The Leopard 2 main battle tank was developed by Krauss Maffie in 1969-1979. The first experimental tank Leopard 2K (RT-1) was assembled in 1972. Since 1987, serial production of 380 tanks has been organized in Switzerland under license. During serial production from 1979 to the present, Krauss Maffie and MaK Maschinentnbau GmbH have produced more than 3,200 Leopard 2 tanks of all modifications.
Description of the design of the Leopard 2 tank
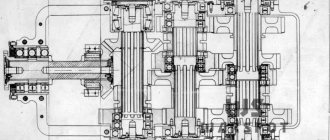
The main battle tank Leopard 2 has a classic layout with the control compartment located in the bow of the hull, the fighting compartment in the middle of the hull, and the engine-transmission compartment in the rear of the hull. The reserved volume of the tank is 19.4 m³. The tank's crew consists of four people: a driver - whose place is in the bow of the hull; tank commander, gunner and loader - whose places are in the turret.
The tank body is welded. Upper frontal plate General view of the Leopard 2K tank with a 105 mm cannon has a large angle of inclination. The sides of the hull are located vertically. The design of the armored hull uses combined armor and side screens made of reinforced rubber.
The driver's seat is located on the starboard side in the bow of the tank. For its landing and disembarkation, there is a hatch in the roof of the tower. Two monitoring devices are mounted in the hatch cover, the third one is to the left of the driver's hatch in the hull roof. There is an emergency hatch under the driver's seat. To control the tank, the driver uses a steering wheel, two pedals (the right one for fuel supply, the left one for brakes) and a gear switch block. A control and instrument panel is installed to the left in front of the driver. The volume of the control compartment is 2.3 m³.
To the left of the control compartment in the bow of the tank hull there is a stack of 120 mm rounds. In the bow of the hull, fuel tanks are located inside along the sides.
The tank's turret is of welded construction and is located in the center of the hull. The turret design uses combined armor. The internal surfaces of the tank's fighting compartment are covered with fabric mats (lining) made of high-strength aramid fiber. The turret houses a weapon system with a 120 mm smoothbore cannon. The main sight is installed on the right side of the turret. The roof of the turret is equipped with hatches for the tank commander, on the right, and the loader, on the left. Six viewing devices are installed along the perimeter of the tank commander's hatch. On the chase of the tank commander's hatch there is a bracket for attaching a turret for an anti-aircraft machine gun. An optical head of a PERI-R-17 panoramic sight is installed in front of the tank commander's hatch. A movable viewing device is installed in front of the loader's hatch. A turret for an anti-aircraft machine gun is installed on the loader's hatch chase. A fixed viewing device is installed in the roof of the turret, above the gunner's position.
The tank commander's workplace is located to the right of the gun behind the gunner's position. To the right, in front of the tank commander's seat, a PERI-R-17 sight is suspended from the turret roof. In front of the tank commander's seat there are controls for sights, smoke exhaust devices and built-in control of some systems. Behind the tank commander's seat, in the rear niche of the turret, there is a central control unit for the fire control system and two VHF radio stations.
The gunner's workplace is located to the right of the gun in the front of the turret. The gunner controls the weapon's aiming using his control panel. Behind the control panel there are flywheels for manual drives for weapon guidance. The main sight EMES-15 is installed above the control panel. To the left of the main one there is an auxiliary telescopic sight FERO-Z-18 (on the Leopard 2 tank there is a PZB-200 night sight monitor between the eyepieces of the main and auxiliary sights). To the right of the EMES-15 sight is the gunner's control panel. To the right of the gunner's control panel is the fire control system control panel.
The loader's workplace is located to the left of the gun. On the right side of the loader’s workplace is the gun breech, with a coaxial machine gun mounted on it and a box of cartridges for it. On the left side of the turret there is a mount for a submachine gun, a hatch for loading ammunition and a button for the mechanism for opening the armored door for storing shots on the left side of the rear niche of the turret. The loader's folding seat is attached under this button. The volume of the fighting compartment is 10.1 m³.
The main armament on the tank is a 120-mm Rh120 L/44 main gun from Rhtinmetall. The gun is installed in the center of the turret and has a manual lifting mechanism and a hydraulic lifting drive, providing declination and elevation angles from -9° to +20°. The gun barrel has a heat-insulating casing made of plastic and an ejector. The gun bolt is wedge, vertical. Loading is manual.
The tank's additional armament includes one 7.62 mm MG3A1 machine gun coaxial with a cannon and one 7.62 mm MG3 anti-aircraft machine gun.
The gun's ammunition load includes 42 120-mm rounds (15 are stored in the turret ammo rack, 27 in the stylized ammo rack in the tank hull) DM-12 MZ (with a cumulative multi-purpose projectile) DM13 KE (with an armor-piercing sub-caliber projectile). The ammunition load for the machine guns is 4,750 rounds.
The tank is equipped with an automated fire control system. It is based on the EMES 15 sighting system with a head mirror stabilized in two planes, developed by the American company Hughes (manufactured in Germany under license). The sight combines daylight optical and laser rangefinder channels. For shooting at night, a PZB 200 sight based on a low-level television camera is used.
The FERO-Z18 monocular optical sight is used as an auxiliary sight for the gunner. For the tank commander, a PERI-R17 panoramic sight with a head mirror stabilized in two planes is installed. The sight has only an optical daytime channel.
The tank is equipped with a two-plane electro-hydraulic stabilizer of tank weapons (the gun drive is hydromechanical, the turret drive is electromechanical) and a ballistic computer (located in the electronics compartment in the aft niche of the turret). The tank is equipped with a power unit in which a V-shaped 12-cylinder multi-fuel diesel engine with turbocharging MV873 Ka-501 is connected. 1500 hp and Renk HSWL354 automatic transmission. The power block is quick-detachable.
The chassis of the tank has, on one side, seven road wheels, a front idler wheel, a rear drive wheel and three support rollers. Individual torsion bar suspension with double-acting friction shock absorbers (on the first, second, third, sixth and seventh suspension units). Diehl 570F lantern tracks.
The tank is equipped with a quadruple automatic fire-fighting system, a collective protection system against weapons of mass destruction, and 16 smoke grenade launchers.
For external communications, the tank is equipped with two SEM 25/30 VHF radio stations. Underwater driving equipment is used to overcome water obstacles along the bottom.
Two contracts
The Leopard 2A7V MBT modernization project was first presented to the public in 2016. It proposes replacing some equipment and updating weapons, after which the tank receives new capabilities and increases its characteristics. Quite quickly, the new modification of the tank passed the necessary checks and was recommended for adoption.
In the spring of 2016, the German Ministry of Defense announced new plans for the development of a fleet of armored vehicles. To strengthen the Bundeswehr by 2022, it was proposed to increase the tank fleet from the available 225 to 329 units. The construction of new equipment was not envisaged, but it was necessary to carry out repairs and modernization of existing MBTs, incl. according to the newest project "A7V".
In May 2022, KMW and Rheinmetall received an order to modernize the first batch of Leopard 2 tanks. By 2023, 104 armored vehicles of various modifications need to be repaired and updated. For completing these works, contractors will receive 760 million euros. According to the contract, 20 Leopard 2A7, 16 Leopard 2A6 and 68 Leopard 2A4 tanks are subject to modernization.
Completion of the 2022 contract will improve the tank fleet not only qualitatively, but also quantitatively. It is curious that out of hundreds of tanks being converted, only 20 Leopard 2A7s previously belonged to Germany. Armored vehicles of the “2A4” version were purchased from Sweden, and the newer “2A6” from the Netherlands. Thus, the contract will increase the existing fleet of armored vehicles by 84 “used” units.
In March 2022, a new order appeared for the repair and modernization of armored vehicles. For its implementation, KMW and Rheinmetall will receive 300 million euros. The contract provides for the conversion of 101 Leopard 2A6 and Leopard 2A6M2 MBTs. These works should be completed by 2026.
Modifications of the tank “Leopard 2”
“Leopard 2FK” is a project of the “Leopard 2” (Flugkorper - rocket) tank, equipped with an American 152-mm XM 150E5 gun-launcher with a Shillelagh anti-aircraft gun. Due to loss of flexibility of use and a sharp reduction in transportable ammunition, the project was closed in 1970. An experimental tank was not produced.
“Leopard 2K” (Kanone - cannon) - a series of 16 experimental tanks (17 turrets), on which various weapons options were tested in 1972-1974 (the first 10 turrets were equipped with 105 mm smoothbore guns, the rest - with 120 mm), suspension , transmissions, fire control systems. The tank was equipped with an auxiliary power unit OM 363 with a G30E20-51G generator.
Read: German Siemens-Schuckert Eindecker fighter
“Leopard 2AV” (Austere Version - strict version) - 2 experimental tanks (3 turrets), manufactured in 1975 for comparative tests with the XM-1 tank in the USA (held in 1976) and development of mass production technology. Turret No. 19 was first equipped with a 105 mm L7A3 rifled gun, then it was equipped with a 120 mm Rh120 smoothbore gun. Instead of an auxiliary sieve unit, 8 batteries were installed on the tank. The design basically corresponded to the production tank “Leopard 2”
“Leopard 2AGT” - in 1977, at the insistence of the United States. On the chassis of the Leopard 2AV tank, they tested the AVCO-Lycoming AGT-1500 gas turbine engine and the Allisson X1100-3B transmission from the American XM-1 tank.
“Leopard 2” (“Leopard 2A0”) is the first serial modification of the tank, produced from 1979 to 1982. Due to the unavailability of the thermal imaging sight on the tank, the PZB 200 night sighting system was used.
“Leopard 2A1” – 750 tanks produced from March 1982 to November 1984, equipped with an EMES 15 sight with a Zeiss thermal imaging channel.
“Leopard 2A2” - vehicles of the first series, brought to the level of the “Leopard 2A1” tank in 1983-1985.
“Leopard 2A3” – 300 tanks produced from December 1984 to December 1985. The tanks were equipped with SEM 80/90 digital radios. Due to the danger of the tank's seal being compromised, a hatch for loading ammunition was welded on the left side of the turret.
“Leopard 2A4” – 695 tanks built in 1985-1992. Main differences:
– replacement of spaced armor with a combined one: – exclusion from the turret design of the hatch for loading ammunition; – installation of a digital ballistic computer; – the control system includes an interface for connecting the AGDUS preparation and control system and a built-in sight alignment system; – installation of new software from Deugra.
“Leopard 2A5” - 350 tanks that underwent modernization in 1995-1998. Main differences:
– installation of armor modules on the frontal part of the turret; – the installation of the EMES 15 sight has been changed, its optical head has been moved to the roof of the turret; – the FERO-Z18 auxiliary sight has been moved to the top of the gun, its lens is now located on the roof of the turret above the gun mantlet; – a large periscopic observation device is installed in front of the tank commander’s hatch, and the optical head of the commander’s panoramic sight is moved behind the tank commander’s hatch; – the driver’s hatch received a new cover: – the driver’s workplace is equipped with a rear view video camera, its monitor is installed to the left of the driver’s seat: – electromechanical drives for weapon guidance E-WNA were used, in the freed-up space in the aft niche of the turret, mounts were installed for storage of an anti-aircraft machine gun: – the armor doors of the EMES 15 sight lens received an electromechanical drive: – the manual drive for aiming weapons was eliminated, the spare drive was also made electromechanical: – a new panoramic commander’s sight PERI-R17A2 was installed with the integration of a thermal imaging channel into it. The eyepiece part of the sight has been moved to the left side of the tank commander’s workplace: – the tank is equipped with a GPS navigation system. – reinforced torsion bars were installed on the front suspension units.
“Leopard 2 Mixed Lot” (mixed lot tanks) – 350 tanks, modernized by installing turrets from “Leopard 2A4” on the hulls of the first tank releases, and brought to the level of the “Leopard 2A5” modification.
“Leopard 2A6” - was created based on the design of the “Leopard 2A5” tank with the installation of a new 12-mm Rh 120 L/55 cannon. In the early 2000s, all Leopard 2A6 tanks were modernized by welding on the bottom, in the driver’s area, additional armor plate and replacing the driver’s seat with a suspension system called the “dynamically safe seat.” The tanks received the designation “Leopard 2A6M”. In the early 2000s, based on the design of the Leopard 2A6 modification, a tank was developed to be offered for export. Main differences:
– new design of the frontal armored part of the hull and protection of the turret roof from “shock core” type ammunition: – installation of an air conditioner located in a basket at the rear of the turret: – a new positioning system with displays for the tank commander and driver was installed: – an auxiliary system was installed on the right at the stern power point.
“Leopard 2PSO” (Peace Support Operation - peacekeeping operations) - in 2005, based on the “Leopard 2A5”, a tank was developed to participate in peacekeeping operations in urban areas. Distinctive features:
– installation of new armored modules on the hull and turret: – installation of a bulldozer blade: – upon request, a “Euro-Power-Pack” power unit and an auxiliary power unit can be mounted in the MTO: – presence of a package of crew situational awareness sensors: – air conditioning system installed: – digital unit's battle control systems: - on the turret behind the loader's hatch there is a combat module armed with an American 12.7-mm M2QCB machine gun and equipped with a television sight with a thermal imaging channel. The module is remotely controlled by the charger from his workplace.
“Leopard 2A4 Evolution” - developed in 2005 by the German company Ingenieurburo Deisenpoith based on the production tank “Leopards 2A4″. The Evolution concept provides increased tank protection at minimal cost. Distinctive features:
– passive protection of the hull and turret has been increased: – a combined active protection system AMAP-ADS has been installed. ”
Leopard 2 Revolution” – developed by Rheinmetall Defense in 2010. Main differences:
– equipped with the ROSY system (Rapid Obscuring Sysnev – a system for quickly setting up smoke screens): – a modern fire control system and electric machine drives for weapon guidance can be installed upon request: – the tank commander is equipped with a new stabilized optical-electronic sighting system SEOSS; – a situational awareness system for the crew is installed: – a combat module is installed on the roof of the turret, equipped with a 12.7 mm machine gun and a 40 mm automatic grenade launcher, controlled by the tank commander from his workplace: – an air conditioning system and an auxiliary power unit are installed.
“Leopard 2A7” (“Leopard 2A7+”) – created on the basis of the “Leopard 2A6” tank in 2009. Distinctive features:
– the use of additional armored modules made of steel: – the driver is equipped with two video cameras (one located on the front armor plate of the hull, the second on the rear of the tank), equipped with thermal imaging channels: – an auxiliary power unit is located on the starboard side in the rear of the hull; – behind the loader’s hatch there is a combat module FLW 200, with various sets of weapons, equipped with a multi-channel sighting system. The module can be controlled both from the tank commander’s position and from the loader’s position: – a 120-mm programmable high-explosive fragmentation projectile has been introduced into the tank’s ammunition load: – a new high-performance air conditioning system has been installed; – replaced with new final drives, track tracks, and reinforced torsion bars.
German plans
Two existing contracts with a total value of more than 1 billion euros provide for the modernization of 205 Leopard MBTs of 2 different modifications. The equipment for their implementation will come from German armored units, as well as from third countries.
The purchase of tanks abroad and the return of equipment from storage will allow the Bundeswehr to fulfill existing plans and increase the tank fleet to 329 units by 2022. At the same time, the army will have to simultaneously operate MBTs of various modifications, incl. old enough. The process of modernizing equipment under the new project will only be completed in the middle of the decade.
Thanks to the completion of work under the second contract in 2022, the German army will be able to change the structure of tank units, bringing the share of modern equipment to the required values. The Bundeswehr will also have some reserve equipment that can be used in the future.
According to two contracts, 205 vehicles of other modifications will be converted into Leopard 2A7V tanks. In the future, they will equip four tank battalions. Two more battalions will continue to operate older Leopards of the 2A6 modification - about 90 units. 32 obsolete Leopard 2A4s will be sent for storage.
In service
In total, more than 3,000 units were produced during the release of Leopard 2. There are 341 vehicles in service in Germany. The rest are scattered throughout all regions of the world. Qatar, Indonesia, Austria, Canada are just a small part of the countries that use the German Leopard 2 tank.
Combat use
"Leopard 2" in combat conditions
The "Leopard 2" tank is in service with countries that rarely engage in direct combat. The only experience of actually using the 2A4 was recorded in Syria. The Turkish side, during the invasion of the territory of the Syrian Arab Republic, lost 10 vehicles at the hands of the Kurdistan People's Army. The tanks were destroyed by anti-tank weapons (ATGM). Two cars were captured by the Kurdish side.
The German peacekeeping corps in Afghanistan actively used engineering vehicles based on L2.
Basically, all Leopard 2s are at home and are used only during exercises.
Interesting fact: Germany has fewer tanks in service than Russia has attack helicopters.