The new generation regional long-haul aircraft Sukhoi Superjet 100 (SSJ 100) is the main and so far the only serial product of modern Russian civil aircraft construction.
) began delivering production SSJ 100 aircraft to airlines in the spring of 2011. As of April 2019, 138 SSJ 100s were in service. In total, the aircraft performed more than 370 thousand commercial flights lasting over 570 thousand flight hours. In 2022, the 200th SSJ 100 may take off into the sky.
The Russian national carrier Aeroflot is the largest operator of the Superjet 100. Over the past two years, the airline's SSJ 100 fleet has grown from 30 to 49 aircraft. Moreover, the main carrier of the Russian Federation signed a preliminary agreement for the supply of hundreds more aircraft produced by GSS.
:: GSS
Aeroflot. Own equipment
As a key operator of the Superjet 100, Aeroflot receives these aircraft in a specification made according to its special requirements - in the so-called full version.
The full configuration differs from the standard one in the updated flight management system (FMS) and the presence of a weather radar with a function for detecting wind shear. In addition, according to Aeroflot’s requirements, the number of CCTV cameras was increased, separate lighting control was made in the economy and business class cabins, and another flight attendant workplace was added, equipped on the wall of the optional galley in the rear service area.
As for passenger comfort, the extended configuration includes personal airflow for each passenger. The aircraft is equipped with three toilets equipped with changing tables. Each block of three passenger seats has an additional oxygen mask. The number of pantry-kitchen modules has increased from three to four; two stoves have been added to one of them. There is additional space for attaching a baby cradle.
:: Aeroflot
Regional long-haul aircraft of a new generation
The certified base model RRJ-95B and extended range variant RRJ-95LR-100 is a new generation regional long haul aircraft designed and produced by Russia. The SSJ 100 is designed to carry passengers on both short-haul and medium-haul routes.
A high-tech commercial aircraft, created using new technologies in the field of aerodynamics, propulsion and aircraft systems, provides a decent level of operational efficiency, the manufacturer believes.
The Superjet 100 was first introduced to the public in September 2007. Its first flight took place in May 2008. Its first commercial flight was in the spring of 2011.
The SSJ 100 is the first Russian aircraft, the starting point for the creation of which was the product requirements formed by air carriers. It is completely digitally designed.
The implementation of a project of this caliber required a comprehensive program of technical re-equipment of serial aircraft factories in Komsomolsk-on-Amur and Novosibirsk. Its production uses technologies that have not previously been used in the domestic civil aircraft industry - such as, for example, jigless assembly, automatic joining of airframe components, automatic riveting and a number of others.
All models of the Superjet 100 family are equipped with two SaM146 turbofan engines produced by PowerJet, a joint venture between the French Snecma and the Russian NPO Saturn. This theater was specifically designed for the SSJ 100 aircraft.
The SSJ 100 uses modern technologies developed by well-known companies - leaders in the aviation industry.
Improved takeoff and landing characteristics, high cruising speed, and operation in a wide range of climatic conditions make it possible to plan the route network quite flexibly, increasing the number of destinations, as well as use the aircraft on both regional and a number of main routes.
The SSJ 100's maximum cruising speed of 0.81M (871 km/h) and cruising altitude of 12,200 m allow it to fly at the same flight levels as the most common types of short-haul aircraft, thereby optimizing not only fuel costs, but also time costs for the flight.
The extended-range version of the aircraft (long range / LR) differs from the basic one (basic/B) in its flight range reaching 4320 km, increased take-off weight to 49.45 tons and a reinforced wing for the increased take-off weight in order to ensure flight at a given range. The SSJ 100LR is equipped with a SaM146 engine with a 5% increase in take-off thrust. Operation of the SSJ 100 is possible in a wide range of climatic conditions at temperatures from –54 to +45°C - this is the central part of Russia and its Far North, Southeast Asia, and the high mountain regions of Mexico.
What projects are in development
The designers expect to implement the following projects:
- The Sukhoi Superjet 100SV is planned for production in 2022, and it will be able to make its first flight in 2022. The capacity is going to be increased to 125 passengers.
- Sportjet by Sukhoi will be designed to transport athletes.
- Suhkoi Superjet 75, designed for 75 passengers, will be operated on routes up to 2 thousand km long. The developers hope that it will allow companies to reach a new business segment.
- Sukhoi Superjet 100R will include an increased share of Russian components.
As for the results of the already created models, in 2022 it turned out that their flight hours on Russian airlines decreased. But for foreign companies the indicator increased, and there were no complaints about profits. This is due to the fact that Russian carriers are having problems with the supply of components. To correct the situation, a set of measures was introduced to increase flying hours: it is too early to assess its effectiveness.
"Sukhoi civil aircraft"
The SSJ 100 was designed and manufactured by Russia. The company was founded in 2000 to create new types of civil aviation equipment; is located in Moscow, and its branch is represented in Komsomolsk-on-Amur, where the final assembly of aircraft takes place.
SuperJet International (SJI) is located in Venice (Italy) and provides international support to the SSJ 100 program. In coordination with SCAC, SJI is involved in marketing and sales, supply and customization for Western markets, EASA certification, flight test support, flight and maintenance training, and after-sales services worldwide.
:: Safran
Main advantages of Superjet 100
The modern Superjet 100 provides airlines and passengers with new opportunities, including:
- rolling out new routes to the level of demand at which it would be advisable to put narrow-body aircraft of higher capacity on them;
- replacement, if necessary, of more spacious aircraft (such as A320, B-737) operating with a low passenger load during periods of seasonal decline in air travel. SSJ 100 replaces larger capacity aircraft both for a long period in the low season and during the day;
- the airline, if it has larger aircraft in its fleet, can replace them without compromising passenger comfort;
- The SSJ 100 is an active addition to the hub concept, which allows the airline to optimize its costs: transporting passengers on a smaller aircraft to the airline’s base airport.
This plane is designed for passengers. In terms of comfort, the SSJ 100 cabin is comparable to the cabins of larger medium-haul aircraft:
- the height of the cabin in the central aisle is 212 cm;
- comfortable wide seats, comparable to those usually installed on medium- and even long-haul aircraft;
- wide central aisle;
- increased living space for each passenger: large seat pitch in the basic configuration of the SSJ 100 aircraft (81.28 cm) allows even tall passengers to feel comfortable on board;
- large windows for natural light and better visibility;
- spacious and capacious luggage racks 2 m long, without internal partitions for convenient placement of hand luggage;
- LED lighting system with warm spectrum lamps;
- spacious toilets, the toilet in the rear service area is adapted for passengers with reduced mobility; in addition, it is equipped with a wide changing table;
- Passengers can board the SSJ 100 either via a regular stairway or via a telescopic staircase.
:: Safran
Passenger cabin
The passenger compartment of the SSZH-100 is located in the middle part of the fuselage, between the cockpit and the tail compartment. Just like the cockpit, it is hermetically sealed from the environment. It maintains a comfortable temperature, pressure and humidity for humans.
Main parameters of the salon:
- Width - 3.2 m;
- Height – 2.1m
- Passenger seat width: 46.5 cm
To enter the cabin there are two doors on the left side of the aircraft, located in the front and rear of the cabin. Two service doors are used for loading and unloading kitchen products. There are two of them on the plane, one is located immediately behind the cockpit, and the second is in front of the tail compartment. There, next to the kitchens, there are two toilet rooms.
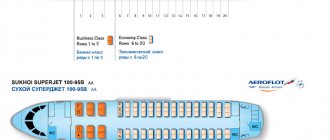
Standard Superjet Economy Class passenger cabin
The interior layout of the Superjet 100 provides for three layout options.
The first is basic, on an airplane with the same amenities for all passengers. In this version, the cabin accommodates 98 seats. The distance between the seats is 81.2 cm, the width of the passage between the seats is 51 cm. In a more compact version of the basic layout, the distance between the seats is reduced to 73.6 cm and part of the interior furnishings is dismantled, which allows the number of passengers to be increased to 108 people.
In the business class version of the aircraft, the total number of passengers is 94 people. The business class cabin accommodates 12 passengers in luxury seats. For their convenience, the distance between the seats increases to 91.4 cm. The remaining 85 economy class passengers are seated in seats with a distance of 81.2 cm. The business class cabin is separated from the economy class cabin by a special curtain.
The seats in the aircraft cabin are installed in nineteen rows. Each row has five passenger seats. There are double seats on the left side, and triple seats on the starboard side. Each passenger seat is equipped with individual airflow and bright lighting. Quite spacious luggage compartments are installed above the seats.
The aircraft cabin has pleasant diffused LED lighting. The passenger windows are elongated from top to bottom, oval in shape, and are one of the largest in aircraft of this class. The cabin also has a wardrobe for passengers, where they can leave their outerwear. During the flight, to pass the time, passengers can watch their favorite movie or listen to their favorite music. For this purpose, the aircraft cabin is equipped with special audio and video entertainment centers. A mandatory attribute of the SSZH-100 passenger cabin is water supply and waste disposal systems.
In terms of comfort, the SSZH-100 interior is the best in its class.
Under the floor of the passenger compartment there are two fairly spacious luggage compartments, volume:
- front compartment - 10.04 cu. m;
- tail compartment - 11.7 cubic meters. m.
Temperature and pressure are monitored in luggage compartments. According to reviews from airport workers, the luggage compartments of the SSZH-100 are quite spacious and convenient for stowing luggage.
Powerplant SaM146
The SaM146 engine is produced by PowerJet, a joint venture between Snecma (Safran Group, France) and NPO Saturn (Russia) with equal shares, and provides economical operation of the Superjet 100 family of aircraft.
The concept of an optimized aerodynamic layout formed the basis for the development of the modern SaM146 turbofan engine. In the regional jet market, specially designed engines are in demand that are designed for frequent flights and are designed to quickly turn around at the destination airport without downtime.
The new SaM146 modular engine combines the proven track record of the world's most successful commercial engine, the CFM56, with state-of-the-art technology and a 20% reduction in component count to significantly reduce operating and maintenance costs and achieve superior performance and reliability.
:: GSS
Materiel
The cold part of a turbofan engine is the fan, compressor and low-pressure turbine. Almost everything is made of metal, so the vast territory of Saturn is home to dozens of metalworking shops of all kinds. Bolts and nuts are turned cold the old fashioned way, but the most high-tech part of the engine - the turbine blade - is cast in a very cunning way.
Wax castings are pressed into metal molds, finished by hand and handed over to robots. More precisely, into one robotic arm, which takes the wax mold, with calculated movements, dips it into the white suspension and turns it a couple of times, allowing the liquid to drain. Even the most experienced master is not capable of such precision, but the robot does everything the same way every time as the previous one, and the suspension always lays on the wax in a layer of the required thickness.
Ceramic molds for casting turbine blades.
As the suspension hardens, it turns into a heat-resistant ceramic form, and then the wax is melted out. A specially grown dendrite crystal is placed at one end of the workpiece - and now the mold, sealed at one end, is ready for casting.
The blades of a gas turbine engine operate under dynamic load, with constant pressure drops, so the requirements for strength are enormous: a palm-sized part must withstand up to 20 tons (for example, you can put a loaded truck on it) and must not melt in the hot gas-air mixture included in the low pressure turbine. It would seem that for this you need to select the most heat-resistant alloy... But this is not necessary: thanks to the specific design of the SaM146 low-pressure turbine blades, they can operate in an environment with a temperature 200-250 degrees higher than the melting point of the alloy from which they are cast. We'll explain how a little later.
Certification
January 2011 Superjet 100 received a type certificate from the Aviation Register (AR) of the Interstate Aviation Committee (IAC), which confirmed the compliance of the aircraft's standard design with aviation regulations and its safety, which allowed the aircraft to begin commercial operation in the fleet of launch customers.
February 2012 The European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) issued a type certificate for the Superjet 100. This certificate confirms that the SSJ 100 has demonstrated compliance with current EASA airworthiness and environmental requirements. The EASA certificate allows European airlines and airlines of countries where EASA standards have been adopted as a standard to receive and operate SSJ 100 aircraft. The Superjet 100 became the first Russian passenger airliner certified in accordance with EASA aviation regulations CS-25 (transport category aircraft).
May 2012. An addition to the type certificate was received from AR IAC to expand the operating conditions of the aircraft at high outside temperatures - up to +45°C.
November 2012 The Superjet 100 received an addition to its type certificate, which expanded its operating conditions for flights in northern latitudes. The tests confirmed the proper functioning of the aircraft's avionics systems, primarily the inertial navigation system and GPS and GLONASS satellite navigation systems, in conditions of high northern latitudes (up to 78° N) and low temperatures (down to –54° C).
June 2013 The first export certificate to Europe for the Superjet 100 was issued.
:: Aeroflot
August 2013 AR IAC issued an addition to the type certificate for the RRJ-95LR-100 - Superjet 100 extended range aircraft.
In March 2014, the IAC AR issued an addition to the type certificate for the Superjet 100 aircraft, which confirmed the ability to perform flights on this type of aircraft under conditions of precise area navigation using the RNAV 1 and P-RNAV systems.
June 2014 AR IAC confirmed the possibility of performing automatic landing on the Superjet 100 aircraft according to ICAO CAT IIIa category and operating the aircraft on a narrow runway, 30 m wide.
October 2014 received an addition to the type certificate, which confirmed the ability of the Superjet 100 aircraft to take off at a reduced engine thrust level. The operating mode, in which the engines operate at a reduced speed and temperature of the gases in the turbine, reduces the load on the engine and extends its service life, which in turn minimizes aircraft maintenance costs.
November 2014 For the first time in Russia, AR IAC issued an addition to the type certificate for the Superjet 100 aircraft, which allows the use of the VNAV vertical navigation function at all stages of flight. This feature significantly reduces crew workload and ensures compliance with all applicable restrictions.
November 2014 AR IAC confirmed the possibility of installing a luxury passenger cabin interior (SSJ 100 VIP) on the Superjet 100 aircraft.
December 2015 The European Aviation Safety Agency certified VNAV vertical navigation and P-RNAV area navigation functions.
December 2016 EASA issued a certificate for the long range version of the Superjet 100 (SSJ 100LR). The certificate will allow us to present to foreign customers the Superjet 100 with a flight range increased by 50% compared to the basic version (SSJ 100 Basic).
February 2022 EASA certified a new aircraft model - the B100, which differs from the basic installation of the SaM146 family engine with increased take-off thrust, which is also used on the SSJ 100 aircraft with an extended flight range. The main characteristics of the SSJ 100 B100, a certified model RRJ-95B-100, are: flight range of 3048 km with a calculated payload in standard atmosphere conditions, maximum take-off weight of 45880 kg, maximum take-off engine thrust of 8055 kgf and reduced by 10% compared to the base take-off distance version.
Design features. How are competitive advantages achieved?
The aerodynamics of the SSZH-100 airliner were obtained by repeatedly simulating the conditions of the oncoming air flow in the aerodynamic laboratories of TsAGI. At the same time, computer modeling of the behavior of various aircraft structural elements under aerodynamic loads was carried out. As a result, extremely perfect aerodynamic contours of the aircraft body were obtained.
When creating the machine, all the designers' aspirations were aimed at meeting user requirements. This was reflected both in the interior and arrangement of the cockpit, and in the amenities provided for passengers in the passenger compartment. The designers also did not forget about the requirements of the airlines that will operate this aircraft. They will be pleasantly surprised by the aircraft's efficiency, ease of operation, flight capabilities, and wide range of its use.
One of the important advantages of the aircraft is its ability to fly in automatic mode. This is also a fuel saving mode.
The increased safety of the airliner is due to the protection algorithm built into the control system against accidental piloting errors. For the first time in the Russian aircraft industry, this aircraft was equipped with a system to prevent the aircraft from touching the runway, which made it possible to get rid of massive shock absorbers and increase the payload.
The modular design of the equipment used in the aircraft made it possible to reduce the number of on-board units by 15%. The airliner's designers abandoned the use of a traditional steering wheel to control the aircraft and, for the first time in Russian practice, used a joystick-type handle.
The main advantages of the SSZH-100 aircraft over its analogues are:
- increased comfort;
- the latest construction, design and assembly technologies;
- high fuel efficiency;
- environmental friendliness;
- high degree of unification;
- a wide range of services and a flexible after-sales support system.
The Sukhoi company provides comprehensive after-sales support, including operational maintenance, training of flight personnel, provision of technical documentation, elimination of identified defects, etc.
Aviation personnel training for the Superjet 100
Two training centers were created: in Zhukovsky (Moscow region, Russia) and in Venice (Italy).
Aviation personnel training centers provide a full cycle of training for flight and engineering personnel of SSJ 100 aircraft customers and have a set of the most modern training tools and training equipment, which includes a comprehensive flight simulator FFS (Full Flight Simulator), CBT training computer systems, FPTD procedural simulator , FTD LV fixed flight simulator, CEET emergency rescue training simulator.
:: Aeroflot
Development of the SSJ 100
The manufacturer is currently implementing a program to improve the Superjet 100 aircraft in order to expand its sales markets, increase operator satisfaction and maintain a high level of its competitiveness.
The updated version of the SSJ 100 is being implemented as part of the program for import substitution of SSJ 100 components. Russian developers and manufacturers have already been invited to participate in this project. The result of the work will be the updating of a number of aircraft systems. The number of foreign-made components will be reduced several times.
The goals set when developing a new version of the SSJ 100 aircraft are to reduce its cost, operating costs, and increase flexibility in the after-sales service of aircraft systems due to the availability of alternative suppliers, which will also help expand the aircraft's sales markets.
In December 2022, the first test flight of the Superjet 100 aircraft with saber wingtips was carried out.
Based on the results of computational and experimental work, it was revealed that the installation of winglets allows one to simultaneously improve takeoff and landing performance and reduce fuel consumption by at least 3%. The expected improvement in takeoff and landing performance will be appreciated by airlines operating the SSJ 100 at the regional network of airfields, as well as in hot climates and high mountains.
The introduction of wingtips, which is part of this aircraft improvement program, will also provide airlines with savings of up to 5 million rubles per year per SSJ 100.
:: GSS
Let's count
The conversation about specialization comes up for the second time during a visit to the AL-100 supercomputer - already the third machine in the history of the enterprise. When asked whether Saturn developers write their own programs for calculating parts, the engineers smile: “Our task is to make engines, and we trust mathematics to mathematicians.”
The room-sized 2,808-core behemoth can store 14.5 TB of data and perform up to 114.5 trillion operations per second. Something is constantly being considered here: new engines are constantly being designed at the plant, and work is also going on with the old ones - the designers are looking for ways to make parts lighter, stronger or cheaper to manufacture.
Now a supercomputer and finite element analysis systems (at Saturn they use the American ANSYS) make it possible to simulate the processes occurring in the engine so accurately that strict aviation officials count the results of virtual tests as full-scale results. To understand how far progress has come, we can recall how gas turbine engines were calculated in the pre-digital era. The calculation engineer shares his memories of his father, who worked on the Tu-104 engine project:
There were about twenty calculators in the room, divided into two groups, who performed the same calculations, checking at control points. If the results differed, everything was recalculated again...
Everything is simulated on the computer - from the smallest part to the entire engine. Mathematical models of turbulent gas flows of different temperatures and heat exchange between the environment and engine parts are created. Instead of breaking dozens of experimental engines that cost hundreds of millions in any currency, the behavior of the engine when a blade is damaged or a bird hits a turbine is calculated virtually. And only when the optimal design of all structural elements has been found, full-scale tests are carried out to compare their results with the calculated data. “When they were designing the Tu-144 engine, they made 48 test models, which, after testing, of course, were no good - and this despite that later no more than 50 engines left the factory,” the engineer recalls. Now virtual models save you from such costs.
But every new engine leaving the assembly shop is still sent for testing. In the test shop, each new car is suspended from a pylon - a complex system that simulates an aircraft suspension.
Aircraft operation
Today, Superjet 100 is operated by Russian airlines and government agencies: Aeroflot, Gazprom Avia, Yakutia, Yamal, IrAero, Azimuth, Severstal, Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia, Ministry of Emergency Situations, SLO Rossiya , RusJet - as well as in foreign Interjet (Mexico) and the Royal Thai Air Force.
:: Aeroflot
ATO special project: Domestic aircraft in the service of Aeroflot
It's not beer that kills people...
To a person far from aviation, it may seem that we are talking about some fatal flaw in the design of the aircraft, due to which the lives of people and crew are endangered.
However, for similar reasons, in February 1996, a Boeing 757 crashed near Puerto Plata, and in June 2009, an A 330 crashed into the Atlantic Ocean. The first disaster claimed 189 lives, the second - 228, but in neither case was the question of the reliability of the airliners raised. The key factor was the human factor, and not the incorrect speed readings.
All cases with the SSJ 100 in question ended successfully, which once again confirms what was said above: a malfunction in the operation of air pressure receivers in itself does not kill anyone. It only requires pilots to have a cool head and professional actions in a difficult, but by no means catastrophic, situation.
Question answer
Passenger aircraft Sukhoi Superjet 100. Infographics