"Dagestan" was launched in April 2011. Initially, the project was supposed to be completed in the fall of the same year, but acceptance tests had to be postponed to 2012. An unpleasant situation happened to the “Dagestan” during mooring tests near Novorossiysk. Due to a sudden storm, the ship was seriously damaged. However, repair and restoration work carried out in a very short time brought it back to life.
A little history of the creation of Project 11661 ships
Patrol ships (corvettes) and missile ships began to be developed in the early eighties. The development was carried out by the Zelenodolsk Design Bureau. The development of anti-submarine ships for coastal zones was carried out as a development of another project 1124M - a small anti-submarine ship, with "Livny" - an anti-submarine missile cruiser. Then they developed two versions of tactical and technical specifications, and a year later they proposed both versions of preliminary designs - an anti-submarine ship with an anti-submarine missile system in accordance with project 1124M and an anti-submarine ship with a displacement of up to two thousand tons with greater effectiveness.
In the same year, following changes in the Navy's claims to the project, the second project was assigned the number 11660 (and the export version - 11660E) and reclassified as a patrol ship. Research analytics in the projects showed that it was possible to deliver the “sentry vehicle” in an export version as early as 1990, while the Soviet version could be delivered no earlier than two years later.
Back in the mid-eighties, a requirement was put forward to equip patrol ships (SKR) with Uran anti-ship missile systems, the development of which was planned to begin in 1987. According to the December Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the USSR, in 1984 they decided to develop patrol ships according to project 11661. The preliminary designs of 11661 with CODOG propulsion systems were completed within a year.
By the beginning of 1986, the technical design of patrol ships under Project 11661 was completed. Later, a decision was made to unify the ships of Projects 11660 and 11661 by eighty-five percent, to begin work and rearrange them into a single structural platform with different weapons, differences in engines and equipment.
In September 1986, they began defending Project 11661. Following modifications for the Uranus and Zarya and other equipment, the concept of the “Basic platform for ship families” was formulated in the final version. In addition to testing hull shapes and the impact of antenna radomes to determine seaworthiness, a ship model was created and tested. The technical design of project 11661 was approved a year later.
Then they set the task of unifying projects 11660 and 11661. Using the “Basic Platform” concept, the Zelenodolsk Design Bureau began to produce working design documentation for project 11661, as well as develop technical projects for project 11660.
After all approvals and approvals, the ships were laid down. And already in 1993, the lead ship of Project 11661 was destined to be launched with the start of its completion. At the beginning of 1995, crew personnel appeared in Zelenodolsk to master the patrol ship. In the same year, a foreign customer (according to some sources, Indian) rejected several ships, and all work on their construction was stopped.
In addition, in the same year, construction of the ship was stopped with ninety-three percent of completion. The crew was disbanded, the ship was mothballed due to underfunding, and also due to the fact that the customer himself (the Russian Navy) had not completely decided on the various types of patrol ships.
However, in the periods 1995-1998, the Zelenodolsk Design Bureau developed export projects “Gepard” and “Gepard-3.9” for a foreign customer.
In 2001, the leadership of the Navy decided to complete the construction of one of the ships according to project 11661K, which was supposed to enter the Caspian flotilla with the name “Tatarstan”. The ship lost its anti-submarine defense weapons. The project was adjusted to meet all requirements. In April 2002, crew personnel arrived in Zelenodolsk to take possession of the new ship.
At the same time, the ship was heeled and it was found that the displacement deviated from the calculations by up to one ton. In July 2002, Tatarstan managed to successfully leave the Zelenodolsk Shipyard to go to the Makhachkala region to conduct test activities. The sea test passed with a five-point sea level. As a result, the ship was adopted by the Russian Navy, and the Caspian Flotilla acquired its flagship in August 2003.
Modifications[ | ]
- Project 11660
is the initial version of the coastal zone TFR. The lead ship was laid down and later dismantled[1]. - Project 11661
- development of Project 11660 with a modified composition of weapons and radio equipment.
The construction of the only ship has been stopped. Project 11661K
is an adjusted project for the Russian Navy based on Project 11661. Two ships were built. They differ (including from each other) in design, composition of weapons and radio equipment. Reclassified as missile ships[1]. - Project 11661E
is an export project of a patrol ship based on the late Project 11661K. They differ in design, armament and radio equipment in export version, and have the ability to accommodate a carrier-based helicopter of the Ka-27 type[1].
-[1]
is a planned modification, with a completely Russian-made power plant[1].
Samples of project 11661 – “Tatarstan” and “Dagestan”
The first-born in project 11661K was the ship, already known as Tatarstan, which entered service in August 2003. He was subsequently sent to the Caspian Flotilla as its flagship.
The second patrol ship was the Dagestan. Its delivery to the fleet was originally planned for the first half of 2012. However, it was postponed due to the severity of the damage received back in January of the same year during Black Sea mooring tests near the city of Novorossiysk. After restoration and repair activities, “Dagestan” managed to reach the Caspian Sea to participate in the second stage of state tests to fire missiles at coastal targets “Caliber-NK”.
Participation in firing at a distance of one hundred nautical miles was carried out safely. The patrol ship "Dagestan" also had to take part in the parade on the Day of the Russian Navy in the city of Astrakhan. In the fall of the same year, he was involved in the Caucasus-2012 maneuvers, in their naval part.
However, three years later the whole world learned about “Dagestan”. So, in October 2022, at night, a naval strike group in the Caspian Sea launched a massive strike using cruise missiles. The strike was carried out by the NK Caliber with a sea-based complex against ISIS infrastructure in Syria. The six ships included the Dagestan.
Project representatives[ | ]
In total, eight ships were laid down at the Zelenodolsk plant named after A. M. Gorky. The first and only one laid down under Project 11660 was not completed; after the collapse of the USSR, the ship was dismantled in 1993. Two ships were built for the Russian Navy according to the adjusted project 11661K: “Tatarstan” and “Dagestan”, now both ships are part of the Caspian flotilla of the Russian Navy. Construction of the ship (build number 953), laid down under project 11661, was stopped in 1995, the hull was mothballed. The ships are offered for export in anti-submarine configuration according to project 11661E. In particular, two contracts were concluded with the Vietnamese Navy (in 2006 and 2011) for 4 ships, which received the general designation “Cheetah 3.9”[19].
Table colors:
- Green - operating as part of the Russian Navy
- Yellow - operating as part of foreign navies
- Red - written off, scrapped or lost
Project 11660/11661[ | ]
| Name | b/n | Head No. | Pawned | Lowered | In service | Fleet | State | Notes |
| "Hawk" [1] | — | 901 | 1990 | — | — | — | Canceled | Dismantled on the slipway in 1993[1] |
| "Petrel" [20] | — | 953 | 1990 | — | — | — | Canceled | Dismantled on the slipway in 2012 |
Project 11661K[ | ]
| № | Name | b/n | Head No. | Pawned | Lowered | In service | Fleet | State | Notes |
| 1 | "Tatarstan" | 691 | 951 | 05.05.1990 | 01.07.1993 | 31.08.2003 | KFL | In service | Until 03.10.1996 - SKR-200[1][21] |
| 2 | "Dagestan" | 693 | 952 | 05.05.1990 | 01.04.2011 | 28.11.2012 | KFL | In service | Until 2002 - SKR-201[1]. |
Project 11661E[ | ]
| № | Name | b/n | Head No. | Pawned | Lowered | In service | Fleet | State | Notes |
| 3 | Đinh Tiên Hoàng | 011 | 954 | 10.07.2007 | 12.12.2009 | 05.03.2011 | Vietnam Navy | In service | |
| 4 | Lý Thái Tổ | 012 | 955 | 27.11.2007 | 16.03.2010 | 25.07.2011 | Vietnam Navy | In service | |
| 5 | Trần Hưng Đạo | 015 | 956 | 24.09.2013 | 27.04.2016[22] | 06.02.2018 | Vietnam Navy | In service | |
| 6 | Quang Trung | 016 | 957 | 24.09.2013 | 26.05.2016[23] | 06.02.2018 | Vietnam Navy | In service |
As of December 21, 2022, Russia has successfully delivered four Project 11661 Gepard-3.9 corvettes to Vietnam.
Cases
Ship hulls are ten waterproof compartments. The material for their execution was low-alloy steel, and for the superstructure blocks - a marine-resistant aluminum-magnesium alloy. In the event of flooding of two adjacent compartments, the ship will remain afloat, moving while maintaining combat effectiveness.
Protection against submarine attacks
In order not to leave the Project 11661 ship "Dagestan" defenseless in the face of a possible attack by enemy submarines, two torpedo tubes with a caliber of 533 mm are structurally provided. Note that the RBU-6000 model rocket launcher is mounted on export versions of ships of the same project. It is possible to land and deploy the Ka-27 anti-submarine helicopter. For its refueling, in particular, separate fuel tanks are provided on board. Subject to its transportation, the helicopter can be located in a special hangar (with folded blades).
However, all this is not very necessary when discussing the ship “Dagestan”. The Caspian flotilla (693 vessels are assigned to it), as well as maritime formations of other countries in this region, simply do not have a single submarine here. But here you need to remember that the ship can be sent to the Black Sea at any moment, and there is a hypothetical probability of an attack from under water.
Armament of the ships “Tatarstan” and “Dagestan”
Project 11661 ships have powerful missile, anti-aircraft missile and artillery weapons. The main weapon of Tatarstan is Uranus. This is a strike complex that has X-35 anti-ship cruise missiles with a firing range of up to one hundred and thirty kilometers.
"Dagestan" is armed with a universal missile system - "Caliber-NK", which can use several types of high-precision cruise missiles. They hit surface and coastal targets with a range of up to three hundred kilometers. Artillery weapons include the 76.2-mm AK-176M artillery complex and the 30-mm AK-630M automated twin artillery mount, which ensure the destruction of sea, ground and low-flying air targets.
Zelenodolsk "Buyans" are growing in the sea
Meanwhile, the Zelenodolsk "Buyans" made their way out to sea. At the solemn ceremony of launching the Ingushetia MRK, the head of the shipbuilding department of the Russian Navy, Vladimir Tryapichnikov, said that their serial construction will increase to 12 ships until 2023 inclusive. According to him, today the largest series of rocket ships has been deployed at the Zelenodolsk plant. “Although the ships have a small displacement, they have a balanced composition of weapons,” he noted.
Currently, the enterprise is building two more ships of the Grayvoron and Grad projects, and two more will be laid down this year. The average ship construction cycle can be shortened by establishing rhythmic supplies of diesel engines, whereas the last ship took almost 5 years to build (it was laid down in 2014 - editor's note).
Rear Admiral of the Fleet Vladimir Tryapichnikov expressed hope that by 2024 the fleet will receive a modernized version of the Zelenodolsk Buyans, but in what quantity it is too early to say. In turn, the chief designer of the ZPKB project, Yakov Kushnir, assured that the bureau is not standing still and is developing a modernized version with enhanced air defense and increased missile potential.
“The Zelenodolsk people surprised us once again,” Vladimir Tryapichnikov, head of the shipbuilding department of the Russian Navy Main Command, praised the shipbuilders at the ceremony. “The small missile ship Ingushetia was launched in Zelenodolsk, and the St. Andrew’s flag was raised in Novorossiysk on the patrol ship Dmitry Rogachev, which, by the way, was also made at the Zelenodolsk shipyard,” he said. The rear admiral does not rule out that in the near future, not two, but three events at once may occur on the same day - the laying down of one ship, the launching of another and the raising of the flag on a third.
The main hero of the occasion was the head of Ingushetia, Hero of Russia, General Yunus-Bek Yevkurov. Photo prav.tatarstan.ru
Frigates "Gepard-3.9" - ships of a new generation
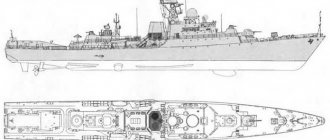
Frigates of the Gepard-3.9 type are ships of a new generation. They were developed by the Zelenodolsk Design Bureau with an already existing universal base platform. The prototype for "Gepards -3.9" was a rocket ship with the name "Tatarstan" from project 11611, and "Dagestan" is the second such domestic rocket ship built, a version adjusted at the insistence of the customer in project 11611K.
The construction of frigates for the Vietnamese customer is still being carried out according to the established requirements of the Navy of this state. With a total displacement of up to 2,100 tons, they have a length of 102 meters, a beam of just over 13 meters, and a draft of just over 5 meters. The ships have a combined diesel-gas turbine power plant (in accordance with the CODOG scheme).
With this power plant, ships reach speeds of up to 28 knots at full speed, and an economical ten-knot speed allows frigates to sail at ranges of up to 5,000 nautical miles. Autonomous navigation is twenty days. Well-placed residential and service premises, the presence of a system that air-conditions the air and maintains the necessary microclimate conditions, will contribute to good habitability conditions, which is simply vital in tropical climate conditions.
"Gepards-3.9" are multi-purpose ships designed for patrolling in territorial waters and exclusive economic zones, striking enemy surface targets, providing fire support for landing units, and providing air defense and anti-submarine defense during convoy operations.
As a result, their weapons are varied and well balanced. They include Urany-E anti-ship missile systems, universal 76.2 mm AK-176M artillery mounts, and a small-caliber anti-aircraft system. Control over the management of all these weapons is carried out by the Sigma-E combat information and control system, which meets all the highest standards of our time. The stern of the ship has a helipad. In addition, the helicopter also has a special shelter - a hangar, which will protect it from sea winds and waves.
Soon the Cheetahs will make the transition to the Baltic Sea, where they will be tested. The implementation of the contract for the construction of patrol ships for the Vietnamese customer may change the correlation of the ships produced by the enterprise. Thus, approximately forty percent will go to military products and sixty percent to civilian products (previously, 30% went to military products and 70% to civilian products).
If you have the basic Gepard platform, you can not limit yourself to building only multi-purpose ships, but you can also build ships with enhanced strike, anti-submarine and anti-aircraft missile weapons, with a wide variety of power plants and electronic equipment. Using the same ZPKB platform, a modification of ships for patrolling on the high seas has been developed, which have greater navigation autonomy. It is especially worth noting that the Gepard family is relatively inexpensive compared to similar ships built abroad.
Notes[ | ]
- ↑ 12345678910111213
Project 11660 patrol ships - “Tatarstan”, Project 11661 patrol ship (frigate) of the “Gepard” type (unspecified)
(inaccessible link). arms-expo.ru. Archived from the original on February 27, 2012. - The Military Balance 2022. page 196
- ↑ 1 2 Press service of the Southern Military District.
The missile ship "Dagestan" entered the Caspian Sea to carry out missile firing (Russian). Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation (July 23, 2012). Access date: July 24, 2012. Archived August 6, 2012. - Flying the flag of Vietnam
- Vietnam buys Russian stealth ships (unspecified)
. "Independent Military Review" (October 29, 2008). - Vietnam bought the second batch of Russian frigates "Gepard"
- Zelenodolsk plant will build two Gepard corvettes for Vietnam // March 7, 2013
- Press: The sixth “Rook” is on the slipway // May 7, 2013
- The Zelenodolsk plant will begin construction of the second pair of Cheetahs for Vietnam in September // July 5, 2013
- Press release on the occasion of the laying down of two Gepard-3.9 frigates for the Vietnamese Navy Archived copy dated November 1, 2013 on the Wayback Machine // September 19, 2013
- Ceremony of laying down two frigates "Gepard-3.9" for the Vietnamese Navy // September 24, 2013
- Two Cheetahs for the Vietnamese Navy will be assembled by Tatarstan shipbuilders // flot.com, September 24, 2013
- Ukraine disrupted the delivery of Russian Gepard-class patrol ships in the interests of Vietnam // 02.29.2016
- Vasily Isakov.
Incidents of Togliatti (emergency, road accident)
(unspecified)
. Social network “VKontakte” (August 17, 2016). Access date: August 19, 2016. - The Caspian flotilla will receive a modernized flagship “Tatarstan” (unspecified)
(inaccessible link). Access date: June 2, 2016. Archived August 12, 2016. - The Ministry of Defense published a video of a massive attack on Syria from the sea (unspecified)
(inaccessible link). Retrieved October 8, 2015. Archived October 8, 2015. - The flagship of the strike against ISIS was “Dagestan”
- Alexey Ugarov.
The Zelenodolsk plant completed the construction of the combat frigate "Gepard" for the Vietnamese Navy (Russian)
(undefined)
.
Army and defense industry
. TASS (April 25, 2016). Date accessed: March 8, 2022. - Domestic military equipment (after 1945) | Articles | Project 11661 Cheetah – GEPARD
- Project 1161K patrol ship "Tatarstan"
- Press center of the Zelenodolsk plant named after.
A.M. Gorky. The frigate "Gepard 3.9" was solemnly launched (Russian)
(undefined)
. OJSC Zelenodolsk Plant named after. A.M. Gorky" (April 27, 2016). Date accessed: March 8, 2022. - The second frigate Gepard-3.9 for the Vietnamese Navy was launched on Thursday
Purpose
"Gepards-5.3" are frigates designed for:
- Defeats air, surface and underwater enemies;
- Performing tasks during escort;
- Conducting service and combat activities on patrol;
- Fire support for landing units;
- Installation of minefields;
- Tasks for the protection and patrol of maritime state borders and economic zones;
- Supporting maritime operations;
- Displaying the flag in areas that represent state interests.
Frigates are capable of performing a wide range of tasks, both independently and as part of tactical groups.
Versatility
Rapid-fire cannons and an effective anti-aircraft fire system significantly increase the ship's combat survivability, allowing the creation of layered air defense. In fact, all these circumstances make it possible to call the Dagestan missile ship a universal vessel. In principle, the developers themselves say that it can safely be classified as a frigate.
The only thing that contradicts this is the lack of truly powerful anti-submarine weapons, but there are simply no submarines in the Caspian Sea. So the ship “Dagestan” (Caspian Flotilla, 693) fully corresponds to the place of use, being able to perform all the tasks assigned to it.
One of the main highlights of the vessel is the material of its superstructure (a special alloy of magnesium and aluminum). This alloy makes it possible to effectively disperse the radar signal, making the Project 11661 Dagestan missile ship less noticeable to potential enemy detection systems. In addition, there are active jamming systems. This entire complex effectively hides the true contours of the ship and protects it from damage by “smart” ammunition, including cruise missiles.
Finally, “Dagestan” was designed taking into account the maximum autonomy for ships of this class: it can sail for at least two weeks, covering about five thousand nautical miles
To ensure an acceptable level of comfort for the crew (and with such a small displacement this is important), active pitch dampers were introduced into the design. This allows people to withstand even moderate excitement well
The active air conditioning system makes operation possible even in tropical and subtropical climates.
Armament of the Cheetahs
Strike missile weapons
In order to eliminate surface targets, the ships have at their disposal the Uran-E anti-ship missile system and four deck-mounted inclined launchers of four missiles each, as well as a ship-based fire control system.
Artillery weapons
Complementing the artillery weapons of the frigate of the Gepard 5.1 project, Gepards 5.3 have two Palma missile and artillery systems and Sosna-R anti-aircraft guided missiles.
Anti-submarine and mine weapons
The anti-submarine and mine weapons of the Cheetahs are expressed as follows:
- Two twin-tube rotary torpedo tubes DTA-53 of 533 mm caliber;
- Rocket anti-submarine complex RPK-8E;
- A set of devices for controlling “Purga” - anti-submarine weapons.
During peacetime, the ships are equipped with search and rescue versions of the Ka-28 or Ka-31 helicopters, and during wartime, with anti-submarine variants.
Content
- 1 Development history
- 2 Construction 2.1 Export supplies
- 3.1 Hull and superstructure
- 5.1 Combat use
- 6.1 Project 11660/11661
Power plant
The main power plant is a diesel twin-shaft unit with adjustable pitch propellers, designed according to CODAD designs. The main power plant includes four diesel engines with a capacity of 4700 horsepower, but can have two diesel engines with a capacity of 6494 horsepower and two diesel engines with a capacity of 2425 3298 horsepower, two gearboxes and a local protection and control system.
How they looked for a replacement for the Germans
Recently launched, the eighth in the series of RTOs has incorporated all sorts of improvements to eliminate the shortcomings of the Chinese diesel engine. It must be said that it was precisely for this reason that the seventh RTO “Vyshny Volochek” was commissioned a year late. It became part of the Black Sea Fleet only in mid-2022. All this time, engineers in the field of engine building, together with Zelenodolsk shipbuilders, brought it to the technical characteristics required for military purposes.
According to sources, initially ten ships from the Buyanov-M series under construction were planned to be equipped with German MTU engines. The cessation of supplies of German engines hit the ZPKB project hard. Due to anti-Russian sanctions, only five RTOs, which were transferred to the fleet in 2014-2015, are equipped with them. The subsequent sixth and seventh turned out to be, one might say, experimental models of the Russian Navy, but there is no other choice. Russian mechanical engineering is not ready right now to produce its own diesel engines for shipbuilding. According to Realnoe Vremya’s interlocutors, Chinese diesel engines are supplied not by the Chinese themselves, but by a company operating in St. Petersburg.
However, the Zelenodolsk residents failed to get the warships of the Karakurt project out of the “shipbuilding diesel gate”. According to sources, the military has stood up to the death against Chinese engines, so rescheduling may happen more than once.
Vladimir Tryapichnikov said that serial construction will increase to 12 ships until 2023 inclusive. Photo tvzvezda.ru
Design
Hull and superstructure
The hull of the missile boat is smooth-deck, made of steel, has a slight sheer appearance and combined contours. It is divided into nine compartments by eight waterproof bulkheads. The boat's superstructures (with the exception of gas deflectors) are made of light alloys. The main mechanisms are located in two adjacent compartments in the aft part of the hull.
The main dimensions of the missile boat: hull length - 56.1 m, maximum width - 10.2 m. Hull draft - 2.5 m (2.3 m for Project 1241RE boats), propeller draft at full draft - 3.60 m , operational draft (for project 12421) - 2.55 m. The displacement of various modifications of the project varies slightly, but lies within 500 tons. The height of the side amidships is 5.31 m.
Power plant
Due to a delay in the development of a diesel-gas turbine power plant (EP), the first boats of project 1241.1, 1241RE, 12417 were equipped with a twin-shaft gas-gas turbine power unit (gas-turbogear unit) M-15, consisting of two afterburning turbines of the M-70 type with a capacity of 12 000 l. With. each, two propulsion turbines of the M-75 type with a capacity of 5000 hp. With. and four gearboxes. Having a number of advantages, including greater efficiency, the gas turbine power plant turned out to be inconvenient for controlling a boat at low speeds and, especially, when mooring. The main engines each drive their own fixed-pitch propeller. The maximum speed developed by boats with gas turbine propulsion is 42 knots, the economic speed is 13 knots. Cruising range: at full speed - 760 nautical miles, at economic speed - 1400 nautical miles.
The power plant of project 12411, 12418, 12421 missile boats is a two-shaft diesel-gas turbine. It consists of two M-70 afterburner turbines with a capacity of 12,000 hp each. With. and two sustaining diesel units M-510 with a capacity of 4,000 hp. With. (each of the diesel units consists of an M-504 diesel engine with a two-speed gearbox and a torque converter). The main engines each drive their own fixed-pitch propeller. Maximum speed is 41 knots, economic speed is 14 knots. Cruising range: 36-knot speed - 400 nautical miles, economic speed - 1600 nautical miles, 12-knot speed - 2400 nautical miles.
The boats of all projects are equipped with two DG-200 diesel generators with a power of 200 kW each and one DGR-75 diesel generator with a power of 100 kW.
General ship devices
Steering device
The steering gear group of Project 1241 boats includes two fixed-pitch propellers.
Mooring, anchoring and towing devices
The bow electro-hydraulic capstan is located on the forecastle for releasing and removing the anchor chain, as well as for mooring the bow of the ship. On the poop there is an electro-mechanical capstan for mooring the aft part. There are a total of four mooring views on the ship.
Rescue devices
Rescue devices on Project 1241 boats are represented by five life rafts, three of which are located on the roof of the first tier of the superstructure (in the aft part, between the AK-630 guns), and two - forward of the wheelhouse.
Seaworthiness
The boat's seaworthiness ensures safe navigation at low speeds in sea conditions up to 7-8.
Habitability
The crew of Project 12411-T boats is 41 people (on Project 12411-M boats it is reduced to 40), including 5 officers, including the commander. The commander is accommodated in a double cabin located on the first tier of the superstructure (under the wheelhouse) on the port side. The remaining officers are accommodated in two four-berth cabins side by side. Sailors live in three cockpits located under the main deck in the bow of the boat. The bow cockpit (for seven double berths) is located forward of the ammunition shaft of the AK-176 artillery mount, the other two cockpits, smaller in capacity than the first, are located at the rear and to the side of the ammunition shaft of the AK-176 artillery mount. The personnel mess, measuring 5x4 meters, is located on the main deck in the poop area.
The ship's autonomy in terms of provisions is 10 days. For the storage of provisions, storage rooms are equipped, located on the main deck in the area of the forecastle in the bow from the sailors' quarters; There is a fresh water tank under the AU AK-176 ammunition shaft.
Gifts from Evkurov
However, the main hero of the occasion was the head of Ingushetia, Hero of Russia, General Yunus-Bek Yevkurov. He arrived, as befits eastern guests, with the state song and dance ensemble. For the first time, the name of Ingushetia will appear in the name of military equipment. The transfer of the ship was timed to coincide with the 27th anniversary of the founding of the republic.
“It so happened that these days our region celebrates the 27th anniversary of its formation. And today this holiday is marked by an important event - for the first time in the history of the republic, a small rocket ship is launched, which will bear the name “Ingushetia”. You successfully completed the task in a short time, and today the most modern ship is leaving the slipway, which will solve the problems of protecting and defending our state. Our republic will take patronage over the ship,” Yevkurov promised.
It is interesting that during the ceremony he awarded the title “Honored Builder of Ingushetia” to the head of the Ak Bars holding, Ivan Egorov, and the general director of the Zelenodolsk plant, Alexander Karpov. The head of the shipbuilding corporation, Renat Mistakhov, was at the Novorossiysk naval base at that time and handed over the Project 22160 patrol ship Dmitry Rogachev.
The launching of the Ingushetia MRK turned out to be so important for the republic that it took place to the sounds of the anthem, which was specially recorded by the Honored Artist of Ingushetia Lema Nalgieva and Deputy Prime Minister of the Government of the Republic of Ingushetia Maret Gazdieva. In fact, she was named the godmother of the ship and walked down a special platform into the docking chamber and broke a bottle of champagne.
Louise Ignatieva
IndustryMechanical EngineeringMilitary Industrial Complex Tatarstan
Power point
The main engine is diesel, two-shaft, CODOG model. Diesel type – 61D, medium speed. The total engine power is 8000 hp. With. This power plant is responsible for standard driving modes. There are also two gas turbines with a total power of 29,000 hp. With
They can accelerate the ship to 28 knots, and are intended for use in combat mode, when the degree of maneuverability of the ship becomes vital. To provide all ship equipment with electricity, there are three diesel generators, each with a power of 600 kW