Although grenade launchers are currently considered quite outdated weapons, significantly inferior in their characteristics to guided anti-tank missiles, they are still in service. Recent combat operations in Iraq have proven that the most modern American tanks at the time, costing millions of dollars, become easy targets for local infantry armed with old Soviet grenade launchers.
The most successful examples of rocket-propelled grenade launchers, which were created in the Soviet Union back in the 1950s, were the RPG-7 and SPG-9. Unlike the RPG-7, which became probably the most famous grenade launcher in the world, the SPG-9 easel grenade launcher could not achieve such fame. In reality, the 73mm SPG-9 is more powerful and modern than its "little brother" RPG-7, but since its weight class does not contribute much to its mobility, it has not seen much use in irregular armies.
The history of LNG-9
Already in the second half of the 1950s, it became clear to the command staff of the USSR Army that all models of infantry anti-tank weapons had long been out of keeping with the spirit of the times. In addition to the fact that they cannot penetrate the thick armor of modern tanks, they are also too massive for use by paratroopers. Since airborne units were rapidly developing in those years, the question of the need to develop new models of anti-tank weapons became acute.
According to the technical specifications, which were drawn up by military experts, the new weapon had to meet the following requirements:
- Be simple in design;
- The design of the weapon must be so reliable that it can be fired for 5 days without cleaning. According to statistics, in five days of fighting, an average of about 35 shells should have been fired from an anti-tank grenade launcher;
- The power of the shot should have been enough to penetrate at least a 30-centimeter layer of armor.
At the same time, the desired weight of the new weapon should not exceed 30 kg.
The development of new weapons was entrusted to the State Union Design Bureau No. 47 (GSKB-47), which is currently called FSUE "Basalt". The project, which was called “Spear”, was developed over a long period of time. The main problem that the design engineers faced was difficulties with the weight of the finished weapon. Despite all the efforts, it was not possible to create a weapon of the required power, while “squeezing” it into the weight limits indicated in the technical specifications.
The development of the Spear project was completed in 1962. At this time, the designers were able to present a prototype of the new grenade launcher for testing. The prototype weapon, whose weight turned out to be about 50 kg, coped with all the assigned tasks during the first test. The customer was forced to agree with the new weight of the grenade launcher, since the designers assured that by reducing the weight, they would also reduce the power of the new grenade launcher.
During 1962, the new army grenade launcher passed all internal and external tests, and in 1963 it was put into service. At the same time, it received the official name “73-mm mounted anti-tank grenade launcher SPG-9.”
AGS-30
An automatic mounted grenade launcher was developed in the early 1990s. engineers of the Instrument Design Bureau in the city of Tula. The designers were given the task of creating a new grenade launcher to replace the AGS-17 model. Serial production has been carried out since 2008 at the KZTA JSC enterprise. The automatic grenade launcher operates using the recoil energy of the bolt. In order to give the gun stability during firing, a special tripod machine was developed for it.
According to experts, the AGS-30 can be used from any surface and unprepared position. The grenade launcher can be disassembled for transportation in 3 minutes. A weapon with optical and mechanical sights. The AGS can also be connected to a portable radar system. Shooting at long distances is carried out using PAG-17 optical sights, which have a 2.7-fold magnification. The grenade launcher is equipped with 350-gram VOG-17 rounds. The mass of the explosive is 36 g. At the point where the grenade falls, the area is affected within a radius of 70 m2. The upgraded VOG-17M rounds are equipped with fuses with self-liquidators. This mechanism begins to work 25 seconds after the shot under the influence of a pyrotechnic moderator. In VOG-30, the weight of the explosive is increased to 185 g.
In an effort to increase the destructive impact of fragments, designers use the cold volumetric deformation method in the production process. Thus, half-finished fragments are formed on the inner surface of the body. In VOG-30, the presence of a fragmentation jacket as a separate part is not provided. As a result of the increase in explosives, the affected area increased - 110 m2. This figure is increased to 131 m2 with the GPD-30 with a total mass of 340 g and an explosive of 185. During testing, it was noted that drag and ballistics were reduced by almost half. This, in turn, had a positive effect on the projectile’s flight range. Such a grenade can hit a target at a distance of no more than 2200 m. In addition, the accuracy of the battle has been improved by one and a half times.
Features of the SPG-9 grenade launcher
The operation of the LNG-9 grenade launcher is based on a recoilless system. The peculiarity of this scheme is that when a weapon is fired, powder gases are discharged through a nozzle specially designed for this purpose, which is located in the breech of the barrel. Thanks to this, shooting from the LNG-9 has become much more comfortable.
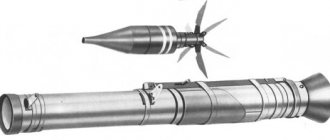
The main unit is a 73 mm caliber barrel. If you believe the folk legend that circulated in the early 1960s, this caliber was chosen completely by accident. Allegedly, the design engineers developing the LNG-9 were constantly drunk, and 73 mm is the diameter of the vodka bottle of those years, which they hid in the barrel of a prototype grenade launcher.
In fact, this barrel diameter did not appear by chance. The initial version of the grenade launcher had a caliber of 70 mm. This weapon had one significant drawback - after 7-8 shots, so much soot accumulated in the barrel that not only shooting, but even loading the grenade launcher became a big problem. Since the new grenade launcher had to operate without cleaning for at least 35 shots, it was decided to add one specific part to the grenade. A thin belt appeared that encircled the grenade in the front of its body. This belt cleaned off carbon deposits that had accumulated during the previous shot. It was the appearance of the extra element that added an extra 3 mm to the SPG-9 caliber.
Conducting fire, monitoring its results and adjusting
103. When firing, the crew is obliged to observe its results. Observing the results of fire from the gunner and loader is difficult, especially with a tailwind, so the grenade launcher commander, located at some distance from the grenade launcher on the windward side, must carefully observe the results of fire and adjust it.
The results of the fire are monitored along the route and the grenade explosion.
104. If the target is not hit by the first shot, then in order to fire the next shot, it is necessary to make amendments (corrections) to the initial data corresponding to the amount of deviation of the grenade from the center of the target.
Fire adjustment can be made by moving the aiming point, choosing a new sight setting, marking the gap, or by combining the first two methods.
105. When adjusting fire in the lateral direction, by moving the aiming point out, the deflection of the grenade in the target figures is determined and the selected initial aiming mark (aiming point) is moved out from the middle of the target by the amount of deviation in the direction opposite to the deflection of the grenade (Fig. 54).
Rice. 54. Adjusting fire by moving the aiming point out
If conditions allow the gunner to observe the results of the fire, then to introduce corrections in the lateral direction by selecting a new lateral aiming mark, it is necessary to restore the aiming of the grenade launcher after the shot, note at which division of the lateral correction scale the grenade exploded, and aim with this new lateral mark for the next shot (Fig. 55)
Rice. 55. Adjusting fire by marking a grenade explosion
a - mark on the grenade explosion; b - guidance after marking a grenade explosion
106. If the grenade deviates slightly from the target in range, the fire is adjusted by moving the aiming point out in height. After receiving an undershoot, move the aiming point in height up by 0.5 figures (aim at the top edge of the target), when receiving an overshoot - down by 0.5 figures (aim at the bottom edge of the target).
If you receive large deviations of the grenade from the target in range, it is necessary to determine the magnitude of the deviation in meters and, accordingly, select a new sight.
107. If a grenade is deflected from the target in the lateral direction and range, then the fire is adjusted in range and lateral direction simultaneously.
108. When adjusting fire while shooting at a moving target, it is necessary to take into account the approaching (moving away) of the target during the time spent preparing for the next shot.
Performance characteristics of LNG-9
The SPG-9 grenade launcher has the following performance characteristics:
- This weapon was developed by designers Silin and Alekseev;
- Entered service in 1963;
- Caliber SPG-9 – 73 mm;
- The weight of the production copy was slightly reduced to 47.6 kg;
- The length of the weapon was 2110 mm, of which the barrel accounted for 670 mm;
- The grenade launcher is capable of firing at a rate of 6 rounds per minute;
- The maximum engagement range is 1,300 meters, with a recommended target range of 800 meters;
- Since the weight of the grenade launcher was significant, it was served by a combat crew of four people.
The PGO-9 sight and the PNG-9 night sight were used as sighting devices. Outside the barrel were located all the elements that ensured the launch of the grenade.
Determining distances
87. Distances to targets can be determined (measured) by eye, using the rangefinder scale of an optical sight and using the “thousandth” formula.
Knowing the ranges to local objects (landmarks) makes it easier to determine distances to targets. Therefore, if the situation allows, distances to local objects (landmarks) should be determined in a more accurate way.
88. Visual determination of distances
is carried out over sections of terrain that are well imprinted in visual memory, according to the degree of visibility and apparent size of targets (objects), as well as by combining both methods.
When determining distances along terrain segments
it is necessary to mentally set aside some familiar distance that has been deposited in visual memory, for example a segment of 200 m, from oneself to the object (target). It should be taken into account that as the distance increases, the apparent value of the segment gradually decreases.
When determining distances based on the degree of visibility and apparent size of targets
(objects), it is necessary to compare the visible size of the target with the visible sizes of this target imprinted in memory at certain distances.
If a target is detected near a local object (landmark), the distance to which is known, then when determining the distance to the target it is necessary to take into account its distance from the local object (landmark).
At night, distances to illuminated targets are determined in the same way as during the day. To determine distances to targets based on flashes and the sounds of shots, it is necessary to multiply the time interval in seconds from the moment the flash appears to the moment the sound is perceived by 340 (340 m/s the speed of sound propagation in the air).
89. To determine distances on the rangefinder scale of the “KUM” grid
optical sight, it is necessary to point the scale at the target so that the target is located between the solid horizontal and inclined dotted lines (Fig. 47, a).
The scale bar located above the target indicates the distance to the target, which has a height of 2.7 m. If the target has a height of 2.7 m, then it is necessary to subtract (add) an amendment equal to the product from the distance determined on the scale number of tenths of a meter difference in target height by the constant number 4 and by the scale number located above the target
.
Example. Determine the distance to a heavy enemy tank with a height of 3.2 m if the top of the tank touches the dotted line of the rangefinder scale, indicated by the number 10.
Solution. The difference in target height is 0.5 m, or 5 tenths of a meter (3.2-2.7 m); the correction is 200 m (5 tenths of a meter x4x10); the distance to the target is 1200 m (1000 + 200 m).
Rice. 47. Examples of determining distance on a rangefinder scale:
a - on the rangefinder scale of the “KUM” grid (distance to target 800 m); b - according to the rangefinder scale of the "OSK" grid (distance to target 900 m)
90. Rangefinder reticle scale "OSK"
The optical aisle is designed for a target height of 1.7 m. To determine the distance, it is necessary to point the scale at the target so that the target is located between the solid horizontal and inclined dotted lines (Fig. 47, b). The scale bar located above the target indicates the distance to the target.
The distance to the target on the rangefinder scale of the sight reticle can only be determined when the target's height is completely visible. If the target is not completely visible in height, then determining distances on this scale can lead to gross errors (the ranges will be overestimated).
91. To determine distances using the thousandths formula
it is necessary to know the width or height of the target (object) and measure the angular value of the target (object), and then calculate the distance using the formula.
Example. An enemy tank with a width of 3.5 m is visible at an angle of 0-05. Determine the distance to the tank.
Solution. We determine it using the formula “thousandth”.
How to place and prepare for a shot
In order to bring the SPG-9 grenade launcher into firing position, you need to place it on a special tripod, which is included in the kit. Thanks to the tripod, you can aim the grenade launcher at targets. When a special modification of the SPG-9 appeared, intended for paratroopers, the tripod received wheels.
To transport a grenade launcher, it must be disassembled into parts, after which the grenade launcher can be easily moved by its own crew. According to the instructions, the assembled grenade launcher can only be moved over short distances. Most often, such movements occur within a trench or to change positions in a certain area.
Target selection
85. Fire from a grenade launcher with cumulative grenades hits armored targets: tanks, self-propelled artillery mounts, ATGMs on armored personnel carriers, etc. Fragmentation grenades hit enemy personnel and fire weapons located openly or in light shelters.
In some cases, in the absence of armored targets, cumulative grenades can hit enemy personnel and fire weapons located in wood-earth, brick and reinforced concrete structures.
Targets on the battlefield can be stationary (appearing) or moving.
86. The target is selected and indicated to the crew in battle, as a rule, by the grenade launcher commander. Therefore, the calculation must listen carefully and accurately follow all commands.
From several simultaneously detected targets, you need to select the most important one that threatens the unit with which the crew interacts. When goals of equal importance appear, choose the closest one.
How to shoot the SPG-9
In order to start firing from the SPG-9 grenade launcher, you need to carry out the following manipulations:
- Open the barrel by turning the bolt handle;
- Next, you should send the charge to the breech of the barrel;
- After this you need to close the shutter. When carrying out this manipulation, the electrical start circuit will close;
- Next, the gunner points the weapon at the target and fires a shot.
In order to fire a second shot, you need to open the barrel again by turning the bolt. When the shutter is opened, residual elements from the previous shot are automatically extracted. Next you need to insert a new grenade.
Purpose of spare parts, tools and accessories (SPTA)
30. Each grenade launcher is supplied with:
spare parts
— two contacts of the contact device;
tool
- hammer, file, punch, drift, wrench, screwdriver;
belonging
- a bathtub with a cover for cleaning and lubricating the barrel bore, a brush with a cover for cleaning and lubricating the expansion chamber, a brush, covers for the muzzle and breech parts of the barrel, a diopter - a probe for aligning sighting devices and checking the serviceability of the grenade launcher's electrical circuit.
For carrying by the crew of shots, there are two bags, each of which contains three grenades and three pencil cases with powder charges (Fig. 34).
There is a handle to carry the bag in your hands, and two shoulder straps with shoulder pads to carry the bag behind your back. The shoulder strap carabiners attach to the half-rings attached to the bottom of the bag.
For the calculation of the grenade launcher, artillery helmets are worn, which are worn during firing, and for the loader, in addition, gloves are used to protect the hands from burns in the event of removing the diaphragm with the tube from the barrel during incomplete extraction.
Rice. 34. Shot Carrying Bag:
a — view in a closed position; b - view in open position; 1 — shoulder strap; 2 - handle; 3 — shoulder pad;
4 - cumulative (fragmentation) grenade; 5 — pencil case with a powder charge
An individual set of spare parts for the grenade launcher is placed in a bag, which is stored in the grenade launcher box along with the banner and brush.
In addition to the above, for every six grenade launchers a group set of spare parts is provided, designed for complete disassembly of grenade launchers, carrying out maintenance, medium repairs and replenishment of an individual set of spare parts.
Various modifications of LNG-9
Based on the basic modification of the SPG-9, several modifications of grenade launchers were created, which differ in various additions and additional or modified devices:
- SPG-9D. This modification was created specifically for use in airborne units. Since the landing party must act quickly, the tripod was equipped with wheels;
- SPG-9N. This modification was practically no different from the base model. The letter “N” in the name indicates that instead of an optical sight, the grenade launcher was equipped with a PGN-9 night sight;
- The SPG-9DN is an airborne modification of the grenade launcher, equipped with a night sight;
- SPG-9m is a modernized version of the SPG-9 grenade launcher. It has a sighting device of the new PGOK-9 model. A front telescopic leg appeared on the machine;
- SPG-9MD – landing version of the updated model;
- SPG-9MN – version with night sight;
- SPG-9DMN - airborne night updated version.
All modifications have proven themselves in military conflicts of the second half of the 20th century (after 1965).
Capping and painting pomegranates
28. Grenades are placed 6 pieces in wooden boxes and secured with inserts. To ensure long-term storage, the grenades are additionally sealed in sealed film bags. In the same box, 6 powder charges in pencil cases are placed in special compartments.
29. Grenades in combat equipment are painted in a protective color, the head of these grenades is filled with explosives. For grenades with inert ammunition, the head part is painted black (for the PG-9V, the jet engine is in a protective color), in addition, these grenades have the additional marking “Inert”. The head of grenades in inert ammunition is filled with inert mass.
Inert grenades are intended for use for educational and practical purposes.
Unit personnel must be firmly aware of the differences in the coloring of live and inert grenades.
Ammunition for LNG-9
When the SPG-9 was put into service, the list of available ammunition consisted of only one item - PG-9V. Currently, the list of ammunition has been supplemented with the following shots:
- PG-9VS. This projectile is a modernized modification of the basic ammunition. Can penetrate 100mm more armor;
- OG-9V. Heavy high-explosive fragmentation shot. Does not have a jet engine.
All grenades except OG-9V have a launch speed of 700 m/s. Og-9V has a speed of 315 m/s.
Although the LNG-9 grenade launcher was put into service back in 1963, it has not yet lost its relevance. An interesting fact is that it was on the basis of the SPG-9 that the “Grom” gun was created, which was installed on the BMP-1 and BMD-1.
Combat use
The history of the use of weapons goes back more than half a century; even the Russian army still uses LNG. In the second half of the last century, the grenade launcher was used in most local conflicts, both by regular troops and partisan detachments. In the troops of the Soviet Union, the system received the nickname “Boot”, derived from the abbreviation itself.
In addition to purchasing from the USSR and Russia, independent production was mastered in the following countries:
- Bulgaria;
- China;
- Egypt;
- Pakistan.
The most widely used version of the weapon was the Soviet/Russian one, as well as the Bulgarian one. LNG-9 of various modifications participated in operations in the Middle East, especially in Syria.
Notes
- Sergey Kudryavtsev.
“Designer of ammunition and grenade launcher systems E.I. Dubrovin" // "For engineering personnel": newspaper. - St. Petersburg, 2022. - No. 04. - P. 02-03. - The Military Balance 2022, p.212, p.218
- The Military Balance 2022, p.208
- The Military Balance 2022, p.209
- “ It was discovered that the Ukrainian Armed Forces had infantry pro-Titan forces, which were disintegrated and adopted for the formation of a larger army even within hours of the USSR.
For example, the mounted anti-tank grenade launcher SPG-9M “Spear” was adopted at the time of the formation of the Radyansky army in 1963. “Effective “barrels” against enemy armor are not less, but about the particularities of the stagnation of anti-tank armor in the current minds of the ATO // newspaper “People's Army” dated 23rd 2016 - The Military Balance 2022. - P. 488.
- Use of LNG-9 by ISIS militants
- Kato Dağı'nda çok sayıda mühimat ele geçirildi
- Bulgaria donated Soviet weapons to Afghanistan (inaccessible link). RBC, August 21, 2002.
- History of Arsenal and brief description of its activities Archived copy dated March 7, 2014 on the Wayback Machine (English). Arsenal J.S.Co.