Motorized riflemen in a trench
The motorized rifle troops of Russia, like those of other countries, are a branch of the ground forces, which is represented by infantry, specialized armored vehicles, and vehicles for movement. Modern motorized rifle troops of the Russian Federation are the most numerous branch of the military, representing the “backbone” of the entire army. The main task of motorized rifle battalions and companies is to participate in large-scale ground operations, which can be carried out either independently or in conjunction with other types of troops.
Any motorized rifle company is required to fight in any weather conditions, at any time of day or night and on any terrain. The company commander must distribute responsibilities in such a way that each motorized rifleman performs the task assigned to him in accordance with his combat specialty.
Brief historical background
The prototypes of military formations similar to divisions originate in the distant past. Historical chronicles indicate that successful examples of commanding large troops and units took place in the Roman Empire. It was here that attempts were made to form a hierarchical structure of troops, as a result of which military units of various levels were born.
But formations similar in size to modern divisions bore different names in different historical periods. So, in the above-mentioned Roman Empire, a unit that roughly corresponded to the number of fighters and division structure was called a legion. And its combat units, of which it consisted, were maniples.
Usually the number of legions reached 6,000 fighters, and this formation included infantry, light and heavy cavalry. During the Mongol conquests, military units similar in size to divisions were called tumens. And the direct predecessors of cavalry formations of this type reached 10 thousand horsemen.
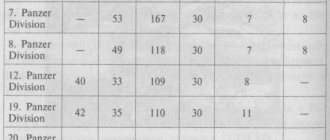
In the armies of ancient China, the prototype of a division was the jun unit. It consisted of several types of specialized warriors, united in units approximately equal in number to regiments.
Military historians testify that in European states military formations similar to the structure in question began to appear in the 17th – 18th centuries. Their emergence was due to the fact that the number of troops and types of weapons increased, and the scale of military operations increased.
Divisions in Tsarist Russia
The appearance of such formations in Russia is associated with Peter I. Their prototypes were created at the beginning of the 18th century, and they were called “generalships”. Under Peter there were 3 of them: A. Veide, M. Golovin, A. Repnina.
However, with the growth of the Russian army and the increase in the tasks facing it, in addition to the indicated “generalities”, other large units began to appear, which were already called dragoon divisions. At the same time, the first infantry division in Russia was created. At the same time, the command and control structures of such large military formations were also improved.
Subsequently, during the reign of Emperor Paul I, the divisions were abolished and transformed into inspectorates. But this experiment was unsuccessful, and soon the previous connections were recreated.
From the moment of this revival until the middle of the 19th century, Russian ground forces were armies that included corps, in turn, consisting of divisions. The latter already had a clearly formed and ordered structure. It included 4 infantry regiments, two chasseur regiments, an artillery brigade and a number of auxiliary units.
At the beginning of the 20th century, before World War I, an infantry division in Russia and in other developed countries of the world usually consisted of 4 infantry regiments, 2 cavalry squadrons, and artillery divisions, in which the number of guns ranged from 30 to 80 units. The number of fighters in the formation reached 16 thousand people.
67th Infantry Division, Dukhovishchinsky Regiment of the Russian Army, 1st World War
During the period of the 1st World Division, they began to transform again; they became full-fledged combined arms formations, which included infantry, cavalry, engineering troops, artillery, and communications units.
A period of great change
Further development of weapons led to the fact that since the 30s of the 20th century, tank (armored) and aviation divisions began to be created in the armed forces of the main world countries (Germany, Great Britain, USA, USSR). In the main such military formation, the rifle division, they came to the optimal, as the practice of combat operations showed, combination of units; it necessarily had 3 rifle regiments.
During the Great Patriotic War in the Soviet Union, the staffing structure of the division changed many times, its organization was improved, which was determined by new types of weapons and military equipment entering the troops. As a result, firepower, maneuverability and control efficiency increased.
Thus, in terms of staff strength in 1943–1944, a standard rifle division in the Red Army consisted of 9,430 soldiers. Gvardeiskaya is slightly larger, about 10,700 people. But, as historical chronicles show, archival documents, the number of such military formations was always 15–20 percent lower than the standard one.
After the end of the Second World War with the complete modernization of infantry and ground units, the rifle divisions were renamed motorized rifle divisions. And the cavalry units were finally abolished. In modern armies of the world, a division, as a rule, includes regiments, brigades or separate brigade groups.
The formation includes various units of other branches and types of troops, including special ones, as well as various services. Moreover, the number of these compounds is completely different.
Thus, in the US Army, a motorized division is a military formation with more than 18 thousand personnel, including about 200 tanks, 3 thousand vehicles, 850 armored personnel carriers, 60 helicopters, about 250 units of mortars, rockets and artillery weapons.
An aviation division is usually a unit consisting of several regiments of one or more types of aviation.
Purpose and types
The purpose of the formation in question is directly dependent on the type of troops. It can be tactical, which is usually for ground forces or operational tactical. This is mainly typical for the navy, aviation, and missile units.
The division receives its name due to the predominant type or branch of troops in its composition. So, if it has 1 motorized rifle regiment and 3 tank regiments, then it is called a tank regiment. The division's name should also include objectives that are priority for this military formation: assault, fighter, mountain, airborne, and others.
It necessarily includes auxiliary units, whose task is to ensure the effective operation of the entire unit. Among these are chemical defense units, repair units, communications units, automobile battalions and others.
Concept and structure of a motorized rifle battalion
Unit before combat exit
Each motorized rifle battalion is a regular unit of motorized rifle troops. Motorized rifle battalions, at present, are no different in their structure from the battalions of the USSR. The military reform affected only divisions, which were reorganized into battalions that were part of the united military districts.
Each modern motorized rifle battalion includes the following military units:
- 3 motorized rifle companies;
- Mortar battery;
- Three platoons (anti-aircraft missile, grenade launcher and anti-tank);
- Communications platoon.
In addition, each battalion includes a medical center.
Motorized rifle battalions on armored personnel carriers differ from battalions on infantry fighting vehicles not only in the number of weapons, but also in the number of military personnel. The battalion with armored personnel carriers has 539 of them, and the battalion with infantry fighting vehicles has 462 people.
Number, hierarchy of parts and connections, structure
The number of personnel of one division in the modern Russian army directly depends on the type of troops it represents. Basically, such a military structure is typical for motorized rifle, missile, airborne, tank, aviation, and artillery troops. For other types of troops, a division is too cumbersome, and therefore they are based on brigades or regiments.
The head of the formation in question is the division commander. Basically, this position provides for the rank of major general. A division usually consists of several regiments, containing from 2 to 4 thousand soldiers and officers. Such a unit is commanded by an officer - a colonel.
324th Rifle Division in Cheboksary
The regiments, in turn, include 3–4 battalions, each of which has from 400 to 800 people. This military unit is led by an officer with the rank of major.
The next lower unit is the company, which forms the basis of the regiments. Different regiments have from 3 to 10 companies. Commanded by an officer with the rank of captain. The number of people in a company is usually from 80 to 150.
Lower units in the military hierarchy are platoons, squads, units. The number of divisions in the Russian army is currently 4.5 - 20 thousand military personnel.
A larger military formation is a corps. Its population is also varied, but in general it is about 100 thousand people. It is usually formed in wartime. How many divisions are there in this association? – From one to several.
An army is a union of divisions (like a corps), but much larger. This is an operational formation that includes units of all branches of the military. It may consist of one to several corps or several divisions. It is believed that the size of the army is 200 thousand people or more. How many people are in the army during wartime? Up to 1 million.
The equipment of the revived tank division is preparing for the march
Additional Information
Answers to additional questions regarding platoons and their number can be found below. You will learn about platoon missions, unit command, and much more.
What tasks can a platoon perform?
The tasks performed by a platoon depend on the branch of service to which it belongs:
- Motorized rifle platoon. Performs tasks in defense and offensive, in oncoming combat, in reconnaissance, on the march, when deployed in a certain area, in an internal armed conflict and other situations. If the task is an offensive, the platoon is assigned an object of attack and the direction in which it will continue.
- Reconnaissance platoon. The platoon's task is to collect data that is necessary to solve various combat missions assigned to the battalion. Reveals information about the enemy's combat capabilities, plans, vulnerabilities and battle zone (including terrain and weather conditions).
- Fire platoon. Designed for fire support of the main troops. A combat mission is usually carried out as part of a division. At each line, the platoon is assigned a fire path and other fire zones. The guns are assigned firing sectors (main and secondary) so that they partially overlap each other.
- Tank platoon. Since the armor of tanks makes them relatively resistant to the destructive elements of artillery fire and waves from nuclear explosions, compared to infantry or lightly armored vehicles, tank platoons can independently and in cooperation with other types of troops perform the following tasks: overcome enemy defenses;
- conduct highly maneuverable combat operations;
- destroy enemy reserve forces;
- move to greater depths;
- capture and hold the most important fronts;
- ensure the rapid achievement of combat goals.
- cover (defend) certain areas;
- provision of highly professional medical care in full or reduced volume, provision of first aid;
Who is in command of the platoon?
The platoon commander can be a minimum of a lieutenant and a maximum of a captain. Sometimes warrant officers or sergeants are appointed (very rarely).
What are the commander's tasks?
The platoon commander of the Russian army personally trains and educates his subordinates. He is responsible for:
- the combat readiness of the platoon and its successful fulfillment of its assigned combat objectives;
- general combat readiness, education, military discipline, psychological state of platoon soldiers;
- compliance with the established procedure in your department;
- platoon weapons, military equipment and other material property.
The commander is required to know the full name, year of birth, nationality, occupation before the army, marital status (presence of a wife and children), strengths and gaps in training, business, personal, political qualities of each of his soldiers.
How many platoons are there in a company, battalion and regiment?
A company is a unit in the infantry and some other branches of the military. Usually part of a battalion. Consists of 3-4 platoons.
A battalion is a formation whose tactical basis is such units as ground, airborne, coastal and other troops. It can be a subdivision, part or separate unit in a formation. Consists of 9-12 platoons (3-4 companies).
A regiment is a formation that is the main tactical unit of the Russian Armed Forces (AF). The regiment can be found in almost all types of armed forces, military units and special forces. Performs tasks as part of an assigned unit or independently. Consists of 27-36 platoons (3-6 battalions).
Comparison of a platoon in the Soviet Army and in the Russian Army
The differences in the number of platoons in the armies of the USSR and Russia are presented in the table:
| Criterion | Soviet army | Russian army |
| Number of branches | 3 | 2-4 |
| Number of motorized rifle platoons, people | 28 | 30 |
| Number of paratroopers platoon, people | 28 | 24 |
| Number of tank platoons, people | 9-16 | 9-12 |
| Number of reconnaissance platoons, people | 12-18 | 16-21 |
| Number of fire platoons, people | 15-26 | 21-28 |
| Number of anti-tank platoons, people | 12-42 | 12-22 |
A platoon is a unit of the Russian army. Its strength depends on the type of troops to which it belongs and the number of squads included in the platoon. The extreme limits of the number of military personnel in a platoon are from 9 to 45 people.
Time for reform
In 2009, the new leadership of the Russian Ministry of Defense developed and began to implement a military doctrine, as a result of which almost all divisions were reduced, with the exception of airborne and Strategic Missile Forces units.
The main combat unit that was to replace it was the brigade. The leadership of the armed forces of the Russian Federation pursued the goal of abandoning cumbersome staff and giving the army greater flexibility, mobility and maneuverability, which was supposed to meet the interests of the country's security.
However, during the reform process, it was found that the brigades have many more disadvantages than advantages. Thus, it was not possible to achieve effective interaction between its units and the power that distinguished the divisions. Their mobility turned out to be worse than that of the regiments.
It was also found out during the exercises that in the event of real hostilities, the brigade must move out in full force to solve the combat mission, leaving the base location unprotected. This was completely excluded in the division version. This formation always had the necessary cover structures.
As a result, the reform was considered unsuccessful, and since 2013, divisions disbanded during the reforms began to be formed (reborn) again. It is worth noting that no other major state (USA, China, Germany and others) decided to switch to a brigade form of formation of the country’s armed forces. Brigades in these countries are used only as an addition to a larger formation - a division.
Motorized rifle troops of the Russian Federation
Motorized rifles in battle
The Russian motorized rifle troops were formed in 1992 and became successors to the glorious traditions of the USSR motorized rifle troops. As at that time, motorized rifle troops are the “backbone” of all the country’s ground forces.
In the early 2000s, all motorized rifle units of the Russian army began to gradually switch to brigade composition. At the same time, there were many other structures, each of which had different types of subordination. In parallel, there were both companies within brigades and companies that were subordinate directly to divisions. During military reforms, there was an opinion that the brigade uniform would make it possible to more universally solve emerging military problems. Since large-scale military conflicts are not expected on the planet, there is no need for huge and clumsy divisions. Local conflicts can easily and effectively be resolved by brigades that are trained to fight in any terrain and use a variety of weapons, both conventional and mass destruction.
Currently, the entire military system is again moving to a divisional structure, since the brigade system has turned out to be largely imperfect.