| 1st Tank Army (1942 - April 1944) 1st Guards Tank Army (1944–1999, 2014–) | |
| Large coat of arms of the 1st Guards Tank Army | |
| Active | 1942–1998, restored 2014 |
| A country | Soviet Union (1942–1991) Russia (1991–1999, 2014–) |
| Type | Armored |
| Role | Breakthrough and use in deep operations |
| Size | 500–800 tanks |
| Engagements | The Second World War
|
| Decorations |
|
| Commanders | |
| Current commander | Lieutenant General Sergei Kisel |
| Notable commanders | Kirill Moskalenko Mikhail Katukov |
Breastplate for veterans of the 1st Guards Tank Army.
1st Guards Tank Army
is a tank army of the Russian Ground Forces.
The army traces its origins to the 1st Tank Army, formed twice in July 1942 and January 1943 and transformed into the 1st Guards Tank Army in January 1944. The army fought as part of the Red Army on the Eastern Front during World War II. . The army was commanded throughout most of the war by Mikhail Katukov. It participated in the early defenses during the Battle of Stalingrad and Operation Uranus, and also participated in the Battle of Kursk, Proskurov-Chernivtsi Operation, Lvov-Sandomierz Operation, Vistula-Oder Offensive Operation and the Battle of Berlin. After the war, the army was stationed in East Germany as part of the Group Soviet troops in Germany.
After the end of the Cold War and the withdrawal of Soviet units from Germany, the army was transferred to Smolensk, disbanded in 1999. The army was reformed in 2014 as part of Russia's military expansion.
Second formation[edit]
The Second Tank Army was formed on January 30, 1943 (order No. 46021) from the headquarters of the 29th Army under the command of the famous commander of tank forces, Lieutenant General of Tank Forces Mikhail Katukov, personally appointed by Stalin. The army was transferred to the Northwestern Front. The 3rd Mechanized Corps (later to become the 8th Guards Mechanized Corps) and the 6th Tank Corps (later to become the 11th Guards Tank Corps) joined it at formation and served with the army throughout the war. [1] He was quickly transferred to the Voronezh Front to defend the southern shoulder of the Kursk salient. He was awarded the Guards and in April 1944 became the 1st Guards Tank Army
, and Katukov received the rank of Colonel General.
On January 1, 1945, the main battle formations of the army were: [2]
- 8th Guards Mechanized Corps
(Major General Ivan Dremov) (January 3, 1944 - May 9, 1945) 19th Guards Mechanized Brigade - 20th Guards Mechanized Brigade
- 21st Guards Mechanized Brigade
- 1st Guards Tank Brigade
- 48th Guards Separate Tank Regiment
- 353rd Guards Self-Propelled Artillery Regiment
- 400th Guards Self-Propelled Artillery Regiment
- 265th Guards Mortar Regiment*
- 405th Guards Mortar Battalion*
- 358th Guards Anti-Aircraft Artillery Regiment
- 8th Guards Motorcycle Battalion
(Colonel Hamazasp Babajanyan) (August 25, 1944 - May 9, 1945)
- 40th Guards Tank Brigade
- 64th Guards Tank Brigade
*Guards mortar regiment (or battalion) (Russian: Грдиейский момерный Regiment (division)) is an open designation used for Katyusha missile launchers.
He participated in the Battle of Kursk, Proskurov-Chernivtsi Operation, Lvov-Sandomierz Operation, Vistula-Oder Offensive Operation and the Battle of Berlin.
The 1st Guards Tank Army was awarded the Order of the Red Banner after the war and became part of the Soviet occupation forces in Germany, known as the Group of Soviet Forces in Germany, with headquarters in Dresden. In 1968, it participated with the 11th Guards Tank and 20th Guards Motorized Rifle Divisions in the Soviet invasion of Czechoslovakia, but then immediately returned to its garrisons. [3] In the late 1980s, the army included the 20th Guards Motorized Rifle Division, the 9th Tank Division and the 11th Guards Tank Division. The headquarters was moved to Smolensk, in the Moscow Military District, in the early 1990s, and in 1995 it lost “Tank” from its name. In its final period of existence within the Russian Army, it consisted of the 4th Guards Tank Division "Kantemir" and the 144th Motorized Rifle Division (withdrawn from Tallinn in Estonia). Disbanded in 1998.
Structure 1988[edit]
The composition of the army in 1988 was (with main weapons), with honorary titles in italics: [4] [5]
- Army Headquarters, Dresden 234th Separate Defense and Security Battalion, Dresden
Signal Regiment, Dresden
Missile Brigade, Kochstadt
- 303rd Separate Repair and Reconstruction Battalion, Dresden
, Riza
, Dresden
, Grimma
1st Tank Army
1st Tank Army, I Formation formed on July 26, 1942 on the basis of the Supreme Command Headquarters Directive No. 994125 dated July 22, 1942 on the basis of the 38th Army (I Formation) of the Stalingrad Front. It included the 13th and 28th tank corps, the 131st and 399th rifle divisions, the 158th tank brigade, artillery, engineering and other units.July 22, 1942 Directive of the Supreme Command Headquarters No. 994125 on the formation of the 1st Tank Army as part of the Stalingrad Front on the basis of the 38th Army by July 28 and on the appointment of Major General K. S. Moskalenko as commander of the army.
July 25 - August 4, 1942 - participation of the 1st Tank Army in the Stalingrad defensive operation (July 17 - November 18) specifically in the counterattack of front forces against the enemy group that broke through to the Don north of Kalach.
July 27, 1942 - the 23rd Tank Corps (99th and 189th Tank and 9th Motorized Rifle Brigades) was transferred to the 1st Tank Army from the 4th Tank Army.
August 4, 1942 Directive of the Supreme High Command Headquarters No. 994140 on the formation of the South-Eastern Front control by August 9 on the basis of the control of the 1st Tank Army.
August 5, 1942 Directive of the Headquarters of the Supreme High Command No. 170554 on the division, for the sake of convenience of control, of the Stalingrad Front into two fronts: Stalingrad (63rd, 21st, 62nd, 4th Tank Armies and 28th Tank Corps) and South-Eastern (64th -I, 51st, 1st Guards, 57th Armies and 13th Tank Corps); Directive No. 994145 Headquarters of the Supreme High Command to the commander of the Stalingrad Front on the transfer, no later than 12.00 August 5, to the commander of the South-Eastern Front of the control of the 1st Tank Army with support units and service institutions for the deployment on their base by August 6 of the control, support units and service institutions of the South -Eastern Front.
In the active army:
- from 07/27/1942 to 08/06/1942
The 1st Tank Army of the II Formation was formed on February 7, 1943 by Directive of the Supreme Command Headquarters No. 46021 of January 30, 1943 on the basis of the 29th Army in the reserve of the Supreme Command Headquarters. It included the 6th Tank and 3rd Mechanized Corps, the 112th Division. tank brigade, 15th, 22nd and 23rd ski brigades, 11th anti-aircraft artillery division, 4 separate tank regiments, artillery and other separate units.
January 30, 1943 - GKO resolution “On providing tank armies with guards mortar units”; Directive of the Supreme Command Headquarters No. 46021 on the formation of the 1st Tank Army by February 8, the appointment of Lieutenant General of Tank Forces M.E. as army commander. Katukov, a member of the Military Council of the Army - Major General N.K. Popel, Chief of Staff of the Army - Major General N.S. Dronova.
From February 15, 1943, the army was part of the special group of General M. S. Khozin
March 11, 1943 General Staff Directive No. 37022 on assigning responsibility to the commander and chief of staff of the 2nd Reserve Army for the timely dispatch of the 1st Tank Army to the reserve of the High Command; Directive of the Supreme Command Headquarters No. 30072 on the transfer of the 1st Tank Army from March 13 to the subordination of the commander of the Voronezh Front.
March 21, 1943 Directive of the Supreme Command Headquarters No. 30079 on the transfer of the 1st Tank Army from March 21 from the Headquarters reserve to the reserve of the Headquarters representative Marshal G. K. Zhukov.
April 12, 1943 Directive of the General Staff of the KA No. 37903 on the transfer of the 100th Tank Brigade from the North-Western Front to the command of the commander of the 1st Tank Army.
On April 28, 1943, by Directive of the Supreme Command Headquarters No. 46126 dated April 25, 1943, the army was included in the Voronezh Front.
June 4, 1943 – Directive of the General Staff of the KA No. 39041 to the commander of the Voronezh Front troops on the inclusion of the 31st Tank Corps, formed in the 1st Tank Army, the 112th, 1st Guards and 49th Tank Brigades, excluding two the last of the 3rd Mechanized Corps. Instead, the 7th and 62nd separate tank regiments were transferred to him from the 1st Tank Army.
June 17, 1943 - Directive of the General Staff of the KA No. 39175 on changing the composition of the 31st Tank Corps: instead of the 112th, 1st Guards and 49th Tank Brigades, it included the 100th Tank Brigade and newly formed on the basis of the 7th , 62nd, 63rd and 64th tank regiments, 237th and 242nd tank brigades.
July 5 - 23, 1943 - participation of the 1st (until July 14), 2nd and 5th Guards (from July 12) tank armies in the Kursk strategic defensive operation.
August 3 - 23, 1943 - participation of the 1st and 5th Guards Tank Armies in the Belgorod-Kharkov strategic offensive operation (code name "Commander Rumyantsev").
September 8, 1943 Directive of the General Staff of the KA No. 40717 to the commander of the Voronezh Front and the 1st Tank Army on the withdrawal of the army (6th, 31st tank corps, 1547th self-propelled artillery, 79th Guards mortar regiments, 385th a separate communications aviation regiment) to the reserve of the Supreme Command Headquarters in the Sumy area by the morning of September 12.
November 26, 1943 Directive of the General Staff of the KA on the dispatch of the 1st Tank Army (Army Directorate, 8th Guards Mechanized, 11th Guards Tank Corps, army reinforcement and support units, rear institutions, without the 31st Tank Corps) by rail to the Brovary, Darnitsa area to the reserve of the Supreme Command Headquarters.
November 28, 1943 Directive of the General Staff of the Spacecraft on the inclusion of the 18th and 1st Tank Armies arriving in the reserve of the Supreme High Command Headquarters in the Darnitsa, Boryspil area from 24.00 on November 29 into the troops of the 1st Ukrainian Front.
December 9, 1943 - Directive No. 30263 of the Supreme Command Headquarters to the commander of the 1st Ukrainian Front and the Headquarters representative, Marshal G.K. Zhukov about the concentration of the 1st Tank Army as it arrived in the area of Kolonshchina, Bashev, Shnitki.
December 24, 1943 - January 14, 1944 - participation of the 1st and 3rd Guards. tank armies in the Zhitomir-Berdichev offensive operation.
January 24 - February 17, 1944 - participation of the 1st, 2nd (from February 11), 5th Guards. and the 6th Tank Armies in the Korsun-Shevchenko offensive operation.
March 4 - April 17, 1944 - participation of the 1st, 3rd Guards (until March 28) and 4th tank armies in the Proskurov-Chernovtsy offensive operation.
April 25, 1944 Order of the NKO of the USSR No. 0016 on the transformation of the 1st Tank Army into the Guards Army, the presentation of the Guards banner to the army, the establishment of a one-and-a-half salary for generals, officers and non-commissioned officers, and a double salary for ordinary personnel. 11th Guards tank and 8th Guards. The mechanized corps was given the honorary name "Carpathian".
By order of NKO No. 0016 of April 25, 1944, the army was transformed into the 1st Guards. tank army.
In the active army:
- from 02/07/1943 to 03/12/1943
- from 04/28/1943 to 09/10/1943
- from 11/30/1943 to 04/25/1944
Reactivation[edit]
After a break of 15 years, the army was restored in November 2014 [6] seemingly on November 13, 2014 [ edit
]
The army was formed as the main maneuver and reserve operational unit of the ground forces of the Western Military District in addition to the 6th Combined Arms Army (headquarters in St. Petersburg) and the 20th Guards Combined Arms Army (headquarters in Voronezh). Considered to be the elite of the Russian Ground Forces. The army continues the traditions of the chronologically first army of the Soviet Union, which received the status of “guards”
. In addition, it includes the 2nd Motorized Rifle and 4th Tank Guards Divisions, which are considered elite formations of the respective branches of the military. The most titled divisions of the Soviet Army, they were located in the garrison closest to Moscow. Due to their proximity to the capital, increased scrutiny was applied to the personnel of these formations; which makes these publications especially prestigious. Moreover, these units received the latest equipment and were therefore known as the “economic” divisions of the Soviet Army. Their loyalty to the government was demonstrated by their participation in the 1991 Soviet coup attempt. The divisions retained their elite status in the Russian Army.
Today the army consists of: [7]
- Army headquarters (Odintsovo, Moscow region)
- 60th Brigade Command (Selyatino village near Odintsovo, Moscow region)
- 2nd Guards Motorized Rifle "Tamanskaya" Division (Kalininets, Moscow Region)
- 4th Guards Tank Division "Kantemirovskaya" (Naro-Fominsk, Moscow Region)
- 6th Separate Tank Brigade "Czestochowa" (Mulino, Nizhny Novgorod Region)
- 27th Separate Guards Motorized Rifle Brigade "Sevastopol" (Mosrentgen, Moscow)
- 112th Guards Missile Brigade "Novorossiysk" (Shuya, Ivanovo Region) (9K720 Iskander)
- 288th Artillery Brigade 'Warsaw'
(Mulino, Nizhny Novgorod region) - 49th Anti-Aircraft Missile Brigade (Krasny Bor, Smolensk Oblast) (Buk-M2)
- 96th separate brigade ISTAR (Sormovo, Nizhny Novgorod)
- unknown engineer-sapper regiment (in formation until the end of 2018) [8] [9] (location in the Moscow region is unknown)
- 20th Separate Regiment for Defense against RMP (Central, Nizhny Novgorod Region)
- 69th separate logistics brigade (Dzerzhinsk, Nizhny Novgorod region)
Sergei Kisel: “According to the precepts of the First Guardsmen”
Commander of the 1st Guards Tank Army of the Western Military District, Major General Sergei Kisel / Photo: Press service of the Russian Defense Ministry
Combat training in formations and units of the 1st Guards Tank Army of the Western Military District is planned taking into account the experience of modern armed conflicts.
The commander of the association, Major General Sergei Kisel, tells Krasnaya Zvezda about the peculiarities of organizing combat training in the 1st Guards Tank Army of the Western Military District and other tasks assigned to the army.
– Sergei Alexandrovich, as you know, your association is the direct successor of the legendary 1st Guards Tank Army, which stormed Berlin in 1945... – Yes, that’s exactly it, and we are proud of this continuity.
On the Kursk Bulge, the army under the leadership of Lieutenant General of Tank Forces Mikhail Katukov took the blow, repelled it and defeated the selected formations of the Wehrmacht. The army participated in the largest strategic offensive operations: Lviv-Sandomierz, Warsaw-Poznan, East Pomeranian, Berlin.
After the Great Patriotic War, the army remained on German territory, where it guarded the western borders of the Warsaw Pact Organization as part of the Group of Soviet Forces in Germany and the Western Group of Forces.
After the withdrawal to Russia in 1992, the association was stationed near Smolensk until 1998, when it was disbanded.
I note that many outstanding military leaders served in the army. Among them is Marshal of Armored Forces M.E. Katukov, Chief Marshal of the Armored Forces A.Kh. Babajanyan, Marshal of the Soviet Union I.I. Yakubovsky, Chief Marshal of Artillery V.F. Tolubko, Army General V.V. Gerasimov, Colonel General G.N. Troshev.
– What is the 1st Guards Tank Army today? What challenges does it face? – The army includes motorized rifle, tank, artillery, anti-aircraft missile, missile formations and military units, including the famous Taman Motorized Rifle and Kantemirovskaya Tank Divisions. Today, in terms of combat strength, these are unique formations, which have no equal in terms of combat capabilities in the Ground Forces.
Army units are deployed in several regions of the country. The management bodies and structure of the association make it possible to constantly improve the quality of combat training, solve all assigned tasks as intended, effectively organize and control daily activities, and plan the combat use of troops.
– What are army formations and units equipped with? What modern types of weapons and military equipment are currently being supplied to military formations? – Today, the 1st Tank Army is equipped with modern models of combat vehicles developed by our engineers.
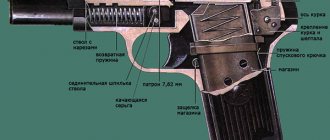
These are modernized T-72B3 tanks with enhanced protection, equipped with the latest multi-channel thermal imaging sight, ballistic computer, improved weapon stabilizer, automatic target tracking and other innovations. Their electronic filling can significantly increase the accuracy of hitting targets. Our main battle tank T-72B3 has sufficient characteristics to detect and destroy any enemy on the battlefield. T-72B3 is a reliable tank. It differs from foreign models in its much smaller dimensions, which makes it less vulnerable. At the same time, it is faster-firing and has good marching abilities.
We also have units with T-90 tanks, which are fundamentally different from other vehicles in the degree of protection for the crew, a long firing range and a more powerful engine.
“In 2022, the army conducted over 1.5 thousand combat firing of squads, platoons, company and battalion tactical exercises”
The well-proven T-80BV and T-80U tanks remain in service. The weapon system on the T-80BV is the same as on the T-72B3 and T-90. The peculiarity of the T-80BV is that this tank is capable of operating at low temperatures. Its gas turbine engine, which is designed without coolant, is unpretentious in cold weather. T-80BV and T-80U are distinguished by unique marching characteristics and are capable of covering long distances in a short period of time. The T-80 was originally developed as a breakthrough tank; it can accelerate to 90 km/h.
In general, the tanks that are in service today fully meet the requirements of the time. Their crews feel confident in modern combat.
There are BMP-3 infantry fighting vehicles in service, and BTR-82A armored personnel carriers are supplied under state defense orders. The association's missile brigade is armed with the Iskander-M operational-tactical missile system. Anti-aircraft missile units are being re-equipped with the latest Tor-M2U complexes and Verba portable air defense systems. I am glad that along with new models of equipment, the corresponding simulators are immediately supplied, which speeds up the process of training specialists.
– What do you focus on today in the combat training of tank crews? – Today, studying includes several main components. Firstly, this is the individual training of crew members, the improvement of which is only possible through practice. Tankers must drive and shoot constantly, and the more difficult the exercise conditions, the more experienced they will be. Underwater driving and combat in the city are practiced. A new test has recently been introduced - a complex shooting exercise, which includes driving while overcoming obstacles and various types of shooting. Secondly, we pay serious attention to the training of managers of all levels. After all, the commander of a tank unit, like a formation, commands not only armored vehicles - army and unmanned aircraft, reconnaissance assets, artillery, motorized rifles, air defense and support units are placed at his disposal. All this makes it possible to solve combat missions both together with the main forces and in isolation from them. And it is from this, by the way, that the third component follows - joint preparation of formations, when units with different missions work together for a common result.
– And what is this result in the past year? – In 2022, the army conducted over 1.5 thousand live firing of squads, platoons, company and battalion tactical exercises, as well as planned combat training events at the brigade-division level.
Army soldiers, sergeants and officers took an active part in the International Army Games 2022 competitions: “Tank Biathlon”, “Suvorov’s Onslaught”, “Sniper Frontier”, “Excellence in Military Intelligence”, “Safe Route”, “Masters of Artillery Fire”, “ Military medical relay race.” By the way, let me remind you that the Alabino training ground of the 1st Guards Tank Army hosted two international competitions this year - “Tank Biathlon” and “Field Kitchen”.
Dozens of teams from different countries took part in them, and thousands of grateful guests attended.
– How did the army servicemen perform at the bilateral regimental tactical exercise, which took place in the fall at the Mulino training ground in the Nizhny Novgorod region?
“The personnel demonstrated high combat skills during this exercise. Army formations made a combined march to the Mulino training ground and adequately completed their intended tasks there. Issues of bringing units to the highest levels of combat readiness, organizing and conducting combat operations, detecting and engaging the enemy by fire were worked out.
Tank, motorized rifle and artillery units carried out joint live firing in the daytime and at night using weapons from T-80, T-72B3 tanks, BMP-2, BMP-3 infantry fighting vehicles, armored personnel carriers, and 152-mm Msta-S self-propelled howitzers. , multiple launch rocket systems "Grad", "Uragan", heavy flamethrower systems TOS-1A "Solntsepek".
When performing combat training missions, the crews of the Iskander-M operational-tactical missile systems practiced transferring the systems from the traveling position to the combat position, reloading the training missile from the transport-loading vehicle to the launcher, performing simulated firing, and also, together with a special-purpose company, organized protection and defense of missile systems after changing launch positions.
“A tank driver must thoroughly know the technology, ballistics, and features of modern combined arms combat, which has become exponentially more complex over the past decades.”
During the active phase of the exercise, Su-34 fighter-bombers of operational-tactical aviation, multi-role Mi-8 helicopters and Mi-24 attack helicopters of the army aviation of the Western Military District destroyed moving targets simulating a mobile group of a mock enemy, and supported with fire motorized rifle and tank units making the transition in a counteroffensive.
I would like to emphasize that the commanders of formations and units involved in the exercise were demonstrated the conduct of combat operations, taking into account combat experience using the example of modern armed conflicts, including in Syria.
All participants in the exercise - from soldiers to commanders - received sets of equipment integrated into the Unified Tactical Level Control System (ESU TZ). Similar samples were installed on military equipment. I would like to note that the ESU TZ is a system of the future; it allows you to take a fresh look at combat, increase the efficiency of using units and weapons, reduce the time for setting a task, and increase the accuracy of fire.
The exercise ended with a review of military equipment. The servicemen showed their skill while marching in a single parade formation, maintaining a certain speed of movement and performing various maneuvers without breaking it.
– Recently, digital technologies, automated control systems, drones, and robotic systems have been actively introduced in the Armed Forces. How does this affect modern tank combat? – Technologies, including digital ones, which are now in service in our Armed Forces, including in the 1st Guards Tank Army, predetermine the success of the battle and ensure the complete defeat of the enemy.
The introduction of increasingly complex technical systems requires a constant increase in the level of knowledge and combat training of military personnel. Thus, a tanker must thoroughly know technology, ballistics, and the features of modern combined arms combat, which has become exponentially more complex over the past decades. Today, tank commanders face the same demands that were once placed on commanders of large units.
– Do you find time for military-patriotic education of young people? - Of course. We pay special attention to interaction with the Youth Army movement. Children, teenagers, boys and girls are frequent guests in the military units of the association and participants in various events.
Thus, in early October, members of the Youth Army and military personnel of the Guards Taman Motorized Rifle Division took part in the annual military-patriotic event “March of the Kremlin Cadets,” dedicated to the feat accomplished by a separate cadet regiment in the fall of 1941. In memory of this, modern young people walked 85 km in less than two days in combat gear with weapons in their hands. It was precisely this distance that the Kremlin soldiers overcame in the fall of 1941 to enter into an unequal battle on the Lama River near the village of Yaropolets, which for many of them was the last.
Military personnel of the Taman and Kantemirovskaya divisions are constant participants in the Victory military parades on Red Square. Recently, Taman residents also participated in the historical reconstruction of the legendary military parade, which took place in Moscow on November 7, 1941.
A search team is actively working on the basis of the association. In August of this year, guys from the detachment discovered, near the village of Byvalki in the Smolensk region, the wreckage of a plane from the Normandy-Neman regiment shot down by the Nazis. Since the Great Patriotic War, the combat vehicle had been lying in a swamp six meters deep. To remove the fighter, the remaining remains of the fuselage were washed away. Small metal elements were recovered by divers from the Russian Ministry of Defense. Previously, the military engineers of the association, together with divers and members of the search party, prepared the surrounding area, including digging more than a kilometer of dirt road through swampy terrain, and conducting ground and underwater reconnaissance to accurately determine the location of the plane crash and the method of lifting the main part of it. After completing the inventory of the fuselage fragments, internal components and assemblies of the aircraft, we will obtain a conclusion about its model. This will allow us to say with 100 percent probability when the plane was shot down and who piloted it in the last air battle. The fact is that the remains of the pilot have not been found. It is likely that he managed to escape the car with a parachute.
Interviewed by Viktor Khudoleev.
MOSCOW, newspaper "Red Star"
12
Original
Army commanders[edit]
- Katukov Mikhail Efimovich - guard [10] ColGen, 1943–1947.
- Belov Eftikhin Emelyanovich - guard lieutenant, 1947–1951.
- Govorunenkov Petr Dmitrievich - Guard Lieutenant General, 1951–1953.
- Yakubovsky Ivan Ignatyich - General of the Guard 1953–1957.
- Tolubko Vladimir Fedorovich - Guards Maigen, 1957–1958.
- Ukhov Vladimir Dmitrievich - MayGen Guards, 1958–1961.
- Ivanovsky, Evgeny Filippovich - Maigen Guards, 1961–1964.
- Kotsasnov Konstantin Grigorievich - Lieutenant General of the Guard 1964–1968.
- Gerasimov Ivan Aleksandrovich - Lieutenant General of the Guard, 1968–1971.
- Lushev Petr Georgievich - General of the Guard 1971–1973.
- Snetkov Boris Vasilievich - guard lieutenant, 1973–1975.
- Popov Nikolai Ivanovich - guard lieutenant, 1975–1979.
- Sovotskin Roman Mikhailovich - guard lieutenant, 1979–1981.
- Osipov Vladimir Vasilievich - guard lieutenant, 1981–1983.
- Shein Boris Pertovich - guard lieutenant, 1983–1986.
- Chernitsov Anatoly Kupyanovich - guard lieutenant, 1986–1990.
- Kolchkin Gennady Andreevich - guard lieutenant, 1990–1992.
- Shevtsov Leonty Pavlovich - guard lieutenant, 1992–1993.
- Sosedov Vasily Petrovich - guard lieutenant, 1993–1995.
- Roshchin Viktor Mikhailovich - guard lieutenant, 1995–1999
- Didn't exist (1999–2014)
- Chaiko Alexander Yurievich - LtGen guard, 2014–2018.
- Kisel, Sergey Alexandrovich – Guard LtGen, 2018-present
Baranets: The T-90M “Breakthrough” tank will strengthen the tank fist of the Russian army
Military observer for Komsomolskaya Pravda Viktor Baranets said that there is not a single part of the T-90M Proryv tank that has not undergone modernization.
Earlier, the commander of the 1st Tank Army of the Western Military District, Lieutenant General Sergei Kisel , announced that the first modernized T-90M Proryv tanks had arrived at the Taman Motorized Rifle Division.
“Several T-90M tanks arrived in the Taman Motorized Rifle Division in April. These are fundamentally new vehicles, they received a new turret and a more powerful engine. The tanks are equipped with a new multi-channel sight, which allows the use of weapons at any time of the day,” Kisel said.
According to him, one of the main and interesting features of the modernized T-90 was the ability to exchange operational information with other combat vehicles on the battlefield in real time.
t-digest.ru / Press service of Uralvagonzavod
“In the Guards Tank Army of the Western Military District, training in control, shooting, and combat on the latest T-90M tanks has now been completed,” the commander concluded.
Commenting on the appearance of “Breakthroughs” in the troops, military columnist for the newspaper “Komsomolskaya Pravda” Viktor Baranets, in an interview with a correspondent of the Federal News Agency , said that at the peak of its military power, the Soviet army had 66 thousand battle tanks, but with the collapse of the USSR, their number was significantly reduced and Currently, military experts talk about the sufficiency of 10-12 thousand combat vehicles.
“Until recently, it was decided to develop the newest Armata tank. The project is still going difficult, but of course it will be a super tank and let’s not rush it, let’s give the designers time to make the car of the century. Therefore, our and the General Staff specialists looked around and realized that the Armata tank was still waiting for who knows how long, it, of course, would be put into service, and decided that it was possible to thriftfully and economically handle the tank fleet that we have in the current Russian army. But here it turned out that the most popular main tank is the T-90, which, like every outstanding weapon, can be modernized very well. We sat down, did the calculations with a calculator, clicked the buttons and realized that we need to give the designers the opportunity to modernize this tank. And this decision was successfully implemented,” says Baranets.
Today, the modernized T-90M Proryv tank has the best qualities of the world's leading tanks. It has a new turret installed, which is equipped with a Kalina fire control system with an integrated combat information and control system, a laser range finder, television and thermal imaging channels.
“Our Western opponents rightfully included it [the T-90M Proryv] not only in the top ten, but already in the top five best tanks in the world. Naturally, the modernized T-72B3 appears there and, of course, for now, theoretically, our newest T-14 “Armata” is in the top ten, but, as they say, it still needs to be tested, established, it needs to go through many more tests and get rid of childhood diseases, so that this unique tank, which has no analogues in the world, takes wing and appears in the army. As for the T-90M “Proryv”, even now it is difficult for me to name such a unit, such a part, protection system, gun, loading system, engine, etc., where something has not been improved. To varying degrees - some radical, some, let’s say, significant. But this tank today, along with the T-72B3, can legitimately be the pride of the Russian army, and the appearance of the Proryv in battle formations really significantly strengthens the tank fist of our army,” the military analyst concluded.
T-90M is a modification of the T-90A, created as part of the Proryv-3 R&D project. The key difference between the tank and previous models was the turret module of a new design with multi-layer armor, placement of the ammunition rack outside the fighting compartment and with a 125-mm 2A82-1M cannon - the same as that of the Armata.