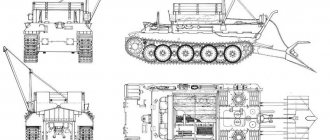
According to the rearmament program, this year continues to equip the motorized rifle formations of the Southern Military District stationed in the Chechen Republic with the latest types of special equipment. According to the press service of the Southern Military District, at the end of November, the brigades received modern command and staff vehicles R-149 BMR based on the BTR-80 armored personnel carrier. These KShMs are equipped with communications equipment that operates in several wavelength ranges, as well as a PC, which allows you to quickly monitor all changes in the situation during the battle. Operators can, while in the command and staff vehicle, quickly carry out operational and tactical calculations, promptly set and clarify tasks for units while commanding troops.
The KShM R-149BMR is equipped with a unique navigation equipment “Azimuth”, thanks to which the coordinates of its location are automatically determined at any point on the route. The press service of the Southern Military District also states that the KShM equipment is organically integrated into the automated command and control system and significantly increases the efficiency, stability and safety of communications during combat.
BTR-80 and command and staff vehicle R-149 BMR
Main characteristics:
- communication range: - in the HF range, km - up to 350; — in the VHF range, km — 30-60;
- power supply from: — main engine; rectifier, autonomous unit, three-phase network 380V;
- weight, kg, no more than 12800;
- number of jobs: — officials — 3; — service personnel — 3;
- deployment time of the CVM by a crew of 3 people: - for work on the move, min - 5; — for work in a parking lot when deployed on all types of antennas, min — 20.
All equipment of the vehicle is located on the maneuverable highly mobile lightly armored transport base K1Sh1, created on the basis of the BTR-80 armored personnel carrier.
KShM R-149 BMR, BTR80, BTR-82A, KAMAZ
For information:
| Command and staff vehicle (early version) based on the BTR-80 | Command and staff vehicle (late version) based on the BTR-80 |
| Sound broadcasting station based on BTR-80 | Artillery control vehicle 1B188 |
| Radiation and chemical reconnaissance vehicle RKhM-4 | Armored medical vehicle BMM-80 |
| Satellite communication station based on BTR-80 | All-terrain floating transport vehicle GAZ-59037 |
| SAU 2S23 "Nona - SVK" based on BTR-80 | |
Main functions of the R-149BMR:
- Conducting radio communications through open and confidential communication channels.
- Organization of information transfer in digital and analog communication systems.
- Possibility of using satellite communication channels.
- determination and transmission of own location coordinates via communication channels.
- Video monitoring of the situation and transmission of the received data either to an electronic map of the area or via communication channels.
Also for reference, the characteristics of the BTR-70 and BTR-80 armored personnel carriers:
BTR-70
| Machine type | BTR-70 |
| Wheel formula | 8×8 |
| Combat weight, kg | 12000 |
| Length, mm | 7535 |
| Width, mm | 2900 |
| Height, mm | 2235 |
| Ground clearance, mm | 475 |
| Booking, mm: | |
| forehead of the body | 8-10 |
| forehead of the tower | 6 |
| Maximum speed, km/h: | |
| along the highway | 80 |
| afloat | 9-10 |
| Cruising range on the highway, km | 400-600 |
| Fuel capacity, l | 290+120 |
| Obstacles to be overcome: | |
| elevation angle, degrees | 30 |
| roll, degree | 25 |
| ditch width, m | 2,00 |
| wall, m | 0,60 |
| Crew (landing force), people. | 3(7) |
Local history. Abstracts. Tourism
The development of an automated combat control system for an anti-aircraft missile brigade armed with the S-300V air defense system or the Buk air defense system (code Polyana-D4, index 9С52) was carried out on the basis of decisions of the Commission of the Presidium of the USSR Council of Ministers on military-industrial issues dated June 29, 1977. and dated August 27, 1981 according to the GRAU TTZ and its supplement. The development of the Polyana-D4 automated control system was carried out by the Research Institute of Automation Equipment of the Ministry of Radio Industry. The chief designer of this automated control system was G. A. Burlakov. …. In terms of its performance characteristics, this system was significantly superior to the Polyana-D1 automated control system and, in general, had characteristics superior to those of the American Missile Minder system, which was used to control the air defense systems of the operational level of the ground forces of NATO countries. …. In 1986, the Polyana-D4 automated control system was adopted by the Soviet Army - the Air Defense Forces. Serial production of PBU, KShM and maintenance machines for this system was organized at the Minsk Electromechanical Plant of the Ministry of Radio Industry, and then transferred to the Penza Radio Plant of the Ministry of Radio Industry.
The Polyana-D4 automated control system included: - a combat control point (CCP) of the brigade (MP06 vehicle); - command and staff vehicle (CSV) of the brigade (MP02 vehicle with KP4 trailer); — spare parts and maintenance vehicle (MP45 vehicle); — two diesel power plants ED-T400-1RAM.
The MP06, MP02 vehicles and the KP4 trailer were significantly unified with the vehicles used at the front (army) air defense command post as part of the front's automated control system. To organize the necessary external connections with all associated objects, the system was equipped with a mobile communication unit.
The PBU was equipped with automated workstations (AWS) for a brigade commander, a senior combat control officer (directed to two divisions and to the air defense command post of the front (army), an Air Force aviation representative, an operational duty officer, a combat control officer (directed to two divisions), and an intelligence chief brigade (senior radar image processing operator), radar image processing operator, engineer and communications technician. The KShM was equipped with automated workstations for the deputy brigade commander for weapons, the operations department officer (alphanumeric display operator - ADC), the senior operations department officer (drawing operator - graphic machine - CHA) and non-automated workstations for two technicians. In the KShM trailer there were workstations of the chief of staff of the brigade and the head of the operational department (head of brigade communications) - the ADC operator and six manual workstations for officers of the brigade headquarters.
…. To ensure the combat operation of the Polyana-D4 automated control system with higher, subordinate and interacting command posts and control points, exits to the attached communication center were provided for the exchange of operational-tactical and radar information (OTI and radar information) using telecode channels, and for negotiations - radiotelephone channels The exchange of information between the PBU and the KShM with the trailer was carried out via cable communication and data transmission lines. To ensure communication on the march, radio stations were installed in the cabs of MP06, MP02 with a trailer, MP45 and in power plants. A BAZ-6950 vehicle with an SKN-6950 body was used as a transport base for the PBU. The KShM equipment was located in the back of the Ural-375 vehicle and in the back of the SMZ-782B trailer. The power plants were located in the bodies of KamAZ-4310 vehicles. The deployment (collapse) time of the Polyana-D4 automated control system by crew forces did not exceed 20 minutes.
The development and production of command staff vehicles in the Soviet Union was carried out by the Radiopribor association. In the distant 50s of the last century, design services, and later with the organization of the Zokbr, and then the zniirsa, became the only specialists in the country in the development of combined radio stations and command and staff vehicles at various transport bases. Later, the Sputnik plant also became a monopoly in their production. After the collapse of the Soviet Union, enterprises producing command and staff vehicles remained in Ukraine. In recent years, the production of this equipment has been reduced to a minimum, despite the fact that it is in demand not only in Ukraine itself, but also in neighboring countries. In the Russian Federation, in the late nineties, they began to repair and modernize command staff vehicles in Tambov.
A striking representative of the galaxy of combined radio stations is the combined radio station R-142N, mounted in the back of a GAZ-66 car. It was also mounted to carry out combat and especially dangerous missions, to participate in hostilities in the democratic republic of Afghanistan on the basis of armored vehicles.
— Command and staff vehicles based on KamAZ and Tiger appeared in our country, I would say, by coincidence. At one time, when the USSR ceased to exist, the main production of KShM remained in Ukraine, in Zaporozhye. And the KShM, which were ordered from Russian enterprises of the Ministry of Defense, were not suitable for us: they installed communications equipment that was unnecessary for our troops, and this equipment itself was very expensive. Therefore, after two years of searching, we took the base of the KamAZ vehicle as a basis, at the factory, according to our technical specifications, we made the appropriate “filling” for the kung, and as a result, the KShM R-142 NSA appeared. Two compartments (for the radio operator and the operational staff) accommodated various means of communication: new HF and VHF radio stations R-168-25U and 168-100K of the Aqueduct complex, ZAS equipment, Erica stations of the military and police range, a station for communications with Ikom airplanes and helicopters (imported, because in Russia we do not yet have stations of this class with similar parameters). This vehicle has two power supply “engines” that are also diesel, just like the engine - we strived to ensure that when operating the crankshaft, we use the same type of oil and fuel. The kung turned out to be so spacious that there are normal opportunities not only for work, but also for short-term rest for the crew. R-142 NSA began to enter the troops in 2005 - at first we purchased 6 vehicles, in 2006 - 11. And in 2007 we even received more vehicles than we planned: there was a program on the state border, additional money was allocated for it and in As a result, we managed to purchase 15 cars in one year. This year we plan to purchase six R-142 NSA KSHMs.
“Tigers” also appeared with us quite recently - the year before last, when the question arose about a command and staff vehicle that could operate in combat formation, “at the front end.” The former “seagulls”, as we call them, the old R-145 B KShM based on the BTR-60 PU, have not satisfied us for a long time both in cross-country ability and in terms of providing communications equipment. We were again faced with the question: what to do? Just at that time, the adoption of the Tiger armored vehicles into service by the Internal Troops was discussed, so we made a technical specification for the KShM R-145 BMA based on this vehicle. Our car turned out to be quite good, I think. At the same time, army CVMs of this class cost the customer one and a half times more. The “stuffing” of the R-145 BMA is practically no different from the R-142 NSA and is even a little more impressive: there is a satellite terminal, and, if necessary, HF government communications equipment can be installed. In the front part of this vehicle there are seats for the driver and the head of the radio station, and in the rear there are two places for operators to work. Two such Tigers are currently in operation in the North Caucasus region, one is in Moscow at the disposal of the commander-in-chief. This year we plan to purchase 3 R-145 BMA KShM based on the Tiger.
…. Today, out of the available satellite communication stations, we have only four new ones at the Gazelle transport base. The rest are stations based on Uralov and ZIL-131, which are 20-25 years old. We received them from the Ministry of Defense when the military commandant's offices in Chechnya were transferred to us. Of course, this does not yet satisfy the needs of the troops. There is also a shortage of command and staff vehicles, especially the new model - based on KamAZ and Tigers. Today, the troops are 82 percent equipped with command and staff vehicles, of which only a fifth are new, the rest were inherited from the Soviet Union. In general, there is something to work on.
= = = = = Mm-yes. I thought that the great pu industry could throw a lot of interesting things onto the tourist market (as happened in the damned times of stagnation), but it turns out that “the king has no clothes”, without the hohlyatsky “backwardness” the glorious Russian generals even have nowhere to go shout.
The simplest option for inexpensive equipment for a command post vehicle or an off-road motorhome for tourism purposes, as well as a mobile headquarters for road construction or filming, is a shift vehicle based on the GAZ-66 .
An off-road powerful car produced by the GDR IFA . The crew of 4 people while driving is located in a double cabin with two rows of seats.
An off-road vehicle based on an IFA truck made in the GDR drove under its own power from Berlin to Beijing for the Olympic Games along the roads of the ancient Great Silk Road.
In principle, the same amount can still travel in the cabin if it is summer time. Some people can spend the night in tents. But even when using the kung (lounge) of a motorhome based on the GAZ-66 for administrative and staff workplaces, two work tables with good mattresses made of non-woven spring materials, for example “Sprut”, become comfortable sleeping places for the night. And folding shelves are possible on the upper tier. There can be a maximum of 6 places for year-round use.
Another low-budget option : the layout of a motorhome based on the UAZ-452 ( tablet , loaf )
Bedroom, toilet, shower, kitchen, dining room, internal trunk and hatch from the interior of the motorhome to the roof to a large external trunk. A basket on the roof of a motorhome can be used as a great filming platform, for transporting bicycles, boats and anything else. Very good decision! Kitchen with window and dining table by the window. Even the toilet and shower are equipped with a window that can be opened and ventilated, it’s super!
A roof rack is no longer a completely relevant solution. To autonomously provide the motorhome with electricity during long movements, the roof is used for stationary solar system panels. A compromise solution is possible: part of the roof, for example above the driver’s cabin (where it would be appropriate to raise the roof of the cabin for a pull-out bed for two), is used for stationary solar panels. And half of the roof above the cabin has a spacious luggage basket with high sides.
Solar systems, as well as a wind generator, can be foldable and deployed during a camp, overnight stay, or day trip, when the need for electricity is much higher than on the road.
Solar panels are now lightweight and dismountable Chinese consumer goods, which can be ordered online
- Read more about modern wind generators and solar systems, mobile lightweight systems for charging batteries and batteries from wind and solar energy - Equipment for solar and wind energy (wind generators and solar systems) from tablet power to street lighting and complex energy for the estate
In modern conditions, a motorhome and a command vehicle must have light transport: a moped, bicycles, motocross motorcycles. All this can be mounted at the rear of the cabin (kung) on a hinged luggage platform above the tow bar. For example, an option for mounting a platform for transporting a moped on the Italian-German motorhome Fleur:
platform above the towbar for transporting a moped on a Fleur motorhome, Fiat Ducato van
BTR-80
| Machine type | BTR-80 |
| Wheel formula | 8×8 |
| Combat weight, kg | 13600 |
| Length, mm | 7650 |
| Width, mm | 2900 |
| Height, mm | 2450 |
| Ground clearance, mm | 475 |
| Booking, mm: | |
| forehead of the body | — |
| forehead of the tower | — |
| Maximum speed, km/h: | |
| along the highway | 80-90 |
| afloat | 9,5 |
| Cruising range on the highway, km | 600 |
| Fuel capacity, l | 300 |
| Obstacles to be overcome: | |
| elevation angle, degrees | 30 |
| roll, degree | 25 |
| ditch width, m | 2,00 |
| wall, m | 0,50 |
| Crew (landing force), people. | 2(8) |
Operating principle and purpose
Unlike an electric motor, the operating principle of a crankshaft in internal combustion engines is much more complicated:
- the pistons are alternately pushed out of the cylinders when the fuel mixture is ignited;
- connecting rod parts of complex configuration are hinged inside them;
- the crankshaft has a U-shaped reciprocal seating surface for the lower head of the connecting rod, which ensures displacement from the axis of rotation of the shaft;
- due to the fixed distance between the piston and the crankshaft, the connecting rod describes an amplitude in the form of a figure eight, due to which the translational movement from the cylinders is converted into torque on the shaft.
The main purpose of the consumable elements of the flywheel (liners, bushings, rings) is to increase the service life of this unit. Since the number of cylinders reaches 16 in modern cars, the design and operation of the cylinder head mechanism must be perfectly balanced.
BTR-80K
| Machine type | BTR-80K |
| Wheel formula | 8×8 |
| Combat weight, kg | 13600 |
| Length, mm | 7650 |
| Width, mm | 2900 |
| Height, mm | 2350 |
| Ground clearance, mm | 475 |
| Booking, mm: | |
| forehead of the body | — |
| forehead of the tower | — |
| Maximum speed, km/h: | |
| along the highway | 90 |
| afloat | 9,5 |
| Cruising range on the highway, km | 600 |
| Fuel capacity, l | 300 |
| Obstacles to be overcome: | |
| elevation angle, degrees | 30 |
| roll, degree | 25 |
| ditch width, m | 2,00 |
| wall, m | 0,50 |
| Crew (landing force), people. | 3(3) |
KShM design
Unlike other car components, the design of the crank mechanism conventionally includes part of the piston group and the crankshaft. The crankshaft consists of moving parts and fixed elements. They have one or more degrees of freedom:
- connecting rod and piston;
- compression, retaining and oil scraper rings;
- piston pin and retaining ring;
- liners, mounting bolt and connecting rod cover;
- flywheel and crankshaft;
- counterweight and connecting rod journals, main ones;
- inserts.
Fixed elements include the cylinder head and block.
Depending on the design of the internal combustion engine and the number of cylinders, the kinematics of the crank mechanism changes slightly:
- in an in-line engine, the plane of the crankshaft and cylinders completely coincide;
- in the VR-shaped motor there is a shift at an angle of 15 degrees;
- in the W-shaped drive, the displacement value reaches 72 degrees.
In other words, in an in-line engine, the working cycle is carried out alternately by 4 cylinders, which allows the load on the crankshaft to be evenly distributed. To achieve compact dimensions, internal combustion engines with a large number of cylinders are placed in a V-shape. This also makes it possible to soften the load on the crankshaft by dissipating part of the energy.
Sectional drawing of the KShM
To ensure that the characteristics of the crank mechanism are stable during overloads (high temperature, high pressure and speed, difficulties with lubrication supply), instead of ball/roller bearings, sliding elements with connecting rod and main bearings are used. The unevenness of the angular speeds of the shaft in individual cycles is smoothed out by a massive flywheel due to the inertia of this part.
BTR-80A
| Machine type | BTR-80A |
| Wheel formula | 8×8 |
| Combat weight, kg | 14550 |
| Length, mm | 7560 |
| Width, mm | 2900 |
| Height, mm | 2800 |
| Ground clearance, mm | 475 |
| Booking, mm: | |
| forehead of the body | — |
| forehead of the tower | — |
| Maximum speed, km/h: | |
| along the highway | 80-90 |
| afloat | 10 |
| Cruising range on the highway, km | 600-800 |
| Fuel capacity, l | — |
| Obstacles to be overcome: | |
| elevation angle, degrees | 30 |
| roll, degree | 25 |
| ditch width, m | 2,00 |
| wall, m | 0,50 |
| Crew (landing force), people. | 2(8) |
Breakdowns and problems of the crank mechanism
Almost all parts of the crankshaft drive are friction pairs, which is clearly confirmed by the diagram of the kinematics of the vehicle drive. If the diagnosis of this internal combustion drive mechanism reveals malfunctions, a major overhaul of the engine is necessary, since it is completely disassembled.
Technical features of crankshaft drive malfunctions include wear of friction parts. The main breakdowns are:
- stuck rings on the pistons - due to high metal production, play appears, misalignment occurs and the piston becomes jammed inside the cylinder;
- wear of the piston pins - instead of a fixed size between the crankshaft/piston, the distance becomes floating, the torque characteristics change;
- development of the piston group - the cylinder mirror or piston surface is ground off, the characteristics of the internal combustion engine change;
- Bearing wear – the connecting rod or main bearings are worn down, causing shock loads on the shaft.
The main causes of malfunctions are prolonged loads, lack of maintenance, poor quality of lubrication or exhaustion of the drive life.
Position of piston rings
The specified malfunctions of the crank mechanism are diagnosed based on the following symptoms:
- interruptions in engine operation;
- a constant decrease in the lubricant level in the crankcase;
- exhaust gases take on a blue tint.
The breakdown cannot be repaired at home, as it requires a highly qualified technician and complete disassembly of the engine.
Wear of pistons and pins
These specific malfunctions of the crank mechanism are identified by the following signs:
- fingers - regardless of the operating mode of the engine, a loud knocking sound is heard in the upper part of the cylinder block, which disappears when the spark plug is unscrewed, and increases as the shaft speed increases;
- pistons - blue exhaust, knocking sound similar to the previous case, but only at idle, after warming up it usually disappears.
After diagnosing this malfunction, a major overhaul of the internal combustion engine is required.
Wear of connecting rod and main bearings
Repair of the crank mechanism will inevitably be required when the bearing life is exhausted, as evidenced by the following factors:
- connecting rod bearing - a warning light indicates insufficient lubricant pressure, a dull, floating knocking sound comes from the middle part of the cylinder block;
- main bearing - the warning light lights up, indicating low oil pressure, a dull knock occurs in the lower part of the cylinder block.
By analogy with the previous options, it will not be possible to do without major repairs.
Repair technology
The main purpose of overhauling a crankshaft is to restore the service life of the piston group and crankshaft. To do this, the seats are restored, fingers and liners are replaced.
Pistons and pins
The piston, which is conventionally included in the crank mechanism of a car engine, is made of aluminum alloys. The finger is made of alloy steel and wears out less.
The pistons have their mirror and the geometry of the grooves for the rings and bosses, inside of which the pin is located, restored. The dimensions of the piston pin are selected at an air temperature in the workshop of 20 degrees, depending on the size group of the piston.
Connecting rod repair
Connecting rods are mainly made from steel 40G, 40X or St45; the following are considered characteristic defects:
- production of metal seats;
- hole wear;
- change in geometry (twisting and bending).
The kinematic element of the mechanism is rejected in case of emergency bending, breakage and crack opening. In other cases, bending and twisting are eliminated by heating to 500 degrees to relieve internal stress. The seating surfaces are milled and then ground to the next resize.
After which, the operation of the crank mechanism again satisfies the requirements of GOST regulations. It is prohibited to remove a metal layer larger than 0.2 - 0.4 mm for diesel engines and carburetor internal combustion engines, respectively. Otherwise, the kinematic diagram of the unit is disrupted.