The Mi-8 is a multi-purpose and widely used helicopter. Designed and developed by OKB designers M.L. Mile in the early 60s. This Soviet development is the most popular twin-engine air transport vehicle in the world (it is on the list of the most common helicopters in the world history of aviation). It has two directions: military and civil.
In July 1961, the B-8 prototype took off for its first flight. A year later, the second copy of the B-8A was released. In 1967, the Mi-8, which had already been fully modified and changed its old name to a new one, entered service with the Air Force of the Soviet Union. Since the model has proven to be one of the most successful, the current Russian Air Force is also ordering this helicopter. At the moment, this unit is used in fifty countries around the world.
The key modification of the 80s was the developed Mi-8MT. The improved version, or, as it is also called, “product 88”, differs from its counterpart in improved power mechanization (two TVZ-117 engines) and the installed power-type auxiliary structure. True, this option is not so widespread around the world.
In 1991, development began on a new civil air transport helicopter, the Mi-8AMT. At the end of the 90s, the Mi-8AMTSh water transport attack helicopter was developed. In total, over 3,500 copies were produced.
History of the creation of the Mi-8 helicopter
With the advent of the Mi-6 heavy helicopter, a new era in helicopter construction opened. However, a heavyweight was not needed everywhere and not always; a “medium” helicopter, like the Mi-4, was much more in demand, but the latter no longer met the requirements of the time.
On February 20, 1958, a Decree of the Council of Ministers of the USSR was issued ordering the development of a new helicopter to replace it, not with a piston engine, but with a gas turbine engine. The working name of the new helicopter was V-8, but it went down in history as the Mi-8 multi-purpose helicopter . The new vehicle was to be designed in two versions at once: the passenger Mi-8P and the transport Mi-8T.
G.V. Remezov (later V.A. Nikiforov) was appointed the lead designer for the V-8 (Mi-8), the general management of the project was carried out by deputy chief designer V.A. Kuznetsov.
Czech passenger helicopter Mi-8P.
In 1959, the preliminary design and full-scale model of the helicopter were approved, after which detailed design began. It immediately turned out that it was virtually impossible to use developments on the Mi-4 due to technical features. Specially for the Mi-8, OKB-117 designed a new engine with a power of 1250 hp. However, according to the decision of the general designer, there should have been two such engines on the helicopter.
The design of the Mi-8 in general was extremely advanced. Duralumin stamping of large parts, glue-welded joints, an automatic engine control system - all this was implemented for the first time specifically for him.
Since the idea was too revolutionary, the USSR Council of Ministers decided to build two versions of the B-8 at once: with one and with two engines.
The first prototype of the Mi-8 with one AI-24V engine and a four-bladed propeller from the Mi-4 first took to the air on June 24, 1961.
The second Mi-8 prototype with two TV2-117 engines and a new five-blade propeller took off on August 2, 1962. Joint state tests of both machines began in March 1963 and ended in favor of the twin-engine version of the helicopter.
The prototype of the V-8AP passenger helicopter was manufactured at plant No. 329 by May 1964, and then until March 1965, it underwent comprehensive testing.
Mi-8T helicopter. Pay attention to the windows - transport versions of the Mi-8 have round ones, while passenger ones have square ones.
Immediately upon their completion, the helicopter under the designation Mi-8P was put into serial production at the Kazan aircraft plant No. 387. By 1969, the Mi-8 had completely replaced the Mi-4 on the assembly line, and in 1970 the plant in Ulan-Ude began producing it. A transport version, the Mi-8T was adopted by the USSR Air Force in 1968.
In 1968, a group of workers at the Moscow Helicopter Plant were awarded the USSR State Prize for the creation of the Mi-8.
At the time of its introduction into service, the Mi-8 set 7 international records. In total, over the years of serial production from 1968 to 1996, about 8,200 Mi-8 helicopters were produced, which makes this helicopter the most popular in the world. At the same time, at least half of all produced machines are currently in good working order and work the same as 20 and 30 years ago.
2800 Mi-8s were exported. The list of its “habitats” includes 40 countries, including: Algeria, Angola, Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bulgaria, Hungary, Vietnam, East Germany, Egypt, India, Iraq, Canada, China, North Korea, Cuba, the Netherlands, Nicaragua, Pakistan , Peru, Poland, Romania, Syria, Sudan, USA, Finland, Czechoslovakia, Ethiopia, Yugoslavia, Japan.
The helicopter is constantly being modernized and the current models are noticeably superior in performance to helicopters of earlier years of production.
Drawing diagram of the Mi-8 helicopter
LOCKHEED AN-56 CHEYENNE – the fastest
Released in 1967 in the USA, this helicopter reached speeds of up to 393 km/h
and was created to provide fire cover for its powerful fellow helicopter, the Chinook. Formally, the Cheyenne is not even a helicopter, since it has a pushing propeller. And super-speed (according to some sources, more than 400 km/h) was due to the use of small wings, which allowed the rotorcraft not to lean forward and avoid excessive drag. It’s a pity that the fate of this record holder of the top 10 helicopters in the world was short-lived: an incident with a blade that came off, pierced the canopy and killed the pilot, forced the military to withdraw the high-speed helicopter from the series. The hingeless design of the propeller turned out to be to blame for everything, but the warriors did not have time to debrief the flights - realities were pressing on deadlines.
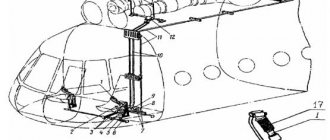
Design of the Mi-8 helicopter
The Mi-8 helicopter has a single-rotor design with a five-blade three-hinge main rotor and a three-blade tail rotor. The fuselage is framed and has a tail support to protect the tail rotor.
The landing gear is tricycle, non-retractable, with a self-orienting front strut that is fixed in flight.
The power plant consists of 2 gas turbine engines TVD TV2-117. From the engines to the shafts of the propellers and auxiliary mechanisms, power is transmitted through a three-stage main gearbox VR-8A. The fuel supply is located in 3 fuel tanks. It is possible to install 1-2 additional fuel tanks of 915 liters each in the cabin (in the cargo version).
The passenger Mi-8P differs from the transport Mi-8T by rectangular windows and the absence of a Doppler antenna for the DIV-1 ground speed and drift angle meter on the tail boom. Its interior has 28 soft passenger seats (as an option, there were models with 20, 24 and 26 seats). The Mi-8P can be used as an ambulance and transport, carrying cargo, including on an external sling.
In the transport version of the Mi-8T, semi-rigid folding seats for 24 passengers are installed in the helicopter cabin along the sides. Access to the salon is through the side sliding door. On the floor of the cabin there are mooring units and pulley rollers, and in the front part there is an electric winch. For loading large-sized plows and equipment, there is a cargo hatch with two doors in the rear. An electric winch boom is installed above the front door. There is an external cargo suspension system. The control is duplicated, with rigid and cable wiring, with hydraulic boosters.
Military versions of the Mi-8 can be equipped with a 7.62 mm or 12.7 mm machine gun in a mobile nose mount. Blocks of unguided projectiles, machine gun containers, or bombs with a caliber of 50-500 kg can be mounted on external double/triple side holders. Up to 6 anti-tank guided missiles can be placed on top of the holders on the guide rails. Machine guns and grenade launchers can be installed in the side openings of the troop compartment.
BELL UH-1 – the most legendary
“Iroquois” - an iconic symbol of the Vietnam War The UH-1, nicknamed “Huey”, became a favorite not only of the American military, but also of all movie lovers
, because without this proud profile with the figure of a soldier, his legs carelessly dangling overboard, not a single decent Hollywood film about the war can do.
The tenacious, beautiful
helicopter was so successful that its series includes more than 16 thousand aircraft. Veterans warmly remember how the Huey became their home, a flying “warehouse” with provisions and a long-awaited transport for evacuating the wounded. During the hostilities, 3,000 vehicles did not return to base, but this helicopter was still considered successful, because the “hard worker” made so many forays behind enemy lines that there was one loss for every 18 thousand sorties! And this despite the fact that the Huey was not even protected by armor.
Characteristics of the Mi-8
A country:USSRType:Multi-role helicopterYear of issue:1961Crew:2-3 people + 28 passengersEngine:2x TV2-117A, 1500 hp each.Maximum speed:250 km/hPractical ceiling:Static: 1300 m, dynamic: 4200 m.Range of flight:425 kmEmpty weight:7000 kgMaximum take-off weight:12000 kg (normal takeoff 11570 kg)Wingspan:Main rotor diameter: 21.288 m.Length:Fuselage: 18.168 m, total length with propellers: 25.24 mHeight:To the main rotor hub: 4.38 m, along the tail rotor: 5.65 m.Wing area:—Weapons:Not available in passenger version
Characteristics are given for the Mi-8P model
KA-50 – the most maneuverable
“Black Shark” is the Soviet “Chamberlain’s answer” to the latest developments of the American aviation industry; this 1982-made helicopter did not manage to become legendary (it has now been replaced by an updated modification of the Ka-52), but managed to become a record holder. The coaxial propeller design allows the Black Shark to perform aerobatic maneuvers, including the “Dead Loop”
and the unique
“Funnel”
: while maintaining guidance on the target, at 180 km/h the helicopter moves around it in a sideways slip with a constant negative pitch angle of up to 35 degrees, dodging enemy air defenses.
Optimal characteristics and attractive price - Robinson's competitive advantage
Robinson helicopters are lighter and more compact compared to similar aircraft from other manufacturers. Thanks to this, they can be used comfortably in urban environments. To store and operate rotorcraft from an American manufacturer, large hangars and landing sites are not needed.
The performance characteristics of Robinson aircraft ensure safe passenger transportation and low operating costs. The manufacturer's helicopters are considered among the safest in the world.
BOEING A160 "HUMMINGBRI" - the most "smart"
Modern drone
2002 model made it possible to finally remove the weakest link from flights - the pilot. From now on, helicopters can fly faster, further, and climb higher (this “bird” flies to 9,000 meters). The Hummingbird is controlled independently, in accordance with combat missions along the route. True, this helicopter is still just a prototype, but according to experts, it is the future. Therefore, “Kolibri” gets its rightful place in the top 10 helicopters in the world.
Publication date: 2015-03-13
RAH-66 "COMANCHE" - the most secretive
In 1996, the Boeing/Sikorsky concern released this invisible aircraft into the sky. The flat outer surfaces of the fuselage, made using stealth technology, are partially made of composite materials with special radio-absorbing coatings
. All the weapons of this reconnaissance and attack helicopter are also hidden inside. This miracle of technology is worth looking at at least once and... forgetting, because the military of the 21st century decided that most of the Comanche’s functions could be better handled by drones, and after admiring as many as two prototypes of the machine, they closed the project.