Brake system ZIL 5301 bull, principle of operation - Special equipment
09.08.2017
ZIL-5301 “Bychok” was the first “swallow” of the Likhachev plant, which had not previously produced cars of this class. The new car went into production in 1995 and was produced until 2014.
During this time, the ZIL 5301 device was learned not only by specialists, but also by ordinary owners of these cars.
The repair scheme for this car is quite simple, so it is not difficult to do it in a garage.
The ZIL “Bychok” mini-truck is an excellent assistant in various situations
The light-duty truck brand 5301 of the Likhachev Plant, known as the ZIL “Bychok”, was put into mass production in 1995.
During its existence, the truck received many modifications and firmly took its place in the Russian truck market.
The main advantage of the model, which received the nickname “Bull” on the initiative of Yu. Luzhkov, is its accessibility.
content .. 11 12 17 ..ZIL-5301 Bull. BRAKE SYSTEM
ZIL-5301 vehicles are equipped with a combined pneumatic-hydraulic brake drive with two independent hydraulic circuits according to the “L” scheme and two independent pneumatic circuits.
Attention! With this brake drive scheme, there is no direct mechanical connection between the brake pedal and the hydraulic brake master cylinder. Therefore, the car’s braking system only works if there is air pressure in the pneumatic drive above 0.5 MPa
regardless of the driver's foot pressure on the brake pedal.
Mechanisms of service and parking brake systems
Braking mechanisms of the car: front wheels - disc with floating double-cylinder calipers, double-pad;
rear wheels - drum type with two internal pads.
When operating a vehicle, it is necessary to constantly monitor the wear of the brake pads of the front wheel disc brakes. If the total thickness of at least one brake pad and lining is 8 mm or less, then all pads on the front axle of the vehicle must be replaced.
One of the signs of excessive brake lining wear is a significant decrease in the brake fluid level in the master cylinder reservoirs without noticeable signs of brake fluid leakage.
In this case, you need to inspect and replace the pads. To replace the pads, do the following.
1. Raise the car until the wheels hang out. Turn the steering wheel all the way to the left when replacing the left brake pads and to the right when replacing the right brake pads.
2. Unscrew the wheel nuts and remove the wheel.
3. Remove pin 8 (Fig. 27) from retaining pin 7 and pull out the pin.
4. Remove the protective caps and place rubber hoses on the heads of the bleeding valves. The free ends of the hoses must be lowered into a transparent container.
5. Unscrew the valves one turn. Push the pistons into the cylinders of the bracket body until they stop, avoiding damage to the piston collars holding the dust covers. This will cause some brake fluid to leak out of the valves. Close the valves.
6. Check the ease of movement of the bracket on pins 13 and 17. The bracket should move freely by hand.
7. Holding the upper guide pin 13 from turning with a special (thin) wrench, unscrew the bolt 15 securing it to the bracket body. In this case, it is necessary to take measures so as not to damage the cover 14 of the pin. Rotate (raise) the bracket body 11 relative to the second pin 17 until it stops in the caliper and remove the pads.
Fig.27. Front brake caliper. 1 — caliper; 2 - bypass bolt; 3 - piston; 4 - sealing ring; 5 — psrshnya cover; 6 — brake pads; 7 — pad finger; 8 — pin pin; 9 — bleeder valve cap; 10 — bleeding valve; 11 — right bracket body; 12 — dirt cap of the breather; 13 — guide pin; 18 — pin cover; 15 — pin fastening bolt; 16 — auxiliary pin bushing; 17 — auxiliary pin; 18 - nut; 19 — ring
8. Check the condition of the piston protective covers. It is not permitted to operate the vehicle with damaged covers.
9. Clean the end surfaces of the pad seats from dirt. Insert 1 new pads into the caliper and install the caliper housing 11 in place, taking care not to damage the rubber protective covers of the pistons.
10. Tighten bolt 15 securing the guide pin to the bracket body. Place the 7 pads in place and pin the retaining pin.
11. Press the brake pedal several times, after filling the pneumatic drive with compressed air.
12. Add liquid to the tanks to the required level.
When replacing brake pads, make sure that the markings on the linings are the same for all wheels.
Caution should be exercised after replacing the pads as braking performance may vary before and after replacing the pads.
Maintenance of the rear wheel brake mechanisms involves adjusting the gaps between the pads and drums, as well as periodically inspecting, cleaning them and checking the fasteners.
During inspection, it is necessary to check the condition of the friction linings of the rear wheel brakes. If the distance from the surface of the linings to the heads of the rivets is less than 0.5 mm, the brake linings must be replaced. When lubricating parts, it is necessary to protect the brake pad linings from getting oil on them, since the friction properties of oiled linings cannot be achieved? completely restored by cleaning and washing. In case of extreme wear or failure of one of the linings of the left or right brake mechanism, it is necessary to replace all linings of both brake mechanisms.
To adjust, do the following:
— turn off the parking brake;
— raise the rear wheels;
— remove the spring plugs from the rear brake shields;
— through the hole in the brake shield, use a special blade 1 (Fig. 28) (or a wide screwdriver) to rotate the sprocket of the adjusting screw 2 (on the left brake from bottom to top; on the right - in the opposite direction), spreading the pads until the wheel brakes (does not turn by hand) .
Then rotate the sprocket in the opposite direction to ensure free rotation of the wheel. When the sprocket rotates, characteristic clicks are heard
-insert spring plugs.
Rice. 28. Adjusting the gap between the shoes and the drum: 1 - special blade; 2 - adjusting screw
content .. 11 12 17 ..
Bull brakes, rear and front | Zyl bull
ZIL “bull” received this name due to its resemblance to a similar animal, which is how the people nicknamed it. The people who have been using this car since the end of the 20th century and the beginning of the 21st century have never known grief. Although it depends on you, some people experience difficulties, even serious ones. It happens that the ZIL “bull” brake system also causes complaints. That's exactly what we'll talk about.
The ZIL “bull” brake system is a dual-circuit system. Each circuit is independent of each other. The first circuit includes the front right wheel and the rear left wheel, and the second circuit includes the front left wheel and the rear right wheel. The brakes are driven by a hydraulic system. But the brake booster is powered by pneumatics.
A spare brake is any circuit that has not failed. In more advanced models of the “bull” family, an anti-lock braking system (ABS) is installed on the brakes.
The handbrake is equipped with a mechanical drive, which is connected by a cable to the rear brakes. The front wheels are equipped with disc brakes, while the rear wheels are equipped with brake drums.
Also, a hydraulic pressure regulator is installed on the brake system of the ZIL “bull” car. With its help, when braking a car, the pressure of the brake fluid is distributed so that the rear wheels do not completely lock when the car is empty or not loaded to its full weight.
Well, so, what problems does the ZIL “bull” brake system cause for car enthusiasts?
Most argue that disc brakes fail after 15-20 thousand kilometers. And the discs themselves are crooked, which also reduces the service life of the front brakes and degrades the quality of braking. Another disadvantage some call is the inconvenient location of the barrel for the brake fluid of the rear wheels. It is located under the frame and is difficult to access.
As for the service life of the front brakes and their curvature, such problems were encountered in the first releases of the ZIL “bull”. In the “bulls”, which were produced a little later, such problems were not observed. And such problems can be corrected by boring the brake disc.
As for the location of the brake barrel, this is a design feature of the car, and there is no escape from it.
And finally, the last piece of advice: lubricate every 5 thousand km. run the caliper guide pin, and then you will not have any special problems with the bull brakes. A mixture of lithol and tada can be used as a lubricant.
Owner reviews about ZIL-5310 “Bychok”
valera163valera:
I took the “bull” a year ago, the car was built in 1997... I drove it for a year, I’m happy with the car. Of course, the car requires care, like any other. In order not to freeze in winter, I insulated the cabin. I agree about the brakes - they are weak, but if you try it yourself, the ZIL 5310 brakes will be normal. I missed the cuff on the steering bipod. I bought about 5 repair kits, of which only one turned out to be “high-quality”. Shock absorber pins often break; I haven’t found a quality one yet.
I only changed the high pressure pipe in the engine. no need to skimp on spare parts. so that the axles, axle shafts, and gearbox do not fly, there is no need to overload, this is not a five-ton truck. I travel 60-70 km. at one o'clock. I traveled to Moscow, Tula, Ulyanovsk, Ufa and a lot around Russia and it never let me down. if you drive 90-100 km. per hour, like some, you will have to constantly repair the car, this is a Russian truck, not a Ferrari.
Modifications
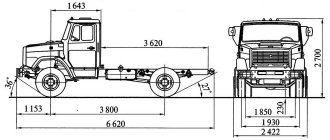
ZIL-5301AO
- Length in mm -3750 (cabin)
- Width in mm - 2254
- Height in mm -2365
- Weight in kg -3695
- Load capacity in kg -3000
- Wheelbase (total) -3650
- Ground clearance in mm -180
- Wheelbase front/rear -1690/1832
- Permissible load on the front/rear axle in kg - 1900/1995
- Power in hp -108
- Transmission - 5 speed mechanical
- Maximum speed in km/h - 95
- Fuel tank volume in l - 125
- Fuel consumption per 100 km in l -16
ZIL-5301BO
- Length in mm -6165
- Width in mm - 2254
- Height in mm -2365
- Weight in kg -3695
- Load capacity in kg -3750
- Wheelbase (total) -3000
- Ground clearance in mm -180
- Wheelbase front/rear -1690/1832
- Permissible load on the front/rear axle in kg - 2350/4900
- Power in hp -108
- Transmission - 5 speed mechanical
- Maximum speed in km/h - 95
- Fuel tank volume in l - 108
- Fuel consumption per 100 km in l -16
ZIL-5301G
- Length in mm -3750
- Width in mm - 2254
- Height in mm -2365
- Weight in kg -3695
- Load capacity in kg -3000
- Wheelbase (total) -3650
- Ground clearance in mm -180
- Wheelbase front/rear -1690/1832
- Permissible load on the front/rear axle in kg - 1900/1995
- Power in hp -108
- Transmission - 5 speed mechanical
- Maximum speed in km/h - 95
- Fuel tank volume in l - 125
- Fuel consumption per 100 km in l -16
ZIL-5301DO
- Length in mm -4385
- Width in mm - 2254
- Height in mm -2365
- Weight in kg -3820
- Load capacity in kg -3000
- Wheelbase (total) -3650
- Ground clearance in mm -180
- Wheelbase front/rear -1690/1832
- Permissible load on the front/rear axle in kg - 1900/1995
- Power in hp -108
- Transmission - 5 speed mechanical
- Maximum speed in km/h - 95
- Fuel tank volume in l - 125
- Fuel consumption per 100 km in l -16
ZIL-5301EO
- Length in mm -6765
- Width in mm - 2210
- Height in mm -2365
- Weight in kg -3050
- Load capacity in kg -3700
- Wheelbase (total) -3650
- Ground clearance in mm -180
- Wheelbase front/rear -1690/1832
- Permissible load on the front/rear axle in kg - 1900/1995
- Power in hp -108
- Transmission - 5 speed mechanical
- Maximum speed in km/h - 95
- Fuel tank volume in l - 125
- Fuel consumption per 100 km in l -16
ZIL-5301IO
- Length in mm -6885
- Width in mm - 2210
- Height in mm -2365/3036 (body)
- Weight in kg -4450
- Load capacity in kg -2300
- Wheelbase (total) -3650
- Ground clearance in mm -180
- Wheelbase front/rear -1690/1832
- Permissible load on the front/rear axle in kg - 1900/1995
- Power in hp -108
- Transmission - 5 speed mechanical
- Maximum speed in km/h - 95
- Fuel tank volume in l - 125
- Fuel consumption per 100 km in l -16
ZIL-5301TO
- Length in mm -2465(cabin)/7185(total length)
- Width in mm - 2319
- Height in mm -2885
- Weight in kg -4490
- Load capacity in kg -2300
- Wheelbase (total) -3650
- Ground clearance in mm -180
- Wheelbase front/rear -1690/1832
- Permissible load on the front/rear axle in kg - 1900/1995
- Power in hp -108
- Transmission - 5 speed mechanical
- Maximum speed in km/h - 95
- Fuel tank volume in l - 125
- Fuel consumption per 100 km in l -16
ZIL-5301YUO
- Length in mm -6765
- Width in mm - 2210
- Height in mm -2365
- Weight in kg -3150
- Load capacity in kg -3600
- Wheelbase (total) -3650
- Ground clearance in mm -180
- Wheelbase front/rear -1690/1832
- Permissible load on the front/rear axle in kg - 1900/1995
- Power in hp -108
- Transmission - 5 speed mechanical
- Maximum speed in km/h - 95
- Fuel tank volume in l - 125
- Fuel consumption per 100 km in l -16