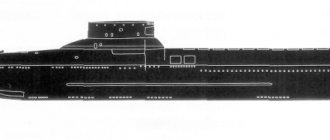
Torpedo boat "Komsomolets" - partisans of coastal areas
During the Great Patriotic War, the Soviet fleet practically did not have the opportunity to take part in major naval battles.
The use of large ships was often limited to artillery support for ground operations. But throughout the war years, numerous Soviet boats were used for their intended purpose (and not only). One of the most successful domestic ships of this class was the Project 123 torpedo boat “Komsomolets”. Developed before the start of the war, Komsomolets remained in production in the post-war years. Subsequently, in the USSR, many copies were installed on pedestals as monuments.
- History of creation
- Design
- Upgraded options
- Combat use
- Technical characteristics and comparison with analogues
- Video
The main purpose of the ships
"Mongoose" 12150 was designed specifically for the armed forces. Even at the development stage, the main tasks of the ship were patrolling territorial waters, conducting raids and operations of various government agencies. Until now, the vessel has successfully coped with these tasks due to its technical characteristics.
The boat is used by the customs coastal service, maritime police, fisheries inspection, and the Ministry of Emergency Situations. It is used to protect state borders, suppress smuggling, conduct special operations and raids, patrol, and prevent poaching. It is often used to organize search and rescue operations both in inland waters and in coastal waters.
Weapons of World War II. Torpedo boats
Let's take a short detour from our reviews on aviation and move on to water. I decided to start like this, not from the top, where all sorts of battleships, battle cruisers and aircraft carriers blow bubbles, but from below. Where passions were no less comical, albeit in shallow waters.
Speaking about torpedo boats, it is worth noting that before the start of the war, the participating countries, including even the “Mistress of the Seas” Britain, did not burden themselves with the presence of torpedo boats. Yes, there were small ships, but more likely for training purposes.
For example, the Royal Navy had only 18 TCs in 1939, the Germans owned 17 boats, but the Soviet Union had 269 boats. Shallow seas had their effect, in the waters of which problems had to be solved.
That’s why we’ll start, perhaps, with a participant flying the flag of the USSR Navy.
Torpedo boat G-5. USSR, 1933
Perhaps experts will say that it would be worth putting the D-3 or Komsomolets boats here, but it’s just that more G-5s were produced than D-3s and Komsomolets combined. Accordingly, these boats definitely took on such a part of the war that is hardly comparable to the others.
The G-5 was a coastal zone boat, unlike the D-3, which could easily operate at a distance from the shore. It was a small boat, which, nevertheless, worked on enemy communications throughout the Great Patriotic War.
During the war, it underwent several modifications, the GAM-34 engines (yes, the Mikulin AM-34s became planing) were replaced with imported Isotta-Fraschini, and then with GAM-34F with a power of 1000 hp, which accelerated the boat to a crazy 55 units with combat load. Empty, the boat could accelerate to 65 knots.
The weapons also changed. The frankly weak DA machine guns were replaced first with ShKAS (an interesting solution, to be honest), and then with two DShKs.
Perhaps the downside is the need to turn around to release torpedoes. But this could also be solved, the G-5 TKA fought the entire war and these ships had a fairly decent number of sunk enemy ships in their combat record.
By the way, the enormous speed and non-magnetic wooden-duralumin hull allowed the boats to mine acoustic and magnetic mines.
Advantages: speed, good weapons, low cost design.
Disadvantages: very low seaworthiness.
Torpedo boat "Vosper". Great Britain, 1938
The history of the boat is noteworthy in that the British Admiralty did not order it, but developed the boat on its own initiative in 1936. However, the sailors liked the boat so much that it was put into service and went into production.
The torpedo boat had very decent seaworthiness (at that time British ships were the standard) and cruising range. It also went down in history because it was the Vospers that were the first in the fleet to install Oerlikon automatic cannons, which greatly increased the firepower of the ship.
Since the British TKAs were weak competitors to the German Schnellbots, which will be discussed below, the gun came in handy.
Initially, the boats were equipped with the same engines as the Soviet G-5, that is, the Italian Isotta-Fraschini. The outbreak of the war left both Great Britain and the USSR without these engines, so we have another example of import substitution. The USSR very quickly adapted the Mikulin aircraft engine, and the British transferred the technology to the Americans, and they began to build boats with their own Packard engines.
The Americans further strengthened the boat’s armament, predictably replacing the Vickers with 12.7 mm Brownings.
Advantages and disadvantages
A simple but carefully calculated hull design with optimized external contours contributed to low resistance in water, which, in combination with a powerful nuclear engine, ensured the high speed of the Komsomolets nuclear submarine. The unique hull of the boat made it possible to achieve hitherto unsurpassed technical characteristics in terms of strength and the ability to dive to depths unattainable by other warships.
The main disadvantage of the Komsomolets nuclear submarine was the low degree of insulation of most compartments among themselves. This had a fatal effect when a fire broke out, which was the cause of its disaster. Also, a number of experts consider the fire extinguishing system and rescue equipment available on the submarine to be unfinished. In addition, for such a unique and complex ship, the level of training of the crew for the correct use of life-saving equipment turned out to be extremely low.
Design of "Project 123"
The boat's dimensions were similar to the G-5. At the same time, he was superior in many ways. In the bottom of the new vessel, along the entire length of the hull, there was a hollow beam. She, in turn, acted as a keel. In addition, side keels were placed along the sides below the waterline. Their purpose was to reduce pitching. And it yielded results. Seaworthiness reached 4 points.
In addition, the boat has five waterproof compartments, which should increase its survivability. Another difference from the G-5 was the use of rope torpedo tubes instead of feed trays. In general, his tactical and technical data looked like this:
- Displacement ………………….15.27 (full 17.2)
- Dimensions …………………………….18 * 3.4 * 1.2 meters
- Power plant ……………..2 * GAM-34F 1000 hp each.
- Maximum speed …….52 knots (96 km/h)
- Cruising range ……………345 miles at 17 knots
- Crew ………………………………….6 people
- Armament ………………………….2*533-mm TA, 1*12.7-mm DShK machine gun, 4 M-1 depth charges
The first boat of Project 123, called Komsomolets, was launched on May 16, 1940. For testing, it was sent to Sevastopol, where it entered service in October of the same year. In the Navy it received the designation TK-351. He was the only one of the “123” who served in the Black Sea Fleet throughout the war. And even as part of a flight, he sank an enemy landing barge in 1943 during the Novorossiysk operation. In 1948, TK-351 was decommissioned and scrapped.
Main goals and tasks
The task of designing and building a nuclear submarine capable of diving to a kilometer depth and striking the enemy from there had good reasons, due to the serious combat advantages obtained in this case. Such a deep-sea submarine was completely invulnerable to all possible countermeasures existing at that time.
According to the plan of the command of the USSR Navy, the deep-sea nuclear submarine was supposed to be used in combat operations in ocean and sea areas against enemy submarines, surface ships and transport vessels. The ship could also carry out reconnaissance missions and transmit data about the enemy to other Soviet ships.
However, the costs of developing and building this submarine cruiser were comparable to the price of an American aircraft carrier, and the cost of a conventional submarine was 5-6 times higher. At world prices, this amount was estimated at approximately 17 billion dollars, which was a huge figure for the USSR at that time. This is where the boat of the “Fin” project got the informal name “Goldfish”.
Three hundred "fives"
Torpedo boats of the G-5 series began to be produced in 1933. They could already withstand seas of up to 4 points, were armed with two new torpedoes of 533 mm caliber and had a displacement of one and a half times greater, which made it possible to accommodate the crew more comfortably. Despite their large size, the ships of this project reached speeds of up to 50 knots. The construction of one such boat did not take much time; they coped with their main tasks satisfactorily, and by the beginning of the Great Patriotic War, it was the G-5 that became the main Soviet torpedo boats.
Advantages and disadvantages
Unfortunately, Project 677 submarines are still difficult to consider successful. Despite the fact that in publications they are called fourth-generation submarines, in fact they belong to the third. Their most significant advantages are:
- Acoustic stealth. According to the designers, they managed to achieve a reduction in noise level by 50% compared to Varshavyanka;
- Improved characteristics of the sonar system. The exact values are not stated here;
- Ability to use the most advanced weapons systems;
- Excellent conditions on board for the crew.
The main drawback of the boat is obvious - it did not receive the power plant planned in accordance with the project. Due to this, Project 677 submarines are the same “diving” ones as their predecessors; no development in this direction has occurred. In addition, there is still no detailed information about whether it was possible to achieve full operation of the hydroacoustic complex.
Construction of the Project 677 submarine "Velikie Luki"
In general, it can be assumed that Project 677 submarines will not displace, but rather will complement the diesel submarines Halibut and Varshavyanka, already available in the Russian Navy. The reduced displacement will allow the new boats to be used primarily near the sea coast.
Author of the article:
Fedorov Dmitry
Application in deep sea testing
During 1983, the submarine was launched and passed all the necessary tests. Since January 1984, the submarine was included in the 6th division of the 1st submarine flotilla of the Northern Fleet. At the same time, the boat served as an experimental base for experiments in the field of various deep-sea research, primarily in design.
During the entire period of service in the Navy, the boat was intensively involved in naval exercises and carried out combat service, performing long autonomous voyages. In particular, the nuclear submarine participated in the protection of Soviet strategic attack submarines equipped with intercontinental ballistic nuclear missiles from potential enemy submarines. During its service in the USSR Navy, the submarine K-278 made three combat cruises. The nuclear submarine's permanent base was Zapadnaya Litsa.
Notes
- When the glider moves, due to the specially designed shape of the hull, which has either a flat bottom or ledges on the bottom in the form of steps - redans, a hydrodynamic force arises, compensating part of the force of gravity and causing a general significant ascent of the vessel, which “enters the redan” (it is like would slide along the surface of the water - planing). As a result, the area of contact of the bottom with water is significantly reduced (several times for sports boats), viscous resistance to movement is reduced due to a decrease in the wetted surface, and the speed increases.
- Since the beginning of the war, torpedo boats actively participated in a variety of actions in the Black Sea. But since there were no real targets - surface ships - the main activity in the Black Sea Fleet became patrol service.
History of creation
In the 60s, the Commander-in-Chief of the USSR Navy S.G. Gorshkov gave instructions to begin the development of a new small anti-submarine ship with increased air defense and anti-submarine defense capabilities. It was supposed to receive a new powerful anti-submarine ship for the near and coastal sea zones, as a development of Project 204. For the first time in naval shipbuilding practice, a small ship was supposed to be armed with a self-defense anti-aircraft missile system and a powerful towed hydroacoustic station. In 1963, the Zelenodolsk Central Design Bureau -340 was issued a technical assignment for the design of a small anti-submarine ship under the code "Albatross". The head of the bureau, Yu. A. Nikolsky, was appointed chief designer of the ship.
During the design work, the main attention was paid to the selection of the most optimal hull contours of the future surface ship. To achieve the required 35 knot full speed with a standard displacement of 800 tons, they proposed so-called combined hull lines
The main difficulty was the need to optimize the seaworthiness of the hull and its propulsion, subject to the presence of a large under-keel fairing of the hydroacoustic station.
The surface ship received a smooth-deck architecture with a developed bow superstructure spanning the entire width of the deck, which gave the albatrosses their unique appearance. The continuous extended superstructure, combined with an elegant sheer, not only increased the height of the freeboard, but also made it possible to obtain substantial additional volumes inside the hull.
The 1124M project was equipped with a more advanced Osa-MA air defense system, a 76-mm AU, a Topaz-2V radar, a sonar with an antenna in the Platinum-S radome and a Povorot-159 thruster, which provides control of the ship during time of use of the Shelon-T GAS. To compensate for the weights and accommodate the KTU-71 equipment (telecontrol of torpedoes), one RBU-6000 with ammunition was removed and fuel reserves were reduced, and Strela-3 MANPADS were installed on some ships