The English captain had trouble hearing
This was stated in an interview with RIA Novosti by the First Deputy Director of the Federal Security Service - Head of the Border Service Vladimir Kulishov. We are talking about the events that took place on October 13, 2022 in the Crimea region.
In December 2022, Deputy Minister of Defense of the Russian Federation Alexander Fomin, in a conversation with Rossiyskaya Gazeta, said: “In 2022, the activity of the alliance’s aviation and naval forces has increased significantly, and situations that could lead to serious incidents are increasingly arising. On the eve of the celebration of the 75th anniversary of the Victory, exercises of a detachment of warships of the joint NATO naval forces took place in the Barents Sea. In August and September 2022, more than 15 flights of American B-52H and B-1B strategic bombers were recorded in close proximity to the Russian border. On October 13, 2022, the British Navy destroyer Dragon sailed through the Russian territorial sea in the area of Cape Chersonesos, and on November 24, 2022, the US Navy destroyer John McCain entered Peter the Great Gulf. The above actions were openly provocative. “Incidents were avoided only thanks to the high level of professional training of Russian pilots and sailors.” At the same time, Fomin did not disclose the details of these cases and focus on the situation with the British destroyer.
Kulishov clarified what exactly happened in the area of Cape Chersonesus.
“On October 13, 2022, despite receiving a warning about the inadmissibility of entering Russian territorial waters, the destroyer URO D35 Dragon of the British Navy crossed the state border of the Russian Federation in the area of Cape Khersones in the Black Sea, taking advantage of the right of innocent passage. In response to demands to immediately leave the Russian territorial sea, the captain of the destroyer announced poor signal reception. As a result of joint actions with the Russian Navy and Aerospace Forces, the warship was expelled to neutral waters,” RIA Novosti quotes Kulishov.
Links
Destroyers and leaders of the First World War HMS Arno* • Medea type • Talisman type • Faulkner type • Lightfoot type • M type • R type • S type • V and W types • Scott type • Shakespeare type • “ “ type Caldwell* • Vicks type* "Standard destroyers" of interwar construction HMS Amazon** • HMS Ambuscade** • Type A • Type B • Types C and D • Types E and F • Types G and H • Type I Leaders of the interwar build Codrington • Exmouth • Faulknor • Grenville • Hardy • Inglefield Destroyers of pre-war types Tribal type • J, K and N types • L and M types "Emergency War Program" types O and P • types Q and R • types S and T • types U and V • type “W” (1943) • types Z and Ca • types Ch, Co and Cr Escort destroyers "Hunt" type Destroyers (1944-1949) "Battle" type • "Whipon" type • "Daring" type URO destroyers type "County" • type 82 • type 42 • type 45 * - foreign built, ** - experimental ships. URO cruisers Tiger type Destroyers Vipon type · Battle type · Daring type · County type · Bristol type · 42 type · 45 type Frigates Whitby type · Blackwood type · Leopard type · Salisbury type · Tribal type · Rothesay type · Linder type · Type 21 · Type 22 · Type 23 SSBN type "Resolution" type "Vangard" Multipurpose nuclear submarines Dreadnought · Valiant class · Churchill class · Swiftsure class · Trafalgar class · Astute class Diesel submarines Explorer-type Stickleback-type Porpez-type Oberon-type Upholder-type Landing helicopter carriers "Bulwark" · "Ocean" Landing dock ships "Firless" type · "Albion" type Landing ships type "Sir Lancelot" · "Sir Galahad" Submarine hunters Ford type Torpedo boats MRB 538 MTB 539 Gay type Dark type Bold type Brave type Minesweepers Tone type · Ham type · Lee type · Hunt type · Venturer type · River type · Sandown type Other "Argus"
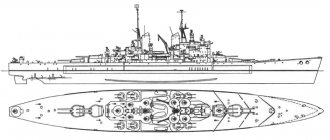
"Dragon" type 45: what is Her Majesty's destroyer?
HMS Dragon (D35) (“Her Majesty's Destroyer Dragon, tail number 35”) belongs to type 45. Ships of this series began to be built for the needs of the Royal Navy in 2003. The lead ship, HMS Daring (D32), was commissioned in 2009. All six of these ships were built, the last of which was delivered to the fleet in 2013.
The Dragon was laid down in December 2005, launched in November 2008 and commissioned into the fleet in April 2012.
The basis of the armament of Type 45 destroyers is the PAAMS anti-aircraft missile system, developed in cooperation with France and Italy. The British version differs from the French-Italian version by using the latest British Sampson radar. In their combat arsenal, the destroyers have Aster 15 and Aster 30 anti-aircraft missiles with active homing heads, which makes it easier to hit low-flying, stealthy and maneuvering targets.
The ship's artillery armament consists of a standard 114-mm 55-caliber BAE Systems Mark 8 universal cannon. The gun can engage ground, surface and air targets at a distance of up to 22 km. The rate of fire ranges from 22 to 26 rounds per minute. The ammunition includes high-explosive fragmentation, long-range (up to 27.5 km), barrage (spraying dipole reflectors) and lighting shells. For close-in air defense, the ship is equipped with two 30 mm Oerlikon guns in single-barrel DS-30B mounts and two 20 mm Mark 15 Phalanx CIWS autocannons. The ship's secondary armament consists of two manually operated 7.62mm M134 Miniguns, designed for self-defense against saboteurs, exploding boats and close-in fire support.
"Congo"
A type of destroyer (series of 4 units) armed with guided missiles. The ships belong to the Japanese fleet. In design, this is an analogue of the American Arleigh Burke-class destroyers.
The hull and shape of the ships' superstructure are optimized in such a way as to minimize radar signature. The installation of equipment made it possible to reduce the level of thermal and acoustic fields. For the first time in the history of Japanese shipbuilding, the Kongo used a system to protect the crew from the effects of weapons of mass destruction.
The destroyers carry radar, tactical strike, artillery and anti-aircraft, missile, mine-torpedo and anti-submarine weapons, and one helicopter.
"Box of wrenches" that is great at catching drug ships
The Sunday Times in 2022 described the combat capabilities of Type 45 destroyers in a rather unflattering manner, citing the opinion of Rear Admiral Chris Parry: “ They are noisy as hell, rattling like a box of wrenches. What’s the point of investing in sophisticated missile defense if a destroyer can be sunk by a submarine that hears it from afar?” The expert believed that Russian submarines would detect these destroyers at a distance of 100 miles. In addition, it turned out that the engine installed on this type of destroyer is not suitable for operation in hot climates and it will take at least 9 years to eliminate this problem.
In October 2016, the Dragon was sent to track two Russian corvettes in the Atlantic during a major Russian naval deployment near the UK. However, the destroyer is best suited for operations involving drug interception.
Thus, on November 26, 2022, “Dragon”, while on an operation in the Middle East, detained a suspicious boat in which 148 bags containing a total of 3048 kg of hashish were found. On March 15, 2022, Dragon seized 224 kg of heroin from a fishing vessel in the Arabian Sea. In total, the destroyer has about a dozen successful operations to seize drug cargo.
HMS Dragon in the port of Odessa. 2022 Photo: Commons.wikimedia.org
Notes
- ↑ 12
[lenta.ru/news/2013/09/27/type45/ Lenta.ru: Science and technology: Weapons: Great Britain armed itself with the last D-type destroyer] - [ship.bsu.by/main.asp?id=101264 Episode 45] (Russian) (asp). Retrieved December 6, 2008. [www.webcitation.org/66LnYRAN3 Archived from the original on March 22, 2012].
- [www.navy.ru/news/vpk/index.php?ELEMENT_ID=52329 The destroyer Daring joined the British Navy] (English)
- [www.shieldsgazette.com/news/local-news/hms_dauntless_set_for_tyne_visit_1_1256764 HMS Dauntless set for Tyne visit - Local News - Shields Gazette]
- [www.lenta.ru/news/2011/05/10/dclass/ Great Britain accepted the third “D” class destroyer into service]
- [www.bfbs.com/news/uk/hms-dragon-commissioned-56645.html HMS Dragon commissioned]
- [www.royalnavy.mod.uk/News-and-Events/Latest-News/2012/July/25/120725-1bn-Defender-signs-for-the-Navy Sun shine as £1bn Defender signs for the Royal Navy]
- [www.lenta.ru/news/2012/04/23/dragon/ Great Britain received a new destroyer]
Crimean provocations
Attempts to penetrate NATO ships into the territorial waters of our country in the Crimea region are a very long history. They were also undertaken during the Soviet years.
The reason for the dispute was the different counting of the 12-mile zone of territorial waters. In the USA they argued that the count should be taken from every point on the coastline. The Soviet Union adhered to the principle of the so-called “baseline”: for example, when determining the zone of territorial waters in bays, the distance to the border was measured not from the coastline, but from the line connecting the entrance capes of the bays.
American warships in disputed areas, relying on their understanding of the boundaries of territorial waters, crossed the border of the USSR, thereby provoking Soviet sailors to retaliate.
On March 13, 1986, the American cruiser Yorktown and the destroyer Caron entered the territorial waters of the USSR off the coast of Crimea, plunging more than 10 kilometers into them. At the same time, the ships sailed with electronic reconnaissance equipment turned on. Having completed the maneuver, they went abroad without consequences.
The command of the USSR Navy developed an action plan in case of a repetition of this situation.
On February 12, 1988, Yorktown and Caron again invaded Soviet territorial waters. The order to carry out the retaliation operation was received by the patrol boat "Selfless" under the command of Captain 2nd Rank Bogdashin and the patrol boat "SKR-6" by Captain 3rd Rank Petrov. The ships were supported by the border patrol ship Izmail and the rescue ship Yamal.
"Vinogradov" against "McCain". What does naval hysteria lead to? Read more
Construction
The ships were built in separate parts by BAE Systems Surface Ships
, which was originally created as
the BVT Surface Fleet
the BAE Systems
surface weapons shipyards and the
VT
.
The two companies have previously built ships in collaboration. Two BAE shipyards in Glasgow
and one in
Portsmouth
They are responsible for building the various "blocks" that come together to form the ship's hull, with this new system of building in separate parts there is no longer a need to install the keel in drydock. Larger, more complex units containing operations and machinery spaces are built at BAE's Clyde shipyards within large, fully covered construction sheds with extended roofs, lighting and essential equipment. For work all year round, even in winter rain and snow.
BAE shipyard in Govan
is responsible for block A (at the stern at the edge of the helicopter hangar).
Scotstoun
Shipyard is constructing Blocks B/C (the 2600 tonne section contains WR-21 gas turbines, starting from the helicopter hangar to the bridge section) and Block D (the bridge section).
BAE Portsmouth
He is responsible for the E/F blocks (bridge to bow) and the faceted construction of the chimneys and masts.
For ships 2-6, AD blocks are assembled at the Ships Block and Outfit Hall at Govan Shipyards and are fully equipped for docking at Scotstoun. Masts and smokestacks are also assembled before launching into the sea using a new welding process to connect the ship's blocks and internal systems, pipes, cables and ducts. Dauntless
block construction in Portsmouth
For the first in class block A was assembled in Govan
and transported to
Scotstoun
, where it was docked with the B/C blocks, which were already fitted with the WR-21 turbine and equipment.
Block D, also installed at Scotstoun, was equipped for these three blocks. The bow (E/F) sections were assembled at Portsmouth
in large covered sheds, mounted on wheeled cargo ships and transported by floating barge to
Scotstoun
.
This was the last block to go. At this point the hull, also assembled from blocks, was dropped onto the Clyde
and towed into drydock at
Scotstoun.
where the masts and chimneys were installed (the masts are partially equipped with equipment, for example the S1850M radar mast is sent from
Portsmouth to
Thales Nederland
for installation of the radar equipment).
Once this is completed, the remaining equipment is assembled; radar installations, sonar in the bow of the hull, propellers, missile equipment and a 4.5-inch gun. This modular construction agreement was agreed in February 2002. However, when the original contract for the three ships was signed in July 2000, BAE Systems Marine was the builder of the first and third, and Vosper Thornycroft (now VT) was the builder of the second. .