The effectiveness of shooting depends not only on the design, technical characteristics of the weapon or the level of training of the shooter, but also on the sight used. It is an integral part of the gun, as important as the barrel, trigger mechanism or stock.
Along with weapons, which have evolved from primitive muskets and arquebuses to modern rifles, machine guns and pistols, the sight has also evolved. At first it was only a front sight, in the 16th century a rear sight appeared, and a little later a ring orthoptic sight was the prototype of the modern aperture sight. Sighting optics began to be used much later, only at the beginning of the 19th century.
Modern small arms use several types of sighting devices, we will talk about each of them in this article. We explain about each type of sight in this order:
- Device and principle of operation
- Main advantages
- Flaws
- Use, including hunting
Open sight
An open sight is the simplest in design and the most common, standard for most models of modern small arms.
Device and principle of operation
The open sight device is a rear sight and front sight located on the same line. Depending on the variant, front sights vary in shape and design, and the rear sight may have a fixed or fixed bar. To aim the weapon at the target, the shooter needs to visually align the rear sight, front sight and the target itself so that they are on the same line, exactly in the middle of the sight slot.
In addition to sights with a movable or folding bar, sometimes there are options with an adjustable front sight. Recently, fiber optic front sights illuminated with green or red LEDs have become popular. This makes the shooter's task a little easier at dusk, but does not make the sight itself more accurate.
Advantages of open sights:
- reliability;
- low cost;
- compactness and light weight;
- ease of maintenance, maintainability;
- simplicity of design;
- mechanical strength;
- unlimited operating temperature range.
Flaws:
- at long distances the front sight covers the target;
- low aiming accuracy, limited by vision capabilities;
- it takes a long time to train skills.
Application
Despite all the disadvantages, open sights are used more often than others. They are installed on almost all types of military, service and civilian small arms, both rifled and smooth-bore. This is due to their exceptional reliability and simplicity.
All hunting weapons, without exception, are equipped with one or another modification of the mechanical sight. It could be argued that the traditional shotgun sight is a European cylindrical or American spherical front sight with or without a rib. But this is also one of the options for an open mechanical sight, quite accurate for shooting shotguns.
Before you decide which scope to choose for you, you should understand the factors that limit the use of open sights. These factors are specific to each type of scope, but we break them down in more detail here.
Most often, such a scope is used for hunting at distances up to 50 meters. In the general case, typical for all sights, the limiting factors of distance can be:
- weapon sighting range;
- sight design;
- target size;
- shooting or hunting tactics;
- shooter skill;
- vision.
There are exceptions to all rules, but for a general understanding we will give examples for each point.
In terms of sighting range, an open sight is used on pistols, smooth-bore guns (both shotgun and slug shooting), small-caliber and pneumatic guns.
The size of the front and rear sights and their distance from each other also affect the effective firing range. It is important to understand that the farther the rear sight and front sight are from each other, the more accurate the shot. So, it is extremely difficult to hit a ten at 100 meters with a pistol.
The larger the target (object of hunting), the easier it is to hit it. A cautious black grouse watching the hunter from the tops of trees is simply not visible from a safe distance without special optical devices. But this does not mean that a wild boar can be taken from 300 meters. Despite the fact that the wild boar is larger than any bird, it should be targeted strictly “in place,” usually under the shoulder blade or withers. Otherwise, there is a risk of getting wounded and looking for an angry animal in the forest. Therefore, even on large animals, scopes with adjustable magnification are used - from 1x (the target is close) to 10x. Such sights are called “driven” sights and are discussed in a separate article.
A duck picked up from the water or a hare from the field, although small in size, allows the hunter to come close to it. This distance and wide angle of shot spread allow for successful hunting without the use of any sighting devices other than a stationary open sight or “barrel” technique. And since the most common type of hunting is waterfowl, most hunters never use additional types of sights. However, as long as vision allows...
First of all, experience in using weapons is acquired with an open sight: in shooting galleries, shooting ranges, and sports games. Self-defense involves the use of short-barreled or smooth-bore weapons at short distances. Open sights are also widely used here, and auxiliary devices such as laser sights or red dot sights can even get in the way if you do not have the appropriate skill. The same applies to shooting “offhand” at raised game. A badger lured out of a hole climbs almost point blank: an open sight will cope with this task perfectly.
Over time, the range of tasks of the shooter or the variety of game expands, and new weapons are acquired that allow one to increase the shooting distance. Usually it is for this reason that the question arises about choosing a new type of sighting device.
But don’t forget about vision: even on smooth-bore weapons, it is sometimes advisable to use an optical sight with adjustable diopters if your vision is not perfect or worsens with age.
Diopter sight
Although a diopter (ring or aperture) sight is a mechanical sight, it is more precisely an open sight. It is easier to use because the shooter needs less effort to aim and it is easier to find the desired position of the eyes, body and barrel of the weapon.
Device and principle of operation
The design of the diopter sight is a combination of a ring or regular stump front sight with a special rear sight, which is a disk with a small hole with a diameter of 0.5 - 1 mm. This hole is scientifically called a diopter or aperture.
The rear sight disk serves as an obstacle that completely blocks the light flow in the direction of the target, and the aperture hole serves as a diaphragm. Through it, a contrast image is projected into the lens. In this case, the shooter is forced to position the pupil exactly on the target line. This is the only possible position in which it will be visible. Aiming is intuitive.
The diopter sight provides the highest accuracy of all iron sights, but has very little light transmission. Do not use it in low light or at dusk.
Starting with the simplest, diopter sight, the question arises of installing it on a weapon. Since it is most often used for small bore or air rifles, a common option is to mount it on a dovetail, a mounting plane that is common on these guns. But some imported shotguns use Weaver or Picatinni rails for greater versatility. We talk about other, more complex fastenings in separate articles or sections of the catalog.
Main advantages:
- high accuracy;
- simplicity, reliability, mechanical strength;
- low cost;
- compactness and light weight.
Flaws:
- narrow field of view;
- low light transmission;
- covers the target (except for the point of impact).
Application
The main area of application for diopter sights is sports shooting. In the Olympic shooting disciplines - 10 meters air rifle and 50 meters small-caliber rifle - diopter sights are used, and optical and other sights are prohibited by the rules.
Exploitation
Diopter sights are used on hunting, air and combat rifles and their analogues. Some users believe that the diopter interferes with normal vision and is inferior to optical and open versions. In fact, you need to know the intricacies of using this mechanism. You just need to put your cheek against the front of the butt so that the eye is in close proximity to the rear sight. This allows you to correctly direct the front sight at the target and see its clear outline.
A typical mistake when using a diopter sight is to align the front sight relative to the rear sight, the hole of which should be visually smaller. The available size is quite enough to operate the weapon. This is confirmed by practical shooting, as a result of which targets were hit confidently and accurately.
Optical sight
To make it easier to shoot at long distances, optics are installed on the weapon - a spotting scope with an aiming reticle. This type of sight is called an optical sight. It simplifies the aiming process, increases accuracy and the chances of a successful shot.
Device and principle of operation
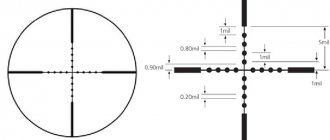
The tubular metal case, indicated in the figure by the number (7), contains a lens (1) and an eyepiece (4) - two lens systems, between which an aiming reticle (3) is installed in one of the focal planes. To obtain a direct, non-inverted image, use a wrapping system (2) - another group of lenses.
The sight is rigidly mounted on the weapon, and precise adjustment of the reticle position is made by a ballistic correction mechanism (5) - two micrometric screws. Many models have LED illumination (6), allowing you to better see the reticle in the dark.
The operating principle of such a sight is no different from a conventional spotting scope or telescope. To fire a shot, simply align the crosshairs with a magnified image of the target. Read more about optical sights here.
Advantages
- high accuracy;
- the ability to see a target at a great distance;
- convenience, simplicity and speed of guidance;
- simple and reliable design.
Flaws
- small viewing angle;
- increase in weight and dimensions of weapons;
- afraid of shocks, mechanical damage;
- blocks the open sight: it is impossible to make a shot at close range (except for the fences).
Application
Despite its weight and size, optics are the second most popular sight after a conventional mechanical one. It is installed on rifled military, hunting weapons and pneumatics. Smoothbore guns, which have relatively low accuracy, are rarely used in conjunction with optical sights. When shooting with shotguns, this simply does not make sense, but for hunting with a bullet, especially for people with myopia, driven scopes of variable magnification are often used: from 1x to 6x. It is worth noting that Lancaster guns are gaining popularity, the accuracy of which allows the use of optical sights.
Rifles deserve special attention, about the optical sight for which we have prepared separate articles - small and pneumatic. The fact is that these guns are very accurate for their ranges, and working with an optical sight on them is no different from high-power rifles. At the same time, the cost of a shot allows you to fully learn shooting techniques.
It is with the optical sight that snipers are associated, starting with the PU 3.5x22 and the Mosin rifle from the Great Patriotic War or the PSO-1 with the SVD - Afghan and beyond. And although thermal imaging sights are gradually replacing optical sights in special forces these days, optics will be used for hunting and recreational shooting for a long time to come.
And the most popular articles were articles about optical sights for the most common models of civilian rifles:
- Optical sight for SKS
- Optical sight for SVD and Tiger rifles
- Sight for Saiga
- Sight for "Vepr"
The shooting process
You can use an optical sight only after the weapon has been checked for its functionality: how well the weapon’s shooting position is equipped, as well as its optics.
Shooting stages:
- Carrying out a test shot. At the very first stage, a test shot must be fired at the closest possible distance, no more than 25 meters. At this stage, it will be possible to identify existing malfunctions in the operation of the weapon, as well as determine the degree of correction for bullet spread and correctly determine the vector of its displacement. Also, thanks to a test shot, it will be possible to quickly determine the average point of impact.
- Sighting from a distance of 25 meters. Next, you need to fire a series of shots from a weapon at a distance of 25 meters. Most often it is enough to fire three shots. Each of these shots will be a specific signal of the properties of the weapon. A lot depends on the results of the hit. However, the radial spread of hits in some situations does not depend on the quality of the weapon or sight. A lot depends on the qualifications of the shooter himself. An inexperienced owner will also be able to identify certain defects and the need to center the sight at a distance of 25 meters. The sight of any optics pursues precisely this goal.
- Sighting at a distance of 100 meters. In order to finally select the optimal sighting of the gun, you need to move away to a distance of 100 meters. And the results of such an exercise will provide more complete information about the characteristics, quality of the weapon, as well as its behavior in real conditions. If the optics were installed on a carbine or rifle correctly, that is, in full compliance with the requirements and rules of the manufacturer, then the results of such zeroing will be quite acceptable. And this despite the fact that the distance for wind weapons is quite large.
Collimator sight
With a conventional open sight, you need to visually align three points located at different distances from the eye: the rear sight, the front sight and the target itself. A red dot sight simplifies the task by replacing the rear sight and front sight with one luminous mark. Collimators do not magnify the target, but speed up the aiming process.
Device and principle of operation
The idea is that with the help of a translucent collimator lens a visible projection to infinity of the aiming mark is created. This is a bright point of light that is located in the shooter's field of view. It must be aligned with the target to make an accurate shot. You can read more about this here.
The main advantage of collimators is the almost complete absence of parallax. This means that no matter how the pupil moves, the visible position of the aiming mark does not change, and aiming is faster and easier. Unlike optical and mechanical sights, the shooter has both eyes open and does not need to take off his glasses.
Main advantages
- do not require focusing;
- high aiming speed, you can shoot offhand;
- wide viewing angle, visual control of the situation;
- both eyes are open;
- light weight and size;
- simple, durable and reliable design;
- low cost.
Flaws
- short range;
- relatively low accuracy.
Application
Collimators are designed for shooting at a direct shot distance. They are successfully used in the armed forces. Some models of small arms, for example, the Israeli TAR-21 assault rifle, do not have an open sight at all, but are produced with a standard collimator sight. Collimators are widely used by special services (in assault groups) and for self-defense. Sometimes they are installed on machine guns, where fire density is more important than accuracy.
Together with an overhead flashlight or night vision goggles, the red dot sight can be used at night.
For hunters, this type of sights is interesting, first of all, on smooth-bore weapons, especially when shooting offhand with a shot load. As we said above, this is the most common type of hunting and red dot sights are the most popular among hunters. Therefore, we devoted a separate article to collimators for smooth-bore weapons.
The use of collimators also gives good results during driven hunting with rifled weapons.
Due to their low weight, only collimators can be installed on some types of smoothbore shotguns, which do not have a sight mount at all (dovetail or Weaver), but do have a ventilated rail. It allows you to mount lightweight sights either directly with the ventilated rail mount or using adapter rails.
Peculiarities
When someone looks through a scope for the first time, they are always surprised by the amount of free space around the front sight. Maximum brightness is concentrated at the center of the hole, so the eye naturally aligns itself and the front sight there. To force the eye to look somewhere other than the center of the hole, a certain amount of force must be applied.
The device in question allows you to increase the depth of field. To check this effect, a repeated experiment is carried out with visually pointing the object at the fingertip, after which they look into a small hole in a piece of cardboard. This element must be brought as close to the organs of vision as possible. As a result, the image will be less blurry due to the fact that a small gap cuts off scattering rays. The main thing is to choose the required aiming diameter, otherwise the image clarity will decrease.
Prismatic sight
The concept of a prismatic sight is a recent one compared to all other types. “Prismatics” got their start in use on automatic weapons of special services and smoothly switched to hunting carbines. Prismatic sights have many similarities with optical sights, since they are also equipped with a lens system that gives a slight magnification, and an aiming reticle engraved on one of the lenses. The difference in appearance and application separates them into their own species. Externally, prismatic sights are similar to closed-type collimator sights. They also use reticle illumination by reflection and these sights have an integrated mount, mainly for the Weaver rail.
Main advantages
- light and compact
- ability to work both at short and medium distances
- presence of diopter adjustment
- presence of fastening
- increased accuracy
- specialized aiming marks
Flaws
- slight increase
- low lens aperture
Application
The low magnification of prismatic sights was initially appreciated by assault troops, when it was necessary to use one sight when approaching a building at distances of up to 200 meters, and inside it. Later, hunters shooting at short distances began to use it in driven hunts and from the approach. Compact size and low weight do not burden its carrying on a weapon. Most often, the reticles of prismatic sights have a simple design for quick shooting when raised (similar to red dot sights), but with additional touches for correction (similar to optical ones). A selection of prismatic sights from different manufacturers, as well as a comparison with other types, can be found in the corresponding section - prismatic sights.
Settings
Users often have a question: which diopter sight is considered optimal in diameter? In many ways, this indicator depends on the distance of the rear sight from the eye. It is better to mount an element with a small diameter on the neck of the stock or the erection block. The enlarged hole in the rear sight is usually located in the front of the receiver.
Most of the first options have a diameter from 2 to 2.4 mm. This is aimed at most types of shooting and hunting. As user reviews indicate, when hunting antelope or similar animals, a diopter sight allows you to complete the task perfectly. In this case, you must be careful and calculate the distance to the shot.
Laser pointer
A laser target designator (LTD) is a compact device that forms a light spot on the target that coincides with the middle point of impact. This allows you to increase the effectiveness of using weapons at close ranges, aiming speed and accuracy of offhand shooting.
Device and principle of operation
The laser laser consists of a body mounted on the weapon, a power source and a special laser LED with minimal divergence of the light beam. To turn it on, a remote button can be used, located in a place convenient for the shooter, for example, near the trigger.
A laser designator is not a weapon sight in the literal sense of the word, but an auxiliary sighting device that has a limited range and accuracy. Sometimes the laser sight is used in conjunction with a collimator, night or day optical sight. This is done, for example, in the Russian Ratnik sighting system, developed in 2015 for use in the armed forces.
Advantages
- simplicity and high speed of aiming;
- minimum weight and dimensions;
- simplicity and reliability of design.
Flaws
- short range;
- the light spot of the radiation source is unmasked by the arrow;
- Bright sunlight may illuminate the tag.
Application
Laser target designators are mainly used for self-defense, in the army, law enforcement and security structures to perform tactical tasks, often in combination with other sighting devices. In hunting, LCCs are rarely used, as a rule, with smooth-bore weapons. Remember the cats that chase the laser? A wild animal reacts in approximately the same way: it only becomes frightened by the spot of light and prefers to hide.
Adjustment methods
The diopter sight for the MP-61 rifle is adjustable, like most analogues of the type in question. The mechanism itself is equipped with a pair of drums that serve to correct the position of the user’s eyes in the upper and lower protection. One element is designed to make adjustments up and down. Markings - “B” and “N”. When turning the device at the top mark, the sight moves upward, according to the calculations indicated in the previous sections.
On expensive modifications, the sighting bar is shifted in 12 clicks. In particular, this applies to the Anschutz rifle. The marks are made in Latin letters, turns are made in both directions until the markings “L” or “R”. When using a Gamo diopter sight, the owner must carefully monitor the shift in the midpoint of aiming, making timely corrections. It includes moving the sight in the desired direction. For example, if the target is placed to the right and above, you need to move to the “left” and “down” (“L”/“N”).
Night sight
A night vision scope, called a “night light,” enhances the image of a target that has low brightness. It allows accurate shooting in almost complete darkness - with very weak reflected light from the moon, stars or artificial sources. Modern night sights are classified according to the type of light conversion - electro-optical and digital. This section details the former.
Device and principle of operation
The basis of a night vision sight is an electron-optical converter (EOC). This is a vacuum device that consists of a photosensitive cathode and a phosphor-coated anode. It converts weak light, invisible to the eye, into a bright image. You can read more about this here.
They aim at the night light in the same way as at a regular optical sight - they aim the crosshairs. The main difference is that the shooter sees in the eyepiece not the usual image of the target, but an image enhanced by the device, usually green, which is displayed on a miniature screen.
Advantages of night sights
- high accuracy in poor visibility conditions;
- range up to 300 meters or more, depending on the image intensifier;
- relatively light weight and size;
- long continuous work;
- high reliability (compared to digital ones).
Flaws
- relatively high cost of modern models (generation 2 and above);
- snow, rain, fog, branches and tall grass are obstacles;
- in complete darkness, IR illumination is required (unmasks it from other night vision devices);
- When there is oncoming light, backlight protection is triggered.
Application
Night sights are installed on military, service and civilian weapons, both with a rifled barrel and smooth-bore. Depending on the tasks to be solved, devices are selected that differ in sensitivity, range and, of course, cost. For hunting, inexpensive sights with image intensifier tubes of the first or 1+ (one plus) generations were often used. However, they are now out of production, and second-generation sights are more expensive than digital ones. More information about the classification of NVGs can be found in a separate article, and we compare digital and image intensifiers here.
Review results
A sight with a diopter is similar in schematic design to its ring counterpart. The main difference is the presence of a wide base with a small hole in the middle. This small feature allows you to change the properties of the sight, taking into account its low suitability for hunting purposes. The structure in front of the shooter's eye blocks part of the view, which limits observation of the object. In the case of static targets, this factor does not particularly affect the accuracy of the shot. But it becomes almost impossible to conduct aimed fire at moving targets. It follows from this that this mechanism is more often used in sports shooting at standard targets. This applies to pneumatic entertainment, as well as sports biathlon.
Digital sights
Digital sights see both day and night. This is possible due to the fact that the CCD matrix can record a wide spectrum of light radiation, even invisible to the eye. A special case of a digital sight is thermal imaging, which is discussed in more detail in the next section.
The cost of electronic components of digital sights is constantly decreasing. Thus, the first models were comparable to the price of 2+ generation image intensifier tubes, but now they are no more expensive than 1+ generation night sights, which are practically out of production.
Pulsar Dіgіѕіght Ultra N455 LRF with laser rangefinder on the Tiger rifle
Device and principle of operation
Digital sights work on the same principle as a digital photo/video camera or a modern smartphone. The image is focused on the CCD matrix and displayed on the screen observed through the eyepiece of the sight. Thanks to the sensitivity of modern matrices, the sight can work not only during the day, but also at night – registering infrared light invisible to the eye. In complete darkness (for example, indoors or in a dark forest), IR illumination is used together with the sight - the same as for sights with image intensifier tubes, only operating at a different wavelength (up to 900 nm).
A huge advantage of digital (and thermal) sights is the ability to overlay additional information directly on top of the image. This could be the charge level, the settings menu, a huge number of reticle choices (including the ability to shoot with one cartridge). When working together with a laser rangefinder, the rangefinder readings can not only be displayed on the screen, but also adjust the position of the reticle in accordance with the ballistic trajectory of the bullet! We have collected sights with laser rangefinders in a separate section.
Advantages of a digital sight
- the ability to work both as a night and as a day sight;
- range up to 300 meters;
- impact resistance to any caliber;
- the ability to display additional information on the screen;
- digital zoom.
Flaws
- high energy consumption;
- repair only at a service center or factory;
- in complete darkness, IR illumination is required (unmasks it from other night vision devices).
Application
Due to the fact that digital sights are inferior to sights based on image intensifier tubes in terms of reliability and high power consumption, they are not used by the military. But thanks to its clear image and relatively low price, it is currently the main scope for night hunting. We compare digital and image intensifier sights in more detail here.
Options
Using the Ural diopter sight as an example, let’s look at the main characteristics of the device:
- The bar is shifted one position by clicking.
- To calculate the movement of the device, the switching moment, which directly depends on the length of the sight line, should be taken into account.
- The average pitch of micrometric screws is 0.7 mm.
- The number of clicks in a full rotation of the element is 16.
- Displacement of the plate in one click is 0.043 mm.
- Possibility of adjusting the movement of the rear sight with orientation according to the firing distance.
- At an operating distance of 150 meters or more, the length of the aiming line will be 650 mm, the displacement of the bar will be 1 mm.
The picture that emerges is that with a salvo at 15 meters, one click will correspond to a displacement of no more than 1.1 mm.
Thermal imaging sight
Thermal imaging sight is a device that visualizes the target’s own thermal radiation. It does not require external light sources, allowing you to aim the weapon in complete darkness. This uses data on the temperature of the object itself compared to the surrounding space.
A sight with a thermal imager works not only in complete darkness, but also in daylight. in snow, fog, and smoke. It allows you to accurately aim a weapon at equipment and people in camouflage, and target animals against the background of foliage or snow, regardless of their natural camouflage. Today, this is the most advanced sight option for low visibility conditions. And we have dedicated a separate section of the catalog to the best models.
Operating principle and device
A sight with a thermal imager is a special case of a digital sight. It is also similar in principle to a video camera, which records heat instead of light. All heated objects emit infrared radiation invisible to humans.
The thermal imaging sight is based on a bolometric sensor that is sensitive to thermal radiation. This is a miniature semiconductor matrix of thermistors with a sensitivity of hundredths of a degree. The signal from the matrix is processed electronically and displayed on a liquid crystal screen, which the shooter sees in the eyepiece. Read more about the device, technical characteristics and choice of thermal sights here.
Advantages
- the longest detection distances for thermal targets;
- work in complete darkness;
- can work in the light, there is no illumination;
- accuracy, like optical sights;
- snow, rain, fog, foliage and grass are not a hindrance.
Flaws
- complex design;
- high price;
- additional power supply required.