin rifle model 1891/30 appeared. In 1928, the USSR began producing optical sights for it.
- in 1938, another modification of the Mosinka was developed - the 1938 model carbine. It was designed for targeted shooting at a range of up to 1000 m;
- The next modification adopted by the Red Army was the 1944 carbine. It was distinguished by simplified manufacturing technology and the presence of a permanent bayonet. After its adoption, the Mosin rifle model 1891/30 was discontinued.
Model 1907 weapons
This Mosin carbine has the following characteristics: barrel length is 87 cm, muzzle energy is 900 J. This gun is suitable for aimed shooting at a distance of over 500 meters. It should also be noted that there is no magazine in the specified configuration. The butt in this case is made of wood. In turn, the barrel is classified as rifled.
Only 7.2 mm caliber cartridges are suitable for it. The butt plate of the presented gun is of a blind type. At the same time, the seal above the shutter is made quite durable. The sear in this model is used with a special ball. Due to this, the spring does not fall down. It should also be noted that the diameter of the rod is exactly 3 mm. The safety in the said rifle is used with a clamping nut.
Design
The Mosin rifle has a barrel with 4 grooves. In its rear part there is a chamber with smooth walls. Also at this end of the barrel there is a threaded stump; the receiver in which the bolt is placed is tightly screwed onto it. A magazine box with a feed mechanism, a cut-off reflector and a trigger mechanism are attached to the bolt.
The cartridges inside the magazine are arranged in one row. The reflector cut-off separates the cartridges that are in the magazine box and the cartridge in the barrel. This ensures that there are no delays in feeding that could be caused by the rims of the ammunition catching on each other. This detail also reflects spent cartridges. The reflector cut-off is one of the key elements of the rifle, which was introduced into the design by Mosin. Thanks to it, the rifle works flawlessly in any conditions.
Components of the trigger mechanism:
- hook;
- trigger spring, which also serves as a sear;
- screw;
- hairpin.
The trigger of the Mosin rifle is tight and long, without warning - the trigger stroke is not divided into two stages with different forces.
Components of a three-line shutter:
- stem with comb and handle;
- larva;
- ejector;
- trigger;
- drummer;
- action spring;
- connecting strip.
The mainspring is compressed when the bolt is unlocked by turning the handle. During locking, the firing pin rests against the sear. The firing pin can also be cocked manually with the bolt closed by pulling the hammer back. To put the rifle on safety, you need to pull the trigger back and turn it counterclockwise.
Existing models
Since its creation, the design has not undergone any fundamental changes, remaining the same easy-to-use and trouble-free combat mechanism. Initially it appeared in three versions , which even differed little from each other:
- Infantry rifle . Classic design, with a long barrel and bayonet. It is worth noting that it was the most accurate, but the least convenient in some conditions, precisely because of the long barrel, at the end of which there was also a bayonet. Since each barrel was sighted with a bayonet, it was impossible to remove it without hopelessly losing the accuracy of the shot. Because of this, it was inconvenient to conduct combat operations in trenches, dense forested areas and buildings.
- Dragunskaya . She is also a cavalry soldier. A slightly shorter barrel and bayonet - the dragoons fought as part of the cavalry, shots were fired at a closer distance. And the requirements for accuracy were lower - which affected the length. Also in this version the belt was attached differently.
- Cossack . Similar to the dragoon, but without a bayonet. The melee weapon for the Cossacks was traditionally the saber; a bayonet on a rifle is not so necessary.
Existing models
Sights
The Mosin rifle of the 1891 model was equipped with a stepped sight. On the 1891/30 modification, a sector sight was installed. It consists of an aiming bar with a clamp, an aiming block and a spring, and is marked at a distance of up to 2000 m. The rear sight can be installed in any position from 50 to 2000 m, the step is 50 m. The front sight on the 1891/30 rifle received a ring muzzle.
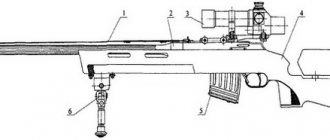
To fully unleash the potential of the Mosin rifle, it is necessary to install an optical sight on it. Owners of this weapon can bet on it like anything, but the situation is complicated by the fact that it was not originally intended for use with optical sights. It is important to choose optics that will not interfere with the use of open sights.
A good solution may be to install a “native” PU optical sight using a Kochetov vertical base bracket. In this way you can get the most authentic and harmonious externally weapon.
Another option is to use modern mounts and modern optical sights.
Reviews of the modification of the 1907 model
This Mosin carbine (model 1907) is not particularly accurate. It should also be taken into account that the gun misfires a lot. This is due largely to the characteristics of the rammer. The sighting bar on the presented specimen is 3 cm wide. It should also be noted that the butt used is quite comfortable. However, there is a lot of recoil when firing. This gun is not very easy to maintain. In some cases, the sear fits quite tightly. Additionally, it should be noted that the rammer mechanism must be cleaned frequently.
Operating principle of the Mosin rifle
To charge the three-line, you need to:
- turn the shutter handle to the left;
- pull the shutter all the way back;
- insert the clip into the receiver;
- drown the cartridges, throw away the clip;
- move the shutter forward;
- turn the shutter handle to the right.
Then all that remains is to pull the trigger to fire. To fire the next shot, simply repeat steps 1, 2, 3, 5 and 6. Four cartridges are fed from the clip into the magazine, the fifth into the receiver. After closing the bolt, it ends up in the chamber.
Consumer opinion about the Los 7.1 model
For hunting, many people choose these Mosin carbines because of the convenient sight. Additionally, it should be noted that the receiver of the presented example is quite wide. Above the pusher there is a latch with a diameter of 2.3 mm. The mainspring is installed with a diameter of 2.6 cm. A fixing nut is provided above the stopper.
The barrel in this case is exactly 95 cm long. The disconnector in it is located near the central axis. If you believe consumer reviews, the magazine is quite easy to remove. It should also be mentioned that the fuse does not require frequent lubrication. If necessary, you can simply remove the sear. Gun misfires are rare, and this makes many owners happy.
Versions and modifications
The Mosin rifle is a weapon intended for military purposes. Some people use these military three-ruler rifles for hunting. Various modifications of the Mosin rifle and carbines created on its basis were developed specifically for hunting purposes - primarily the KO-91/30, OTs-48 and Los carbines.
Carbine KO-91/30
A rifle designed for hunting medium and large-sized animals. Main characteristics of KO-91/30:
- length – 1232 mm;
- barrel length – 745 mm;
- weight – 4.0 kg;
- caliber – 7.62 mm;
- cartridge used - 7.62x54R;
- Magazine capacity – 5 rounds.
The rifle is designed for shooting at a distance of up to 300 m. You can also install an optical sight on it, which, once installed, does not interfere with open use. Recharging is done manually. The design feature of this rifle lies in the safety mechanism that protects against premature firing.
Carbine OTs-48
The OTs-48K sniper rifle was developed by the Tula TsKIB for sporting and hunting weapons in 2000. It was created for the needs of the Ministry of Internal Affairs troops and special forces. The rifle showed excellent results in tests both in terms of firing range and accuracy of fire. It can be aimed at 1300 m, while at a distance of 100 m the spread of bullets does not exceed 3.5 m. For the Dragunov sniper rifle, these figures are 1000 m and 8 cm, respectively.
The OTs-48, in turn, is a hunting carbine based on the Mosin rifle, which is intended for hunting large game. It is designed to use 7.62x54R cartridges. The barrel and locking assembly remained from the Mosin rifle, and the stock and stock were replaced with modern ones. Unlike OTs-48K, which is produced only in small quantities on special orders, OTs-48 went into mass production and turned into a fairly recognizable brand.
Carbine KO-8.2
An 8.2 mm caliber rifle, which was developed for cartridges with semi-jacketed bullets and was produced in the USSR. Its other characteristics:
- rifle length – 1010 mm;
- barrel length – 520 mm;
- weight – 3-3.6 kg;
- magazine capacity – 5 rounds;
- bullet starting speed – 440 m/s.
Designed for hunting medium and large animals. Reloaded manually, trigger without warning. There is also a modification of the KO-8.2M, which has a different rifling pitch, has an active sector sight and a different stock shape.
Carbine KO-38
A hunting rifle, which was created on the basis of a carbine of the 1938 model and was produced in the USSR.
Carbine KO-44
A hunting carbine developed on the basis of a military carbine of the 1944 model, which was produced in the USSR.
Carbine "Los-7-1"
The “Los” family of hunting weapons was developed in the USSR largely on the basis of the Mosin three-line rifle. Main characteristics of the Los-7-1 carbine:
- barrel length – 550 mm;
- weight – 3.5 kg;
- caliber – 7.62 mm;
- cartridge used – 7.62×51 mm;
- Magazine capacity – 5 rounds.
On sale you can find modifications of the Los-7-1 carbine for different types of imported cartridges.
Among experts, opinions about the Mosinka and carbines created on its basis differ. But they are quite popular and suitable for fishing for medium and large game. The main advantages that distinguish the Mosin hunting carbine are the highest reliability and affordable price. This weapon is used by many professional hunters. Thanks to the release of updated versions such as the OTs-48, this combat system still remains relevant.
Owner reviews about modification 91/30
Many owners speak positively about this rifle. Its muzzle energy parameter is very high. All this makes it possible to feel comfortable while hunting. It is also important to mention that the stock is designed for an interestingly shaped gun. It is slightly ground around the edges, so you don’t feel much recoil when firing. The seal in the Mosin 91/30 model is exactly 1.5 mm thick. The butt plate is standardly made in a round shape. If you believe consumer reviews, the sear does not need frequent lubrication.
Additionally, it should be noted that the fuse operates without failure. In turn, the spring retainer is of poor quality. If necessary, the block can be removed very easily. It is also important to consider that the Mosin 91/30 rifle has a fairly wide stock. Due to this, the coupling very rarely becomes dirty. Additionally, this rifle was appreciated by many due to its ramming device. The protective nut on it is quite strong.
Conclusion
What conclusion can be drawn when talking about a weapon model that, without significant changes since the release of the first copy, is still used today, having large numbers of fans in hunting circles and not only?
Low cost, high reliability and lethality - all the main components of a weapon whose last shot will not be fired very soon. Both in forests and in combat zones: according to reliable information, the Mosin rifle is used in the sad events taking place right now in Syria and Libya. Whatever it is, do not forget about safety precautions when handling weapons, more on that later.
Uninterrupted Mosin Rifle
Penetrating power
A 7.62mm cartridge fired from a VM penetrates right through:
- 12mm iron layer.
- A layer of gravel of 1.2 meters.
- A 0.7 meter oak wall.
- Shelters made of 0.7 meter sandbags.
- Helmets, body armor - right through. If a person is wearing heavy body armor, he will “get off” with severe damage to internal organs in the area of impact.
There are reliably known cases from the Second World War when airplanes were shot down with rifles.
Penetrating power
Flaws:
- Outdated cartridge . The edge in the device makes it very difficult to feed it from the magazine, which at one time was solved simply: they introduced a cut-off reflector into the design of the rifle, which is difficult to manufacture and quickly becomes unusable.
- The rifle's trigger is quite heavy and long , interfering with comfortable accurate shooting.
- The fuse fails quickly and is inconvenient to use.
Among pneumatic connoisseurs, there is a fan of the high-pressure air sniper rifle.
See the price of the Gamo Hunter 1250 air rifle here.
Our country is one of the leaders in the production of small arms, including snipers; read about the longest-range sniper rifle in Russia at: