Modern warfare is impossible without minefields. An anti-personnel mine is a reliable means of incapacitating enemy soldiers; in addition, they can be used to create areas of terrain that are completely impassable for infantry. People first started talking about mines in the 14th-15th centuries, when they were stone-throwing landmines.
When a charge of black powder exploded, it threw a cloud of small rubble and fragments towards the enemy, which caused quite a lot of damage to the dense formation. We won’t talk about mines used in fortification; that’s a completely different story. Modern mines do not require much time to install, but their principle remains the same, defeating the advancing enemy with a cloud of fragments.
Classification of anti-personnel mines
Mines can be classified by installation method, by action, and by explosion method. But the most complete division will be their division according to the method of destruction:
- high-explosive, damage due to the energy of the explosion of explosives (explosives), as an example we can cite Soviet mines of the PMD-6, PMN type;
- high-explosive, uninstallable, PFM-1 “Lepestok”, sowing the territory with them is carried out from aircraft cassettes (aircraft) or shells;
- fragmentation action, the famous POMZ;
- directed fragmentation action, MON and American "Claymore";
- surprise mines, fragmentation or high-explosive, are placed in a separate category due to the variety of target sensors, the most famous variants are MS-1 and MS-4;
- fragmentation action, with an expelling charge, for example OZM-72;
- bullet, an analogue of high-explosive, but instead of explosives, a live cartridge inserted into the tube is used, the defeat is carried out by a bullet, PMP.
A mine explosion occurs from impact on the target sensor. In high-explosive mines this is usually a sliding or elastic cover; for fragmentation mines it can be a remote control fuse or a tripwire net made of thin metal wires.
When the tripwire breaks, the mine fuse is triggered.
It should be noted that this is true for Soviet and Russian mines, although anti-personnel mines of the USA and Germany have a similar design, however, they differ in the fuse design and action.
Separately, it is worth mentioning the curious weapon of our sworn friends Pursuit-Deterrent Munition M86, which appeared in the US Army after America signed the Ottawa Mine Non-Proliferation Agreement on December 3, 1997.
In fact, the M86 is an anti-personnel fragmentation mine, but it is called a deterrent munition and is not technically a mine. This is how the United States bypassed the ban on anti-personnel mines.
Again, by the way, despite the signing of the convention, dozens of states currently remain undestroyed at least 150 thousand units of this ammunition.
Moreover, a number of countries have developed various kinds of “deterrent ammunition” bypassing the provisions of the convention.
The Swedes did no better, simply renaming Truppmina 12B to Forsvarsladdning 22. Both the border is locked and the convention is in order. But the Ottawa Treaty nevertheless changed the direction of development of the mine industry.
Nowadays, mine ammunition is being developed taking into account the possibility of their destruction; unlike outdated ammunition, modern mines do not remain on combat duty for decades, but self-destruct after a certain period of time.
To be fair, it is worth noting that Russia has not signed this convention, and today it may well establish the production of obsolete and modern types of mines.
About explosives
You may be interested in: Hunting with a shorthaired pointer: description of the breed, education, training
With the help of engineered ammunition of this group, the military initiates charges in explosives and engineered mines. Corps of Engineers specialists have to deal with igniter caps, blasting caps, electric igniters, electric detonators, detonating and fire cords, incendiary tubes, fuses and mine fuses.
Anti-personnel landmines
Mines of this type usually have a pressure fuse, which is triggered when a certain mass is applied to it. This is done to prevent the fuses from being triggered by the weight of wild animals.
These are mines such as the Soviet PMN or the Italian TS50. They are triggered by pressure on the elastic cover. After this, the fuse is triggered and the explosive contained in the housing explodes.
Which entails the loss of a limb if a TS50 explodes or the death of a person if a PMN explodes. Later high-explosive mines are aimed specifically at incapacitating a person. It is believed that the wounding of one person requires delivery to a medical station, therefore delaying the enemy and weakening his forces by 1-2 people additionally.
Mines of this type can only be destroyed by detonation; removing anti-personnel landmines, which are quite often set to “non-removable”, is a very dangerous task. So, for example, the possibility of not removing PMN-type mines can be duplicated by installing a surprise MS-type mine next to or under it.
Characteristics of PMN, TS50 and M14
| Options | PMN (USSR-Russia) | TS50 (Italy) | M14 (USA) |
| Weight, g | 550 | 200 | 130 |
| Explosive mass, g | 200 | 52 | 30 |
| Overall dimensions, mm | 53x110 | 90x48 | 40x56 |
| Target sensor, mm | 100 | 48 | 38 |
PMD-6
Separately, it is worth noting the Soviet anti-personnel mine PMD-6, its peculiarity is the simplicity of the device. The mine is a wooden box with a hinged top lid; a TNT block weighing 200 grams is installed in it. into which an MUV type fuse with a T-shaped pin is screwed in.
When the mass impacts the mine cover, the side wall squeezes out the T-shaped pin and the fuse is triggered. Ammunition of this type can be mass-produced in any carpentry workshop; to complete them, only fuses and standard-type TNT blocks are enough. The same mine, but with a sealed casing, was called MKF.
PMP
Based on the principle of economy, the PMP mine was created, which is a 7.62 mm TT pistol cartridge, in a barrel, the cartridge itself is spring-loaded, with pressure on the target sensor, the hollow upper part of the cylinder cuts off the pin, the cartridge, under the action of a spring, falls down onto the tip of the striker, after which results in a shot being fired at the enemy’s foot. If necessary, the cartridge can be replaced with any other one.
The peculiarity of a wound from such a mine is that not only the bullet acts on the foot, but also powder gases and dirty fragments of shoes and soil enter the wound channel.
This subsequently leads to gangrene. This reliably incapacitates the enemy, and also requires several people to deliver him to the dressing station.
PFM-1
The PFM-1 high-explosive anti-foot mine is spread by being dropped from aircraft or dispersed from MLRS cluster shells. PFM is known as "Petal".
Liquid explosives are used as explosives; the power of the explosion is enough to concuss a limb even without a wound.
Fragmentation anti-personnel mines: device, methods of use
Fragmentation mines are activated both through direct action on the network of tripwires around the installed ammunition, and remotely using a radio fuse. Mines vary in their effect.
POMZ-2
The simplest version of fragmentation mines is POMZ-2 and POMZ-2M. This is a cast iron jacket with a ready-made notch, inside which a standard 75 g drill bit is inserted. In the lower part of the body there is a hole for a peg, on top there is a glass for placing an MUV tension fuse with a P-shaped pin.
The principle of operation of the fuse is similar to the action of the UZRGM fuse, but without a moderator. The fuse fires instantly. Currently, POMZ is not produced, but, like PMD, production of casings of this type of ammunition can be launched in a matter of days at any foundry.
MES
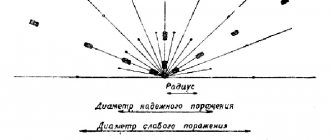
The USSR anti-personnel mines of the MON series are the most famous in the modern world; in fact, they are an analogue of the American Claymore, but with Soviet additions. The body is curved to direct the sheaf of fragments in the desired direction; the body has simplified sighting devices and whisker legs for its installation. Depending on the range of damage there are:
- MON-50, destruction range 50 meters (actually 25-30);
- MON-90, a greatly enlarged and inconvenient version of the MON-50;
- MON-100, a directional mine designed to kill at a range of up to 100 meters. But given its mass and size (the basin is 23 centimeters in diameter, weight 5 kg), it is not the miners’ favorite item;
- MON-200, a monster in the mine kingdom, circumference 45 cm, weight 25 kg. Probably no one except the designers of this masterpiece can imagine how to disguise such a basin during installation.
Defeat due to fragments of the hull and ready-made submunitions located in the hull. Two types of striking elements are used - ball-like and roller-like fragments.
Balls – 540, rollers 485 on MON-50. It is installed with the curved part towards the enemy. Mines of this series can be installed using a radio fuse, or use conventional pull-action fuses.
OZM-72 or simply “Witch”
Fragmentation barrage mine, this is what this abbreviation stands for. When detonated, the ready-made submunitions make a noise similar to a whistle, hence the name. This ammunition was developed on the basis of German springmines or simply “frogs”.
When the fuse is triggered, the expelling charge is detonated first, the body flies up to a height of 1.5 meters above the ground, and only after that the main charge is triggered. A hail of shrapnel is falling all around; the OZM body contains 2,400 ready-made submunitions. OZM-4 is an earlier version of OZM-72, currently not produced.
Characteristics of OZM-72 and OZM-4
| Characteristics | OZM-72 | OZM-4 |
| frame | Steel, ready-made submunitions | Cast iron |
| Weight, kg | 5 | 5,4 |
| Explosive mass, g | 660 | 170 |
| Target sensor | Tensioner, all range | Tensioner, all range |
| Damage radius | 25 | 12 |
Enlarged versions OZM-160 and OZM-152 are also known, which are used in a controlled version. The warheads of these ammunition are 152 mm OFZ and 160 mm mortar mines.
Manual installation of this type of anti-personnel mines is extremely time-consuming, since placing them requires digging a well of decent depth.
About the mine fuse
It is a special device equipped with all fuse elements. The only exception is the detonator cap, or fuse.
With its help, explosive detonation is initiated. Mine fuses can be mechanical, electrical and electromechanical. According to experts, in order to ensure safety during the transportation of engineering ammunition and their operation, these devices are equipped with special elements. In order for the mine to explode, it will require an impact, for example, you just need to press on it. Such mines are considered contact mines. This category also includes engineering ammunition with tension, unloading and breaking action. The group of non-contact mines is represented by magnetic, seismic, acoustic, etc.
Anti-personnel mines of the Russian army
POM-2
Cluster mounted anti-personnel fragmentation mine, also used for manual deployment. The device is similar to the OZM; it also has an expelling charge. Staging is carried out from cassettes, stabilization in flight is carried out due to perforated stabilizer flaps.
Manual installation only POM-2R. The weight of the mine is 1.5 kg, the mass of explosives is 140 grams, it can be damaged by fragments of a metal body and two types of ready-made submunitions. Similar to MON-50.
FOB, replacement for “The Witch”
To replace the OZM-72, a new anti-personnel fragmentation munition was developed, an analogue of the American M86, which seems to be not a mine.
The steel of the body was replaced with plastic, the damaging elements were in the form of flat rings with teeth stacked in the body around the explosive charge.
The expelling charge was transferred, this ensured a vertical position of the hull when rising above the ground. The lifting height was significantly reduced to 0.4-0.6 meters. The weight of the FOB is 2.3 kg, the mass of the explosive is 510 g.
Surprise mines type MS and ML
Mines designed specifically for catching sappers and curious people. All types of fuses are used. Contact, non-contact, vibration and electric induction triggered by the mine detector.
Mine ML-7
Used to install sapper ammunition in the “non-removable” position. The weight is only 100 grams, with a charge weight of 40. The type of target sensor is unloading, in other words, to trigger it, it is enough to remove a load weighing at least 300 grams from the sensor.
Using surprises is quite simple; under the body of an OZM or TM-57 it is enough to put a cocked ML-7, after the long-range cocking time has expired, the fuse is cocked and when the load is removed from the target sensor there will be an explosion, from which the mine being removed will most likely detonate .
MS-5, cigarette case mine
One of the rare booby traps that imitates a specific object. Weight 660 g, explosive weight – 110 g. Unloading type target sensor, reaction to opening a cigarette case or opening its lid.
ML-2 or MS-6M, sapper trap
Mines of this type have a fuse that reacts to the operation of the electromagnetic inductor of the metal detector, no further than 30 cm. The second version is MS-6Shch, with a contact target sensor. Weight 4.4 kg, with electric induction fuse 8.4 kg. Explosive mass – 1.2 kg.
It is used for organizing mine protection of strongholds and for mining anti-tank minefields that are of particular importance. There is only one option to combat this type of mines. Do not pick up anything from the ground, even a box of matches or an empty magazine.
When clearing mines, assume that all mines, including OZM, are set to “non-removable” by default. Tank minefields can be opened by trawls or by using mine clearance systems, although the latter no longer depends on us.