Correct tire pressure for truck
There is a concept of “correct pressure” for truck-type wheeled vehicles. It is divided into 3 main types:
- Maximum pressure. As a rule, this value is equal to that specified by the tire manufacturer itself. It is usually indicated on the side of the tire. But it is not recommended to constantly inflate the wheels to the specified limit or higher, as this affects wear resistance and increases the risk of creating an emergency situation on the road.
- Optimal pressure. Typically, truck owners focus on this type of “correct pressure”. The optimal pressure value is usually indicated in the form of a table on which the number of atmospheres corresponding to the mass of the transported cargo is recorded. This option is considered the best, but in practice it is quite difficult to stick to it, since the wheels will have to be inflated very often. Each car brand has its own standards, but they usually do not take into account the characteristics of different types of tires.
- Recommended pressure. The truck manufacturer indicates this value for each wheel. By default, the indicated pressure is calculated at the maximum load on a specific machine axle. If the load is significantly lower than the maximum permissible, you need to inflate the wheel below the recommended level.
Price GAZ-53
Despite the fact that GAZ-53 trucks have not been produced for a quarter of a century, many of these vehicles can still be found on the roads of the CIS and in the secondary market.
The price, depending on the condition of the car, varies from a completely “penny” 30 thousand to 150 thousand, for a truck on the move, in working condition. There are no problems with spare parts for the GAZ-53: they are also available in abundance on the secondary market.
GAZ-53
Hyundai solaris body dimensions
In 1961, the Gorky Automobile Plant began serial production of trucks called GAZ-53. Initially, the carrying capacity of the GAZ-53 was 3 tons, but a small number of such vehicles were produced.
The GAZ-53 was planned to be equipped with a V-shaped 8-cylinder pre-chamber-torch ignition, however, due to difficulties in its development, the first batch of trucks was equipped with a forced GAZ-51 truck engine with an increased compression ratio. The power of this engine was 82 horsepower, instead of 70. These trucks were called GAZ-53F, their carrying capacity was already 3.5 tons, but later it was again reduced to 3 tons.
After the new 8-cylinder ZMZ-53 engine was mastered (essentially it was a modification of the GAZ-53F engine), in 1964 they began to equip GAZ-53A trucks with it. This 4250 cm3 engine developed a power of 115 horsepower and was capable of accelerating the truck to 85 kilometers per hour. To transmit the increased torque, a reinforced single-disc clutch, a new gearbox and driveshaft were used. The carrying capacity of GAZ-53 trucks with such technical equipment was 3 tons, just like the later GAZ-53F models.
After the release of the GAZ-53A modification in July 1965, the three-ton tanks became history. From that moment on, the carrying capacity of the vehicles was increased to 4 tons and the volume of the body was increased due to the addition of lattice sides. Also, the new GAZ-53A truck received a reinforced front axle, a new cardan transmission and steering mechanism.
The truck was produced in this form until 1983, and then modernized again. From that moment on, GAZ trucks received a new 8-cylinder gasoline engine ZMZ-511 with a volume of 4254 cm3, and at 3400 rpm it produced 125 horsepower. Both 76 and 80 gasoline were used as fuel. In addition to the engine, the radiator lining was changed for the last time - the grille holes were extended and the sidelights were moved. The carrying capacity was also increased to 4.5 tons. Trucks of this modification received the index GAZ-53-12
In 1993, cars of the GAZ-53 family were discontinued and were replaced by the newer GAZ-3307 truck, which is still in production.
The GAZ-53 truck was the most popular truck in the USSR. Its various modifications were used not only in the territory of the former USSR, but were also exported to various countries, such as Cuba, Romania, Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia, Finland, East Germany, Vietnam, Mongolia, North Korea and others. Over the entire production period, more than 4 million cars were produced.
GAZ-53: history
Serial production of the GAZ-53 began in 1961. Over the next thirty-odd years, the car was produced in various versions, changing the indices in the name. In 1993, serial production of the GAZ-53 on the GAZ-53-12 model was completed. The cars were produced at the facilities of the Gorky plant. The equipment belongs to the third generation of GAZ.
Over the years of serial production, more than four million units of equipment were produced. Experts recognize the GAZ-53 as the most popular car in the USSR. It is interesting to note that the technical data of the machines remained virtually unchanged throughout the entire production period. The main changes concerned the design of the cabin and the instrument panel. The latest version of the exterior cladding was first released in 1984. The first GAZ-53 were similar to the classic ZIL-130.
About the history of the legendary truck and its features
Geometric dimensions and control points of the body. Chevrolet Niva dimensions
The first generation of trucks was produced in the 2nd half of the 50s. According to the project, the GAZ family was distinguished by a load capacity of 1.5-2.5 tons and common parts. The 51st test car was supposed to be replaced by the 52nd model.
History and purpose
The 52nd modification was intended for use in urban and rural conditions, so smoothness, maneuverability and cross-country ability were important. By the mid-1950s, employees of the Gorky Automobile Plant developed several samples with a modified hood, which were not accepted for serial production.
At first, they wanted to use a 6-cylinder engine with a pre-chamber block head for the truck. At the same time, we were working on the project of a V-shaped internal combustion engine with 6 cylinders with a volume of 3.75 liters and a power of 110 horses. The design was not implemented; instead, a derated engine from the Chaika was used.
The powerful engine required a change in load capacity to 4 tons, which meant a new frame and suspension. The model was given the name GAZ-52A, which was replaced by LAWN modification 53.
The new motor took a long time to develop, but the plant’s commitment to time the release to coincide with the beginning of the XXII Congress of the CPSU led to the creation of a transitional version. The GAZ-53F was equipped with a power unit from the old model and a lower valve type engine.
The production of the truck began only in 1964. The car did not leave the assembly line until 1993 and went through several modifications:
- in 1964 - production of ZMZ-53 models with a load capacity of 3 tons, a V-shaped engine and a hypoid rear axle. Discontinued and replaced by GAZ modification 53A;
- in 1966 - the Gorky Automobile Plant launched models 53N for army needs. The car received a pre-heater, anti-slip chains, saws, a towing cable, a radiator cover and an additional fuel tank;
- in 1973 - the car received turn signal repeaters and the Quality Mark between the headlight and sidelights;
- in 1978 - the dump truck was equipped with stampings on the roofs, the cabin began to be painted blue;
- in 1982 - the Quality Mark was removed from the facing part;
- in 1983 - GAZ modification 53-12 changed radically - the dump truck could transport loads up to 4.5 tons, received a new engine, reinforced frame, springs and suspension;
- in 1984 - a simplified bumper without stamping was installed, light gray and protective were added to the color scheme;
- in 1986 - rear lights were replaced, two-color sidelights were installed, emergency lights, a brake cylinder, an instrument panel, contactless ignition, hydraulic vacuum brake boosters, and separate brake circuits appeared.
Interesting to know! Production of the dump truck stopped completely in 1997.
Creators
The chief designer of the car was A. Prosvirnin, the leaders were B. Shikhov, V. Zapoynov. The design of the engine for ZMZ-53 was developed by P. Syrkin.
Interior and exterior of GAZ-53
At one time, the GAZ truck version 53 was modern. It has a streamlined shape and a one-piece cladding with places for headlights. A strong and reliable frame made it possible to transport large loads.
The tank was located under the driver's seat. The bay hole is located behind the cab and is located near the driver's door. This ensured the convenience of installing LPG under the body.
The car was started by an electric starter with a retractor relay. The heating system worked well. The windshield wipers were electrically powered.
The seats for the driver and passengers of the truck have a one-piece design. The cabin is spacious, it could comfortably accommodate people in winter clothes. There are special compartments for tools, parts, and personal accessories.
Car export
The truck was exported to countries friendly to the USSR - Romania, Poland, East Germany, Yugoslavia, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, Finland, North Korea, Cuba, Laos, Vietnam, Mongolia.
Interesting to know! Assembling a dump truck from 1983 to 1991. was engaged in Bulgarian. The series was distinguished by a diesel engine produced under license from the English company Perkins.
Modifications of GAZ-53
Three main, basic modifications of the truck rolled off the assembly line under the following factory indices:
GAZ-53F (1961-1967) - flatbed truck and universal chassis with a forced in-line 6-cylinder GAZ-51 engine with a power of 82 hp.
GAZ-53A (from June 1965 to 1983) - a flatbed truck, a dump truck and a universal chassis with a ZMZ-53 engine - a V-shaped 8-cylinder, with a power of 115 hp.
GAZ-53-12 (from 1983 to January 1993) - flatbed truck, dump truck and universal chassis with an eight-cylinder V-shaped engine "ZMZ-53-11" with a power of 120 hp.
According to the power, the load capacity of the three generations of the 53rd LAWN also differs. The GAZ-53F was declared to have a 4-ton capacity, although in fact it only carried 3 tons on board, and 4 tons was an almost unbearable load for it. The GAZ-53A became a real four-ton truck. The power of the GAZ-53-12 engine already allowed it to freely carry not only the 4.5 tons declared by the manufacturer, but also 5 tons “with kopecks”.
GAZ-53A (1965–1983)
In addition to the basic ones, there are dozens of modifications and versions of the GAZ-53 made on their basis, intended for use for specialized purposes. Among them -
— Military modification of the GAZ-53N with an additional 105 liter fuel tank, a pre-heater and a set of additional equipment.
— The widely used KAVZ-685 and Kuban based on the GAZ-53. They were produced on the GAZ-53-40 chassis, equipped with softer springs and telescopic shock absorbers, a fuel tank from the GAZ-66, a modified brake system and electrical equipment.
GAZ-53-02 – dump truck. A special chassis designed for the GAZ-SAZ dump truck (SAZ-3503).
GAZ-53-05 is a truck tractor (it was not widely used, because any of the three engines of the 53rd GAZon was too weak for such “exercises”).
GAZ-53-19 and GAZ-53-27 - versions developed in 1984, running on liquefied gas; with engines of 105 and 100 hp. respectively.
GAZ-53 trucks were exported to almost all socialist countries, and from capitalist countries to Finland and Belgium.
Serious assembly production of these trucks, from Soviet vehicle kits, was organized in Bulgaria and Cuba. Moreover, the Bulgarian enterprise Madara produced GAZ-53 from 1967 to 1991, increasing production volume to 3,000 cars per year in the 80s. And already from the beginning of the 70s, it equipped them with Bulgarian-made engines.
Export versions of the truck were produced with the factory designations “GAZ-53-70” and “GAZ-53-50” (especially for the tropics). As already noted, the number of specialized versions based on the GAZ-53 chassis is difficult to calculate. These include mobile repair shops, fire trucks, truck cranes, ladder trucks, garbage trucks, loader cranes, fuel trucks, etc., etc.
About the history of the legendary truck and its features
Unlike all previously developed trucks of the Country of Soviets, the GAZ-53 was originally created purely for the needs of the national economy. In case of war, it was not planned to mobilize it into troops and use it to transport guns, transport ammunition, wounded, etc. army needs. In this regard, the GAZ-53 can rightfully be called the first domestic “NOT dual-use” truck.
This explains the “cheerful” colors of the legendary car. If previously all trucks of the Soviet Union were painted only in a dark green protective color, then the 53rd from the very beginning was distinguished by a very diverse range of colors: its cabs were painted in blue, gray, blue, beige, red, green, yellow, orange and some others colors.
The direct “relative” and “ancestor” of the GAZ-53 was another all-Union hard worker - the GAZ-51 truck. The development of a new generation truck was led by the chief designer of the Gorky Automobile Plant, Alexander Dmitrievich Prosvirnin (1914-2005). By the way, he was in 1946-1947. participated in the development of the GAZ-51, then still in the role of an ordinary designer.
During the summer/autumn of 1961, a pilot batch of GAZ-53F trucks was subjected to serious tests, the main of which was a motor rally along the route Moscow - Tashkent - Moscow, with a total length of ten thousand kilometers. The trucks were driven intensively along country roads and real deserts, steppe sands, marshy soils and mountainous areas. The culmination of the route in Central Asia was the Shahristan pass, in Tajikistan, located at an altitude of more than 3.2 thousand meters above sea level. At the same time, 2 GAZ-53Fs were mercilessly exploited in the Moscow region, in off-road rural conditions, and 4 more were driven along the Moscow-Gorky highway back and forth until the figure of 15,000 km was reached on their speedometer, testing reliability on highways. lines. In total, each of the vehicles performed 18 flights.
By the way, the “brother” of the 53rd GAZon, GAZ-52, also deserves kind words. Also a bestseller, with a circulation of more than 1 million units. This is practically its “twin”. Since the only reliable difference between these models is the model of the installed engine: on the 52nd there is a six-cylinder in-line, on the 53rd there is a more powerful eight-cylinder V-shaped.
By the way, according to the observations of experienced GAZON drivers, the 52nd was distinguished by slightly better cross-country ability in severe off-road conditions or deep snow. The more powerful and resourceful GAZ-53 was more likely to bury itself in mud, snow or sand where the 52nd was slowly passing on its own.
Externally, it was possible to distinguish the “GAZ-52” from the “GAZ-53” by the rims: “GAZ-52” and modifications had smaller rims, with 6 ventilation holes and narrower tires. The GAZ-53 has wider (and, accordingly, more “load-bearing”) tires; wheels of a larger diameter, with three holes placed at an angle of 120 degrees. However, the rims on the 52m and 53m GAZones are interchangeable.
Having looked at photographs of other cars of the late 50s/early 60s, we can rightfully say that for its time the appearance of the cabin and its interior of the GAZ-53 looked very progressive.
A one-piece lining of the radiator grille was made, into which the headlights and sidelights were organically integrated. The driver and passenger seats, according to the canons of those years, were a single “sofa”. However, the ergonomics of the workplace were better thought out than in the GAZ-51.
According to its class, GAZ-53 belongs to the family of universal medium-duty multi-purpose trucks. The GAZ-53 truck has a frame structure and the wheels are driven to the rear axle.
A few words about the characteristics of the GAZ-53-02 version (dump truck). The LAWN dump truck was produced with a frame shortened by 27 cm at the rear. The wheelbase remained the same. Was equipped with a power take-off shaft.
The platform was equipped with a gear-type hydraulic pump, which, through a system of control valves, ensured the operation of a three-link hydraulic cylinder for lifting the body. The capacity of the all-metal body platform is 5 cubic meters; body lifting and unloading are provided both backwards and sideways.
Specifications
Power unit
Iveco trucks
The Gorky Automobile Plant provided as many as 3 engines. Among them was the presence of an 8-cylinder V-shaped 4-stroke 4.67 liter gasoline engine ZMZ-5231.10.
It can be classified as European standards Euro-3. The engine runs on AI-80 or A-76 gasoline. If you apply additional adjustment, you can use AI-92 gasoline. It was also planned to install a 4-cylinder, four-stroke, 4.75-liter, 125-horsepower diesel engine “MMZ D-245”, which had turbocharging, liquid cooling, direct fuel injection and a charge air cooler.
This engine already complied with the Euro-4 environmental framework. His compression was already equal to 17 units, and he weighed all 430 kilograms. The last representative of this line of engines was YaMZ-5344. It was a four-cylinder, four-stroke diesel power unit with turbocharging, liquid cooling, direct fuel injection and a charge air cooler.
The engine complied with Euro-4 environmental parameters and had a 4.43 liter displacement with a rated power of 134.5 horses. The compression ratio was 17.5. The installation of a pre-heater was provided as a separate option.
Transmission
All diesel powertrains have been synchronized with a 5-speed manual gearbox. The work is carried out using an installed single-plate friction dry clutch, which has a hydraulic control drive.
But for gasoline engines, a 4-speed manual gearbox was provided, which could be easily distinguished by the characteristic howl that it emitted while driving.
Suspension
She is presented here as an addict. At the front there are semi-elliptic springs with shock absorbers. At the rear there are semi-elliptic springs with additional springs. The ends of the main sheets of all springs were installed in the rubber pads of the support brackets.
The drive goes to the rear twin wheels. The suspension was slightly redesigned, after which it was possible to better adapt it for Russian roads.
Steering
It has a worm mechanism, similar to a globoidal worm with a three-ridge roller.
Electrical equipment can support its own operation at 12 volts. The model did not receive a hydraulic power steering wheel.
Brake system
It is considered to be one of the most reliable. It includes brakes and hydraulic drive. In addition, the system has a pair of brake circuits, one of which is responsible for the spare brake. Each circuit has a hydraulic vacuum booster, together with a vacuum cylinder with a shut-off valve.
Thanks to vacuum cylinders, it is possible to achieve independent power supply to the circuits. The vacuum number is monitored using special vacuum measuring instruments, which are equipped with red indicators.
If the vacuum volume reaches the minimum reading, the lamp will begin to glow.
There is also a parking brake, and it is represented by a mechanical method of action, and it is installed on the transmission. Drum mechanisms are used to perform braking. Specifications
| engine's type | ZMZ-511.10 |
| Travel speed (maximum) | 90 km/h |
| Load capacity | 4.5 t |
| Engine power (nominal) | 92 kW |
| Rotation frequency | 3200 rpm |
| Number of engine cylinders | 8 pcs |
| Cylinder diameter | 9.2 cm |
| Piston stroke | 8 cm |
| Working volume | 4.25 l |
| Fuel tank volume | 105 l |
| Fuel consumption per 100 km (speed 60 km/h) | 19.6 l |
| Fuel consumption per 100 km (speed 80 km/h) | 26.4 l |
| Front track size | 1.7 m |
| Rear track size | 1.56 m |
| Wheelbase | 3.77 m |
| Clearance under the rear axle | 0.265 m |
| Clearance under the front beam | 0.347 m |
| Braking distance (speed 60 km/h) | 36.7 m |
| Weight (total) | 7.85 t |
| Weight (curb) | 3.2 t |
| Width | 2.33 m |
| Cabin height | 2.35 m |
| Length | 6.33 m |
| Body type | unloadable on 3 sides |
| Body dimensions inside (length, height, width) | 3.52x0.52x2.28 m |
| Body volume (standard sides) | 5 m³ |
| Body volume (extension sides) | 10 m³ |
| Underbody area | 8 m² |
Engine GAZ-53
8-cylinder 4-stroke gasoline carburetor engines “ZMZ-53” and “ZMZ-53-11” have a V-shaped cylinder arrangement. The working volume is 4,254 cubic centimeters. Power, at 3200 rpm per minute is: 115 (“ZMZ-53”) and 120 (“ZMZ-511”) horsepower. Cylinder diameter – 92 mm; piston stroke – 80 mm. The average compression ratio is 6.7. The maximum torque at 2000-2500 rpm is 29 kg/cm. The cylinders operate in the following order: 1—5—4—2—6—3—7—8.
The engine cylinder block is made of casting from Al-4 alloy, and after casting it is sealed by heat treatment and impregnation with synthetic resin. This is a classic monoblock V-shaped design with an angle along the cylinder axes of 90 degrees.
The cavities of the block and cast iron liners for the pistons form the water cooling jacket of the engine. The possibility of repair replacement of sleeves is provided (5 groups with letter designations). The clutch housing is secured to the end of the block with threaded rods.
Pistons are also divided into five repair groups according to their diameter (letter marking), and into four groups according to the diameter of the piston pin holes (color marking). The piston group is cast from aluminum alloy “Al-30”. The piston has a classic round shape with a flat bottom; three grooves are cut along its diameter for oil scraper and compression rings.
The block heads are made of Al-4 alloy. The valve seats are made of cast iron, and the guide bushings are made of copper-graphite ceramics. The block and cylinder heads are connected by threaded rods through gaskets made of asbestos cardboard reinforced with steel. The crankshaft is cast from cast iron, on which the connecting rod journals, bearings and counterweights are formed.
The crankshaft went through a series of mandatory dynamic and static balancing. Axial movement of the crankshaft is eliminated by two washers installed on either side of the first journal support. It is sealed in the block using oil-squeezing grooves, oil seals and asbestos packing.
The gas distribution mechanism, with overhead valve installation, ensures the intake of the fuel-air working mixture into the cylinders and the exhaust of exhaust gases.
This device consists of: camshafts and gears, pushers, rocker arms, rods, valves, guide bushings and springs. The camshaft is forged from steel. It has 5 bearing journals, cams, a gear drive for an oil pump and an ignition distributor.
The device for preparing the gasoline-air mixture is a K-126 carburetor. The ignition system is contact. Spark plugs - “A11-U”.
The lubrication system supplies oil to the contacting parts of the engine both under pressure and by gravity. The oil pump is gear-type, driven by a camshaft, the oil filter is full-flow, serviceable.
The air preparation filter is also serviceable, inertial, with the settling of polluting particles in an oil bath. Cooling system – with a water pump, closed type, liquid. It consists of a water jacket of the cylinder block, radiator, pump, thermostat, shutters, fan, fan casing, radiator cap and connecting hoses. Capacity – 22 liters.
The engine of the third modification of the 53rd GAZon - “ZMZ-53-11” differs from its predecessor in new cylinder heads with increased compression parameters; a sectional oil pump, a full-flow filter device, and crankcase ventilation switched to a closed circuit.
Gearbox, transmission, brake system, chassis, steering
The gearbox consists of four forward “speeds” and one rear. By its design, the GAZ-53 gearbox is a three-way gearbox, with synchronizers in third and fourth gears. The clutch is single-disc, dry.
The cardan transmission is open type, has cardan shafts with needle bearings. The main gear of the drive axles is a conical, hypoid type, with a gear ratio of 6.83. Differential - gear, cam, bevel, limited slip. Rotating axles are flanged, with CV joints.
Springs – 4 pcs., longitudinal semi-elliptical, ends embedded in rubber supports. The rear suspension has additional springs. Shock absorbers – hydraulic, telescopic, double-acting.
Foot brakes - shoe brakes, for 4 wheels. The brake drive is foot-operated, hydraulic, with a hydraulic vacuum booster. The hand brake is central, drum type, mounted on the driven shaft of the gearbox. The type of steering mechanism "GAZ-53" is a globoidal worm with a 3-ridge roller.
Electrical equipment GAZ-53
The GAZ-53 truck uses a single-wire wiring system with a connection between the negative terminal and ground. The mains voltage is 6 Volts. The brand of the “native” battery is “6-ST-68-EM”.
Generator brand, power 350 W – “G130-G”; relay-regulator - “PP130”. The electrical system of the GAZ-53 truck also includes a B13 ignition coil with additional resistance; breaker-distributor “P13-V”; single-cylinder air-cooled compressor; electric starter "ST130-B" with remote activation.
About the history of the legendary truck and its features
Unlike all previously developed trucks of the Country of Soviets, the GAZ-53 was originally created purely for the needs of the national economy. In case of war, it was not planned to mobilize it into troops and use it to transport guns, transport ammunition, wounded, etc. army needs. In this regard, the GAZ-53 can rightfully be called the first domestic “NOT dual-use” truck.
This explains the “cheerful” colors of the legendary car. If previously all trucks of the Soviet Union were painted only in a dark green protective color, then the 53rd from the very beginning was distinguished by a very diverse range of colors: its cabs were painted in blue, gray, blue, beige, red, green, yellow, orange and some others colors.
The direct “relative” and “ancestor” of the GAZ-53 was another all-Union hard worker - the GAZ-51 truck. The development of a new generation truck was led by the chief designer of the Gorky Automobile Plant, Alexander Dmitrievich Prosvirnin (1914-2005). By the way, he was in 1946-1947. participated in the development of the GAZ-51, then still in the role of an ordinary designer.
During the summer/autumn of 1961, a pilot batch of GAZ-53F trucks was subjected to serious tests, the main of which was a motor rally along the route Moscow - Tashkent - Moscow, with a total length of ten thousand kilometers. The trucks were driven intensively along country roads and real deserts, steppe sands, marshy soils and mountainous areas. The culmination of the route in Central Asia was the Shahristan pass, in Tajikistan, located at an altitude of more than 3.2 thousand meters above sea level.
At the same time, 2 GAZ-53Fs were mercilessly exploited in the Moscow region, in off-road rural conditions, and 4 more were driven along the Moscow-Gorky highway back and forth until the figure of 15,000 km was reached on their speedometer, testing reliability on main lines. In total, each of the vehicles performed 18 flights.
By the way, the “sibling” of the 53rd GAZon, the GAZ-52, also deserves kind words. Also a bestseller, with a circulation of more than 1 million units. This is practically its “twin”. Since the only reliable difference between these models is the model of the installed engine: on the 52nd there is a six-cylinder in-line, on the 53rd there is a more powerful eight-cylinder V-shaped.
By the way, according to the observations of experienced GAZON drivers, the 52nd was distinguished by slightly better cross-country ability in severe off-road conditions or deep snow. The more powerful and resourceful GAZ-53 was more likely to bury itself in mud, snow or sand where the 52nd was slowly passing on its own.
Externally, it was possible to distinguish the GAZ-52 from the GAZ-53 by the wheel rims: the GAZ-52 and modifications had smaller rims, with 6 ventilation holes and narrower tires. The GAZ-53 has wider (and, accordingly, more “load-bearing”) tires; wheels of a larger diameter, with three holes placed at an angle of 120 degrees. However, the rims on the 52nd and 53rd GAZon are interchangeable.
GAZ-53 Fuel consumption Dimensions Load capacity Weight Tank volume
The GAZ-53 truck was destined to become the most popular “workhorse” in the Soviet Union. The radiator of this hard worker is one of the most recognizable “brands” of the Soviet era. Which is not at all surprising: after all, over the years of its mass production, from 1961 to 1993, the fifty-third LAWN was replicated in more than four million units. And he traveled all over the world, from Cuba to Kamchatka, from the Far North to the jungles of Laos and Vietnam. Next, we’ll talk about the technical characteristics of this truck, and listen to the live opinions of drivers who have worked for GAZ-53 for many years.
Technical characteristics and design of vehicle components
Thanks to its high technical characteristics and maintainability, the dump truck continues to operate not only in industrial enterprises, but also in private households. The all-metal, durable body has extension sides and is released from the load by tipping on 3 sides.
A hydraulic cylinder is used as a lift. The power take-off drives a gear pump, which fills the system with oil through pipelines.
The GAZ-53 dump truck has a 2-seater all-metal cabin. Inside the cabin there are places to store tools and spare parts. The instrument panel does not contain an ammeter or oil pressure sensor. Instead, there are signal lamps. The passport number is located on the lower flange of the right side of the cab. The gasoline tank is located under the driver's seat, and the filler tank is located behind the cab, near the door.
Engine
The dump truck was equipped with different types of engines. At the initial stage, a GAZ-11 engine with 6 cylinders and a power of 82 hp was used. With. with 4-level transmission. The vehicle reached speeds of up to 75 km/h and had a load capacity of 3.5 tons. Fuel consumption per 100 km reached 22-25 liters. After modernization, a ZMZ-53 unit with 115 liters was installed. With. Consumption of A-76 gasoline remained unchanged.
To increase the power performance, the 53-12 chassis was equipped with a 4-stroke V-shaped carburetor gasoline unit from the Zavolzhsky Motor Plant ZMZ-511.10.
ICE parameters:
- Number of cylinders - 8.
- Working volume - 4.25 l.
- The cylinder diameter is 92 mm.
- Piston stroke - 80 mm.
- The operating order is 1-5-4-2-6-3-7-8.
- Rated power - 88.5 liters. With.
- Engine oil pressure is 250 kPa.
- The fuel consumption rate of the GAZ-53 is 19.6 l/100 km.
Carburetor
The design of the K-135 carburetor differs from the previous version of the K-126B in adjustment parameters. The mechanism has a downdraft flow, opening throttle valves and a balanced float-type chamber.
The principle of operation of the carburetor is as follows. From each chamber the mixture passes through an intake pipe to the cylinders. The chamber on the left supplies fuel to cylinders 5, 6, 7 and 8, on the right - to cylinders 1, 2, 3 and 4.
Cooling system
The engine cooling system is liquid, closed type. Low-freezing Antifreeze A-40 is used as a coolant.
Electrical equipment
The dump truck is equipped with DC electrical equipment. The nominal voltage in the network is 12 V. Electrical wiring diagram: the parts are connected using one wire, the metal parts of the cabin serve as the second wire, attaching all the negative wiring terminals. The 6-ST-75-EM battery is designed to power consumers and start the engine using a starter relay.
To recharge the battery, a 1250-G3 alternating current generator with a power of 560 W is installed, working in conjunction with a voltage regulator. If dust and dirt get into the brush holders, the brush may become stuck and the slip rings may ignite. For this purpose, it is necessary to check the generator.
The ST230-A1 starter is installed to the clutch housing on the right. In case of malfunctions associated with a large voltage drop and a decrease in power, the starter is repaired.
Ignition system - battery, contactless, transistor. To protect against ignition, check the reliability of the wires and clean the coil of dirt and oil.
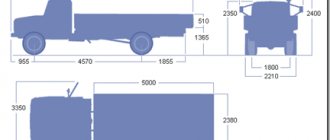
Dimensions and how much it weighs
Overall dimensions of the dump truck:
- length - 6400 mm;
- width - 2470 mm;
- cabin height - 2200 mm.
Onboard vehicle dimensions:
- length - 6395 mm;
- width - 2530 mm;
- height - 2220 mm.
The body dimensions are 3740x2110x1960 mm. The volume of the body depends on the frame and the cargo being transported: bulk materials, long items or scrap metal. The standard is 5.2 m³. To increase capacity, the platform is increased by extending the sides.
In a GAZ-53 car, the unloaded weight reaches 3.75 tons, the total weight is 7.4 tons. The maximum weight of a towed trailer is 3.5 tons, without a brake system - 750 kg. The tires are pneumatic radial with dimensions 8.25R20 (240R508) and diagonal 8.25-20" (240-508"). Tire pressure is 280-390 kPa (front) and 500-620 kPa (rear).
______________________________________________________________________________
GAZ-53 car and its main parameters
The GAZ-53 vehicle with a carrying capacity of 4 tons and drive to the rear axle (rear axle) is designed for transporting various materials and cargo on all types of roads.
The main components of GAZ-53 vehicles (engine, clutch, gearbox, cardan transmission, brakes, etc.), electrical equipment units, components and parts are unified. Technical characteristics of the GAZ-53 car Load capacity, kg - 4000 Maximum weight of the towed trailer with cargo, kg. — 4000 Vehicle weight in running order, kg — 3250 Overall dimensions of the GAZ-53 vehicle, mm: — length — 6395 — width — 2380 — height (in the cabin without load) — 2220 Wheelbase, mm — 3700 Front wheel track (on the ground) — 1630 Rear wheel track — 1690 Lowest points (with full load): — drive axle housings — 265 — front axle — 347 Turning radius along the outer front wheel track, m — 8 Highest speed of a GAZ-53 car with a full load without a trailer (at horizontal section of road with improved surface), km/h - 80-86 Control fuel consumption when measured in summer for a run-in GAZ-53 car moving with a full load in fourth gear at a constant speed of 30-40 km/h, l / 100 km — 24 GAZ-53 engine Number of cylinders and their arrangement — 8, V-shaped Cylinder diameter, mm — 92 Piston stroke, mm — 80 Cylinder displacement, l — 4.25 Compression ratio (average value) — 6.7 Maximum power (limited by regulator) at 3200 rpm, hp — 115 Maximum torque at 2000 — 2500 rpm, kg/cm — 29 Cylinder operating order — 1—5—4—2—6—3—7—8 GAZ-53 transmission
Clutch GAZ-53 - Single disc, dry
GAZ-53 gearbox - Three-way, with synchronizers in third and fourth gears.
Transfer case - Has two gears: direct and reduction with a gear ratio of 1.982
Cardan transmission GAZ-53 - Open type, has cardan shafts with needle bearings. Main gear of drive axles - Conical, hypoid type, gear ratio 6.83
Differential - Gear, Cam, conical, limited friction Steering axles - Flanged, with constant velocity joint Chassis GAZ-53
Springs - Four longitudinal semi-elliptical, the ends are embedded in rubber supports.
The rear suspension of the GAZ-53 has additional springs.
Shock absorbers - Hydraulic, telescopic, double-acting. Installed on the front axle and both axles. Steering GAZ-53
Steering mechanism type: Globoidal worm with three-ridge roller. Gear ratio - 20.5 (average) Power steering (power steering) GAZ-53 - Hydraulic. Brake system of the GAZ-53 car
Foot brakes - Shoe brakes on four wheels. Foot brake drive - Hydraulic with hydraulic vacuum booster.
Handbrake - Central drum type. Location: On the transmission driven shaft. Electrical equipment of the GAZ-53 car
Wiring system - Single-wire with connection of the negative terminal to ground Mains voltage, 6 Generator - G130-G, power 350 W Relay regulator - PP130 Battery - 6-ST-68-EM Starter - ST130-B with remote switching Ignition coil - B13 additional resistance Distributor breaker - P13-B Spark plugs - A11-U GAZ-53 cab - Metal, double, two-door.
Dimensions of the GAZ-53 platform, mm:
— length — 3,740 — width — 2170
— side height — 680 Compressor — Single-cylinder, air-cooled Adjustment data for the GAZ-53 machine Gap between the rocker arms and valves on a cold engine (temperature 15–20°C), mm — 0.25–0.30
It is allowed to set the gap at the outer valves of both rows (intake of the first and eighth, exhaust of the fourth and fifth cylinders), mm - 0.15-0.20
Gap between spark plug electrodes, mm - 0.8-0.9
Gap in the breaker, mm - 0.3—0.4
Free travel of the clutch pedal, mm - 32-42/35-45
Free play of the brake pedal, mm - 8-13 Filling tanks and volumes of the GAZ-53 vehicle (l) Fuel tanks (capacity) - 200 Gearbox housing - 3.0 Gearbox housing with power take-off - 4.2 Transfer case housing - 1.5 Rear axle housing - 8.2 Front axle housing - 7.7 Steering gear housing - 0.5 Shock absorbers (each separately) - 0.41 Winch gear housing - 0.8 Power steering - 1.8 Hydraulic system foot brake drive - 0.76
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
- Clutch GAZ-3308, 3309
- Dismantling the GAZ-3308, 3309 gearbox
- Drive axles GAZ-3308
- Transfer case and cardans GAZ-3308
- Cardans GAZ-3307, 3309
- Rear axle GAZ-3309, 3307
- Suspension GAZ-3309
- Steering GAZ-3309
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
- Clutch GAZ-53, 3307
- Gearbox GAZ-53, 66
- Rear axle GAZ-53
- Steering GAZ-53, 66
- Ignition installation GAZ-53
- Clutch GAZ-66
- Drive axles GAZ-66
- Brake system GAZ-66
- Winch and power take-off GAZ-66
- Operating systems of the GAZ-66, GAZ-3307 engine
- Engine ZMZ-402 Gazelle GAZ-2705
- Clutch Gazelle GAZ-2705
- Gazelle GAZ-2705 gearbox
- Front axle Gazelle GAZ-2705
- Cylinder head and camshaft Cummins ISF 2.8
- Fuel system of the Gazelle Cummins ISF 2.8 engine
- Cylinder block and piston group of the Cummins ISF 2.8 engine
- Crankshaft engine Cummins ISF 2.8 Gazelle
- Engine Cummins Valdai GAZ-33106
- Clutch and gearbox Valdai
- Bridges Valdai
- Steering Valdai
Catalogs of spare parts and assembly parts
Dump truck GAZ-SAZ 53B
The dump truck has a shortened frame by 300 mm, which is why the spare wheel was moved under the body behind the driver. Both suspensions are on leaf springs, shock absorbers are installed only on the front suspension. On the first releases of trucks, the edges of the main sheets were bent and formed an “ear” for fastening, and at this point they were fastened through the bushing using spring pins.
The gasoline tank is located under the driver, the filler neck is located immediately behind the driver's door. The modification was carried out from 1966 to 1984; in addition to Saransk, cars with dumping equipment were produced at the Frunzensky Automobile Assembly Plant.
The most famous truck from the times of the USSR is considered to be the GAZ-53, in addition, it also surpassed its counterparts in terms of production quantity. GAZ-53 can be classified as a medium-tonnage truck.
The GAZ-53 truck has rear-wheel drive, and various modifications of trucks were produced on its basis, including dump trucks. GAZ 53 dump trucks were marked as GAZ-SAZ 53B. GAZ 53 dump trucks were produced from 1966 to 1974.
Cabin
The dump truck cabin has space for two people. Such a dump truck could load 3.5 tons, despite the fact that the weight of the equipped dump truck reached 3 tons 750 kg. The dump truck was 6.38 m long, 2.475 m wide, and 2.575 m high. Its wheelbase reached 3.7 m.
Engine
Like all 53 models, the GAZ 53 dump truck was equipped with a carburetor engine that could run on both natural gas and gasoline. The engine was installed V-shaped with eight cylinders. The engine consumed 24 liters per 100 km, which is not so much for trucks of that time.
V-shaped engine for GAZ 53 dump truck
Transmission
The gearbox is mechanical, consisting of four stages. The GAZ 53 dump truck was equipped with a single-plate dry clutch and a single hypoid final drive. The steering was equipped with a pair of globoid worms with a three-ridge roller. The tire diameter was 20 inches.
Although the production of a dump truck based on the GAZ 53 was discontinued a long time ago, this modification of the truck is still on the road, and therefore a sufficient number of people are interested in its technical characteristics and tips for repairing this truck.
Chassis characteristics
The dump truck was equipped with a 4.25 liter 8-cylinder engine, its cylinder block and cylinder heads were cast from Al 4 aluminum alloy. The gearbox was 4-speed manual, the vehicle had rear-wheel drive.
Dump truck gearbox
- Length/width/height of the cabin – 6.4 m/ 2.47 m/ 2.2 m;
- Load capacity – 3.5 tons;
- Curb weight - 3.75 tons;
- The weight of a fully loaded vehicle is 7.4 tons;
- Ground clearance (clearance) – 0.265 m;
- Wheelbase – 3.7 m;
- Fuel consumption per 100 km at a speed of 40 km/h – 24 l;
- Tire size – 8.25-20 inches;
- The rated power of the internal combustion engine is 115 hp. With.;
- Engine type – carburetor;
- The compression ratio in the engine cylinders is 7.6;
- Steering – worm-type steering mechanism, without power steering;
- The number of seats in the cabin is two, including the driver.
Tipper equipment
The GAZ-SAZ 53B dump truck is released from the load by tipping the body. The direction of unloading can be side or rear. The body of the Gas 53 dump truck is metal, the vehicle's load capacity is less than that of the flatbed version.
Tipping the dump truck body sideways
The dump truck body drive is hydraulic. The lifting device is a hydraulic cylinder; the hydraulic system uses liquid oil; the hydraulic cylinder is rigidly connected to the platform. The cylinder is filled with oil through pipelines by a gear pump, which in turn is driven by the power take-off. Depending on which part of the cylinder is filled with oil, the body is raised or lowered. The lifting and lowering is controlled by a crane; it contains three valves:
- Body lowering valve;
- Safety valve;
- Check valve.
The lowering valve allows oil to flow into the oil tank when the pump is not running and the platform is lowered.
Drawing of the mechanism of the GAZ 53 dump truck
The hydraulic cylinder of the device is telescopic, it contains three plungers. At the bottom of the cylinder (at the bottom) there is a fitting for filling the cavity with oil. The device itself contains three plungers - one per telescopic section of the hydraulic cylinder. The installed protective rings on the plungers protect the rubbing surfaces from dirt and dust.
Source of the article: https://avtomobilgaz.ru/gruzovye/gaz-53/samosval-tehnicheskie-harakteristiki.html
Dump truck GAZ-53: technical characteristics
The repairable and moderately reliable GAZ-53 with a tipper mechanism continues to work in private and commercial households. The fairly durable body is equipped with an automatic lifting device. The dependent leaf spring suspension ensures a rigid ride, which is softened by telescopic shock absorbers on the front axle. The car uses a drum-type brake mechanism. There is no power steering, which makes steering difficult.
Experts attribute the short life of the clutch to the disadvantages of the machine, which affects the smooth start of movement. Fastening the cardan requires constant attention, since the nuts at the joints with the hinges are constantly unscrewed. One of the main problems is a leaking crankshaft oil seal. The electrical equipment of the machine is not reliable. A GAZ-53 with a loaded body is poorly adapted for driving on broken roads.
Engine and transmission
Over the long period of serial production of the GAZ-53, the dump truck was equipped with various engines. The first power unit was the GAZ-11 engine, a 6-cylinder 82-horsepower engine, complemented by a four-speed transmission. A car equipped with such components accelerated to 74 km/h, had a maximum load capacity of 3.5 tons and consumed from 22 to 25 liters of fuel per 100 km.
The following modifications of the GAZ-53 with index A were equipped with ZMZ-53 engines. The six-cylinder engine produced 115 hp. power and was complemented by a four-speed gearbox. The maximum speed of the vehicle reached 85 km/h, the load capacity and fuel consumption did not change. In 1983, the production of such machines was completed.
The last GAZ-53-12 was equipped with a ZMZ-511 power unit. The eight-cylinder engine produced 120 hp. power. At maximum speed, the car consumed 25-30 liters of fuel per 100 km. The lifting capacity of the equipment has increased to 4.5 tons.
“Gluttonous” power units are considered one of the main problems in operating the GAZ-53. However, Soviet mechanical engineering solved this problem. The car can be equipped with a D-245 diesel engine. The unit pays for itself, according to rough estimates, in 40 thousand kilometers.
Some GAZ-53 models were produced with gas-cylinder equipment and could run on methane. The power of such equipment was 100-105 hp, and the maximum speed reached 80 km/h.
List of modifications
- GAZ-53F – flatbed version or chassis with an 82-horsepower unit and rear axle from the GAZ 51;
- GAZ 53 – basic modification with ZMZ 53 engine;
- GAZ 53A - an improved variation of a flatbed truck with increased carrying capacity;
- GAZ 53B – dump truck;
- GAZ 53N - military version of the GAZ 53A with a pre-heater, additional equipment and a second fuel tank of 100 l;
- GAZ 53-02 – chassis for a dump truck;
- GAZ 53-05 – truck tractor (produced in small quantities);
- GAZ 53-40 - an extended version of the GAZ 53A with tails. Used as the basis for KAVZ 685 buses and special bodies;
- GAZ 53-50 – export version for tropical zones;
- GAZ 53-70 – export version for temperate zones;
- GAZ 53-12 - a modernized basic version with a load capacity of 4.5 tons and a 120-horsepower ZMZ 511 unit;
- GAZ 53-19 – a hybrid modification running on liquefied gas;
- GAZ 53-27 is a hybrid variation that runs on compressed natural gas.
There were also several special versions:
- MPR 9924 – mobile repair workshop;
- AL 18 (52-01)-L2 is a ladder truck, the production of which was carried out at the Torzhok plant. The vehicle was used to transport personnel (2 people), extinguish fires, and perform rescue operations.
Differences between the 53A line and the 53
The car models have the following differences: reinforced front axle; new cardan design; more reliable steering gear design; new radiator grille; turn signals are duplicated by repeaters on the wings of the cabin; the presence of electric windshield wipers; cabin heating. In 1973, model 53A was awarded the USSR State Quality Mark. Expanding the functionality of the vehicle, the production of chassis 53 01 for covered bodies and special equipment was launched. Chassis 53 02 was a platform for the use of a dump truck body and was equipped with a power removal device for a hydraulic pump. Trucks of models 53 50 and 53 70 were exported. The vehicles were readily purchased in Belgium, Finland, and in socialist countries. In Bulgaria and Cuba, trucks were assembled from kits supplied from GAZ.
Model 53 12 was produced from 1983 to 1992, as a further development of the 53rd line. The truck was equipped with an eight-cylinder ZMZ-511 engine. Power parameter is 120 hp. With. made it possible to increase the load to 4.5 tons, and the speed indicator to 90 km/h. Gasoline consumption increased to 30 liters, but provision was made for installing equipment for refueling with liquefied or compressed gas.
GAZ-53 - video review
About the areas of application and modifications of the GAZ-53 On its not particularly powerful shoulders, the GAZ-53 nevertheless “rolled” at least half of the entire economy of the Country of Soviets. It's hard to find where this ubiquitous truck has NOT been used. From the “gait” for emergency crews and the “paddy wagon” for criminals to mobile fuel tankers and truck tractors that hauled containers - everything that was not installed on the GAZ-53 chassis!
These cheap, simple and unpretentious trucks have become widespread in agriculture. In the 70s/early 80s of the 20th century, on the average Soviet collective farm, 80% of the truck fleet consisted of GAZ-53. Only in the second half of the 80s did this ratio begin to change towards an increase in the share of ZIL-130. Which, by the way, in Soviet times did not cost much more than a LAWN.
"GAZ-53" of the 60s and 80s are noticeably different from each other in appearance, and in a technological sense these are two quite different trucks. Not only are their engines completely different, but also many other design elements.
After all, over the years of production, the GAZ-53 has experienced three major and many minor upgrades and improvements. The Gorky Automobile Plant tried to promptly respond to “signals from the field” and eliminate problems identified during operation.
Thus, already in the first years of the distribution of the new truck model across the country, it became obvious that the axles from the previous generation - GAZ-51 - were no longer suitable for the 53rd, and the 82-horsepower engine from the 51st GAZon, although forced, does not meet the increased needs of the new machine. During 1964/65, serial production of the GAZ-53 was launched, equipped, instead of an in-line six-cylinder engine, with a V-shaped eight (115-horsepower ZMZ-53 engine), as well as modified and reinforced bridges.
An interesting, half-forgotten fact: the cladding and, accordingly, the appearance of the GAZ-53 of the first releases were very noticeably different from the appearance of the car we are accustomed to. For example, the headlights were located above the direction indicators. However, unfortunately, not a single original LAWN of that very first generation has survived to this day. But he remained captured on film in some famous films of that time, in particular “Happy Troubles” (1964), “Foreigner” (1965), “Beware of the Car” (1966), “Three Poplars on Plyushchikha” (1967).
By the way, a curious film curiosity is associated with the GAZ-53, which has already become familiar to everyone. In the famous film “The Meeting Place Cannot Be Changed,” in the episode when gang members are driving Volodya Sharapov in a GAZ-AA bread van through Moscow at night, a green GAZ-53 was inappropriately inserted into some shots. (The film takes place in 1946).
GAZ-53-12 (1983-1993)
Specifications
The MAZ-6516 car is equipped with all the necessary systems, and the design has been brought to modern traditions. But all this would not be necessary if not for the technical performance of the engine units. Motors produced at the Yaroslavl Metallurgical Plant have been proving their practicality for many years; in addition, other manufacturers of working elements throughout Russia complement the general understanding of the machine’s mechanisms. Trucks of various modifications from “6516” were produced with two types of wheeled chassis characteristics:
- 1 600*2990*1400 mm
- 2 030*2620*1400 mm
Technical characteristics for base No. 1
| Load capacity | ||||
| Parameter name | 651608 | 651A8 | 651A9 | 651669 |
| Maximum vehicle weight when fully loaded, in kilograms | 16 205 | 16 205 | 16 205 | 16 205 |
| Maximum weight of chassis and cabin, in kilograms | 11 705 | 11 705 | 11 705 | 11 705 |
| Maximum permissible weight including driver weight | 41 780 | 41 780 | 41 780 | 41 780 |
| Load distribution on the chassis along the axles, in kilograms | ||||
| To the first | 7 500 | 7 500 | 7 500 | 7 500 |
| On the second | 7 500 | 7 500 | 7 500 | 7 500 |
| On the third | 19 390 | 19 390 | 19 390 | 19 390 |
| On the fourth | 19 390 | 19 390 | 19 390 | 19 390 |
| Maximum chassis load tolerance | 25 500 | 25 500 | 25 500 | 25 500 |
| Engine and gearbox | ||||
| Parameter name | 651608 | 651A8 | 651A9 | 651669 |
| engine's type | YaMZ-7511.10 | YaMZ-6581.10 | YaMZ-650.10 | MAN D2866LF25 |
| Maximum power in kilowatts | 294 | 294 | 303 | 301 |
| Engine horsepower | 400 | 400 | 420 | 412 |
| Environmental class type | Euro-3 | |||
| Fuel consumption calculated as N liters per 100 kilometers. Travel speed 60 km/h | 38,0 | 39,0 | 40,5 | 40,0 |
| Rated speed with limiter in km/h | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 |
| Maximum speed without speed limiter km/h | 95+ | 95+ | 95+ | 95+ |
| Gear box | 12JS200TA | 12JS200TA | 12JS200TA | ZF16S2525TO |
| Number of gearbox stages | 12 (10 forward; 2 reverse) | |||
| Drive axle ratio | 5,33 | |||
| Technical characteristics of base No. 2 | ||||
| Load capacity | ||||
| Parameter name | 6516A9 | 651B9 | 651669 | 6516V8 |
| Maximum vehicle weight when fully loaded, in kilograms | 14 825 | 14 825 | 14 825 | 14 825 |
| Maximum weight of chassis and cabin, in kilograms | 11 425 | 11 425 | 11 425 | 11 425 |
| Maximum permissible weight including driver weight | 41 800 | 41 800 | 41 800 | 41 800 |
| Load distribution on the chassis along the axles, in kilograms | ||||
| To the first | 7 500 | 7 500 | 7 500 | 7 500 |
| On the second | 7 500 | 7 500 | 7 500 | 7 500 |
| On the third | 13 400 | 13 400 | 13 400 | 13 400 |
| On the fourth | 13 400 | 13 400 | 13 400 | 13 400 |
| Maximum chassis load tolerance | 26 900 | 26 900 | 26 900 | 26 900 |
| Engine and gearbox | ||||
| Parameter name | 6516A9 | 651B9 | 651669 | 6516V8 |
| engine's type | YaMZ-650.10 | YaMZ-651.10 | MAN D2066LF01 | MAN D2066LF01 |
| Maximum power in kilowatts | 303 | 303 | 316 | 294 |
| Engine horsepower | 420 | 420 | 434 | 400 |
| Environmental class type | Euro-3 | Euro-4 | Euro-3 | Euro-5 |
| Fuel consumption calculated as N liters per 100 kilometers. Travel speed 60 km/h | 38,0 | 39,0 | 40,5 | 40,5 |
| Rated speed with limiter in km/h | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 |
| Maximum speed without speed limiter km/h | 95+ | 95+ | 95+ | 95+ |
| Gear box | 12JS200TA | 12JS200TA | ZF16S2525TO | ZF16S2525TO |
| Number of gearbox stages | 12 (10 forward; 2 reverse) | |||
| Drive axle ratio | 5,33 |
The manufacturer of the 12JS200TA gearbox is located in China.
Common parameters
| Dimensions | |
| Height | 3 650 mm |
| Width | 2 550 mm |
| Length | 8,910 (9,000) mm |
| Cargo body length | 5 790 mm |
| Cargo body height | 1 600 mm |
| Body angle | 50o |
| Body volume | 21 m3 |
| Other characteristics | |
| Wheel type | Disc 2.00R20; chamber/universal, GOST 5513-97; |
| Tire sizes/tread pattern type | 315/80 R22.5; tubeless (by customer request) / for the first, second axles and spare wheel - road, for the third and fourth - universal |
| Wheel angle | First axis – 36o / Second axis – 25o |
| Fuel tank volume | 300 liters |
The rear suspension is a multi-leaf spring-balancer with a vertical ladder arrangement. Fastenings between the frame and the suspension are provided with bolts made of extra-strong steel. The rear and middle axles are equipped with anti-roll bars. On the move, the work of the stabilizers is very noticeable: when turning, the dump truck has a slight roll, even if it is fully loaded. Despite this reaction, no bouncing is observed, and in general the suspension operates very smoothly.
Additional properties. The standard set of systems includes ABS and PBS. An on-board computer can also be optionally installed, which allows you to monitor the operation of all mechanisms and control fuel consumption.
Technical characteristics of GAZ-53
— Years of production: 1961—1993 — Wheel formula: 4 × 2
Engine
— Name: ZMZ-53 — Working volume: 4,254 cubic centimeters. — Power: at 3200 rpm. per minute, is 115 hp
Fuel consumption GAZ-53
— 24 l/100 km at a speed of 40 km/h
Maximum speed of GAZ-53
— 90 km/h with full load on a horizontal highway
Gearbox: 4 forward + 1 reverse
Overall dimensions of GAZ-53
— Length: 6.395 m; — width: 2,380 m; - height (in the cabin, without load): 2,220 m - Chassis base - 3,700 m; — front wheel track (on ground): 1,630 m; — rear wheel track: 1,690 m — Ground clearance: 265 mm.
Weight GAZ-53
— Curb weight: 3,200 kg
Load capacity of GAZ-53
- 4 tons for GAZ-53F and GAZ-53A; 4.5 tons - for GAZ-53-12.
Tire size GAZ-53
- 8.25-20 inches.
Tank volume GAZ-53
— 90 l
Truck Specifications
One of the indicators of the GAZ 53 is the weight of the car, which is only 3.2 tons. Its total weight is 7.85 tons. Thus, the vehicle’s carrying capacity is 4.5 tons. But such indicators only apply to modification 53 12, for which the cars were designed for only 3 tons of cargo.
Model 53 dimensions are as follows:
| Body length | 6.4 meters |
| Body width | 2.4 meters |
| Body height over cabin | 2.2 meters |
| Axle distance | 3.7 meters |
| Wheel track on the front beam | 1.63 meters |
| Wheel track on the rear beam | 1.69 meters |
| Clearance | 0.265 meters |
| Wheel tires | 8.25-20 inches |
The permissible vehicle speed is 90 kilometers per hour. But in reality, it can go much faster if the load is not very large. The car's fuel consumption is 24 liters per 100 kilometers. But most often this figure rises due to excessive loads and poor car care.
The car's power unit is a V-shaped carburetor engine with 8 cylinders. Its volume is 4252 cubic centimeters. The engine requires 10 liters of oil. The gearbox has 4 gears and 1 reverse. The fuel tank capacity is 90 liters. The car runs on A-76 gasoline.
Reviews GAZ-53
By the way, what do people who have had the opportunity to work on the main medium-tonnage truck of the Union republics and socialist countries say? What advantages and disadvantages will they highlight in this car?
Of the advantages, the first place is the simplicity of the design and direct operation of the machine. On the second - amazing maintainability. To eliminate any minor or major breakdown, no special devices, equipment or tools are required; you don't need to be a qualified specialist. To completely overhaul the engine and gearbox, a couple of days will be enough.
Another undoubted advantage is the durability of the machine during its “killer” operation in extreme conditions. Extremely strong chassis: everything around can “rot” and crumble from old age, but the GAZon hubs and bridges will remain.
“The rear axle is a part that has never been repaired at all, and no one has ever changed the oil there since 1984,” shares the owner of a GAZ-53, who to this day uses it (already converted to gas) in his farm, there is practically no corrosion, everything is intact.”
Indeed, one can only speak in superlatives about the quality of the metal of LAWNs produced in the 80s. On the next generation of trucks, the metal was much worse, much more susceptible to corrosion and less durable.
In general, the average period of active operation of a truck could be different - depending on the conditions in which it had to work and the total mileage. On collective farms, where perhaps the most significant part of the 53s “served,” the truck worked for an average of 12 years before being written off.
The capabilities of the GAZ-53 engine were very limited, and it really could not carry more than the 4-4.5 tons required by the passport. Although, naturally, they tried to overload it often, everywhere and everywhere.
For example, with extended sides, grain was loaded from a combine up to seven tons at a time (instead of four and a half). But with great difficulty the engine power was enough to cope with the high load. A lawn that is loaded “to the fullest” or “with allowance” pulls very poorly, even up a not very steep hill you need to “climb” in first gear, and the engine also begins to overheat.
Under conditions of merciless operation, GAZ-53 engines operated for only 100-150 thousand kilometers before the first major overhaul; where conditions were more favorable - and 400 thousand. The engine overhaul could be done at least three times.
The weak point in the LAWN design is the clutch disc; the splines are only enough for one season of intensive work. The support bearing in the crankshaft also did not always last more than a season; Problems with the release bearing are also noted.
The steering is mechanical, tight, and sometimes hits your hands. But there was no talk of any amplifiers in those days. Another disadvantage - high fuel consumption - was also insignificant in the Soviet era. Now it’s hard to imagine, but then gasoline was cheaper than mineral water: in the 70s, 6-8 kopecks per liter; in the 80s it was already more expensive, but even then the absolute maximum cost of gasoline was 30 kopecks per liter. Therefore, GAZ-53, converted from gasoline to gas, has already become the “child of perestroika.”
Auto device
The design of this unit is simple and reliable, thanks to which the GAZ-53 is widely used as an inexpensive truck that is unpretentious in maintenance. Studying its design, we can identify several key components that deserve separate consideration:
- power unit;
- additional systems and mechanisms necessary for the operation of the car;
- electrical equipment.
You should also note the cardan shaft, an important element of which is a cross in the amount of 3 pieces.
Engine GAZ-53
The power unit of this model is considered one of the most durable, since it relatively rarely requires serious repair work. Its identification number is ZMZ-53, it has a displacement of 4.25 liters and a power of 115 hp. The engine runs on gasoline, is of the V-type, equipped with 8 cylinders.
They are made of a special grade of aluminum, not only the cylinder body, but also their head parts. The diameter of each is 9.2 cm, the operating principle is 4-stroke. Its power is quite enough for driving on the highway exceeding the maximum speed declared by the manufacturer, but only if there is no load.
Be sure to read:
Technical characteristics of GAZ-2747
Despite the fact that, according to the documentation supplied with the car, its fuel consumption is 24 liters per 100 km, such a figure may not correspond to real figures. Consumption increases significantly when the car is loaded, as well as driving on uneven roads, in rain or snow.
Systems and mechanisms
The model's gearbox is equipped with 5 steps, 4 of which are full speed, and 1 is reverse gear. The 53 modification was equipped with synchronizers, which makes switching them much easier.
The clutch is of the dry type and is equipped with one disc. The springs have a long service life, are semi-elliptical, and are installed in the amount of 4 pieces. Overloading the vehicle significantly reduces the service life of these components and leads to their rapid breakdown.
Standard foot brakes are of the shoe type, while the handbrake is of the drum type. Steering in the model is implemented using a globoidal worm mechanism with a special roller equipped with 3 ridges. The body lift hydraulic cylinder is used in dump truck modifications.
Electrical equipment
The flatbed truck in question has a simple electrical equipment system, which is due to the lack of many options characteristic of more modern analogues. The wiring is a 1 wire circuit and is rated at 6v.
The design uses a rare 6-ST-68-EM battery, installed at the time of release, as well as a 350W generator. The alternator belt has a short service life and often requires replacement. Electrical equipment includes an ignition coil, distributor and starter.
Cabin GAZ-53
“A comfortable 2-seater closed cabin, convenient location of controls and instruments, good visibility, reliable brakes, and the presence of powerful lights ensure ease of driving and safety at high speeds at any time of the day,” this is how the GAZ-53 information report described album "VneshTorgIzdata" in 1968.
Well, as they say, what to compare with. From the perspective of our time, the cabin of the GAZ-53 is more than ascetic and spartan.
However, compared to the same GAZ-51, which did not have synchronizers in the gearbox, the clutch had to be depressed 2-3 times before engaging, and the cabin was cramped and poorly heated, the 53rd was simply the pinnacle of comfort!
The two-seater shared sofa seat, covered in faux leather, could easily accommodate three people if desired. The only point: the one who got the seat in the middle could interfere a little with the driver by touching the gearshift lever with his feet. There was also ample space in the cabin for the “creativity” of tuning enthusiasts: Soviet-era drivers decorated their GAZ-53 cabs as best they could.
There were also craftsmen who made homemade insulation and soundproofing of the cabin: they filled it with foam plastic, lined it with felt, achieving amazing silence and comfort in their workplace.