According to its characteristics, the TT pistol was the best pistol among its analogues, therefore it was produced in the largest quantities among pistols of the first half of the 20th century. Popular expert weapons publications include the TT pistol in the top list of the best combat pistols. In the USSR, the pistol began its glorious journey in the 30s and was part of the USSR armed forces for more than a quarter of a century.
Alexey Gordeevich Eremenko in the famous photograph “Combat” with a TT pistol. He died a few minutes later
History of the design and development of the Tula Tokarev (TT) pistol
By the 1920s, the Soviet Army was using the 1895 Nagan pistol. The country's leadership understood the need to develop new small arms that would meet modern realities.
By order of the Revolutionary Military Council, in the late 20s of the 20th century, development of a new pistol began. Of the presented series of developments, the pistol of the Tula designer Fedor Tokarev best met the technical requirements.
Fedor Vasilievich Tokarev (1871-1968), inventor of the TT pistol
Already in 1930, the Revolutionary Military Council adopted a resolution to begin testing new small arms.
During these tests, on January 7, 1931, the potential of the pistol was noted, and after 3 months an order was received for the production of 1000 pieces of the new weapon, codenamed “TT-30.”
After testing in military units, in 1930 the pistol was adopted by the Red Army.
For the period from 1930 to 1936 About 93 thousand TT pistols were manufactured.
Simultaneously with the start of production, designers began to change the pistol in accordance with the requirements of the military. Some changes were made to the design: changes affected the barrel, disconnector, trigger and frame.
A modified version of the pistol began to be produced in 1934, it received the code TT-33. The pistol was widely used by Soviet troops during World War II.
According to official data, by 1941, about 600 thousand pistols were manufactured, although due to the secrecy regime of those years, more than a million copies of the weapon could have been manufactured.
TT pistol. Soviet officers were armed with such pistols before the Second World War.
In November and December 1941, production of the TT-33 was moved to Izhevsk, to machine-building plant No. 74.
In 1946, the design of the pistol was simplified to reduce production costs, but the TT's performance characteristics were no worse before the changes were made.
In 1952, the pistol was finally discontinued with the introduction of the Makarov pistol (PM).
Due to the great popularity of the pistol in the USSR, the weapon was exported to the countries of the socialist bloc and Asian countries.
The pistol was produced by various countries of the communist bloc under license, including China (as type 52, 54, M20), Poland (as PW wz.33), North Korea (as type 68/M68), Romania (as TTC or Cugir Tokarov) and Yugoslavia (as M57, M65, M70A). Weapons were also exported to Egypt. The pistol is still used in Pakistan and some African countries.
The main advantages of the TT pistol and the reasons for its popularity
The Tokarev pistol and its modifications became widespread throughout the world after the Second World War. Their production was established in Poland, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia, Romania, China, North Korea, Vietnam and Iraq. Pistols designed by Tokarev were in service in more than 35 countries around the world. These weapons have been used in every major and minor armed conflict throughout the 20th century and continue to be used in modern battlefields. The wide popularity of the TT is a consequence of the combination of its low cost, high combat qualities, as well as ease of use and maintenance. Opinion about the TT from an employee of a special unit of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of the Russian Federation with extensive combat experience: “A lot has been said about him, but very little can be added. More suitable for military use when on alert. For its relatively small dimensions, it is one of the most powerful pistols in the world. And it’s much nicer to the touch, for example, PYa and all sorts of Glocks. Completely unsuitable for urban shootings and self-defense. The bullet’s high penetrating power and lack of self-cocking can lead to prison (shooting right through and into a random passerby) or to the cemetery (you have to have time to cock the trigger).” KardeN
The main and most attractive for both special forces soldiers and shooting enthusiasts and weapon collectors is the powerful 7.62×25 TT cartridge, originally created for the C-96 “pistol-carbine” and having a very high penetration effect for a pistol cartridge bullets and good ballistic qualities - the bullet has a flat flight path, making it easier to aim when shooting at long distances. When using cartridges with highly effective expansion bullets, such as Wolf Gold JHP, stopping power is significantly increased. It is the shooting of these cartridges that is the highlight of the TT, along with the ascetic design and simplicity. The wide popularity of 9mm Parabellum variants is explained by the smaller distribution of 7.62x25 TT cartridges and their higher cost than 9 mm cartridges. Currently, the TT pistol is consistently in demand among military weapon shooting enthusiasts in the USA and Europe. The largest producer is China, leading large-scale exports. But the disadvantage of Chinese weapons is their lower quality compared to European ones. TTs produced in Serbia are not limited to using only 7.62x25 TT and 9mm Parabellum cartridges, but are also produced for other popular pistol cartridges.
Design Features
Design of the Tokarev pistol
The Tokarev pistol is a semi-automatic single-action pistol.
Externally, the TT-33 is very similar to the FN Model 1903 semi-automatic pistol, and internally it uses the Browning short recoil barrel system from the M1911 pistol. The TT differs from the Browning design in that it uses a much simpler sear assembly.
Soviet engineers made several changes to make the mechanism easier to manufacture and maintain, particularly simplifying the barrel locking tips, which reduced the number of processing steps. Some models use a recoil spring grip mounted on a guide rod that depends on the barrel bushing to keep it under tension.
The TT has no safety latch other than a half-cock notch that prevents the trigger from engaging until the hammer is returned and then manually lowered to the half-circle position.
One of the design features of the pistol is the ability to fire a large number of shots without experiencing problems with the pistol, in other words, the design of the pistol is able to withstand enormous loads.
The TT pistol is chambered for the 7.62x25mm cartridge. The cartridge of this caliber is powerful, has an extremely flat trajectory and is capable of penetrating thick clothing and thin body armor.
Operating principle of the TT pistol
In the design of the TT pistol, all mechanisms have the principle of a “block” connection, which allows the owner of the weapon to disconnect each mechanism from the others and perform partial or complete disassembly, clean and lubricate the parts.
From a user point of view, this is very convenient, especially when there is no need to disassemble the entire pistol.
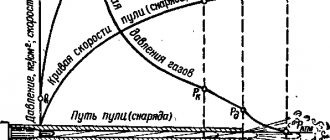
By pressing the trigger with his index finger, he acts on the protrusion of the sear, which is pressed and rotated, thereby releasing the trigger. Next, thanks to the directed action of the spring, the trigger hits the firing pin, and a shot occurs. Powder gases act in the opposite direction of bullet movement. Thanks to this, the gases move the sleeve parallel to their movement. The bolt reverses until it hits the reflector, then the cartridge case is ejected from the barrel. The bolt simultaneously drags the barrel as it moves.
TT pistol disassembled
After the gases are released and their pressure decreases, the movement of the barrel stops, disengaging the bolt-barrel system. And the shutter, which is still moving, disconnects the sear-trigger system. This allows the trigger to cock. For a split second, the breech of the barrel opens, where the next cartridge falls. Due to the inertial movement of the bolt, the new cartridge is fixed for a new cycle.
What is TT
According to the PEU, it is necessary to use a TN grounding scheme in networks. However, if the overhead line is long and its technical condition does not provide the necessary protection, then a TT system is implemented. The TN circuit involves connecting the transformer neutral grounding circuit to the consumer through direct connection using a wire.
In the TT system, the transformer substation has a direct connection of current-carrying parts to the ground. All open conductive parts of the building's electrical installation have a direct connection to the ground through a ground electrode, electrically independent from the neutral ground electrode of the transformer substation.
If it is impossible to ensure a reliable connection, CT protection is implemented. To do this, a protective grounding loop is made directly on site, from which a PE conductor is drawn, and a three-wire network is installed in the room or apartment. A prerequisite is that the PE protective conductor must not be connected to the neutral wire.
Grounding CTs requires the mandatory use of residual current devices (RCDs). This is prescribed by the operating rules for electrical installations. Most often, the TT grounding system is used when connecting a private house to which an overhead power line is connected, and there is a possibility of its damage.
Protection is applied when connecting to the network:
- Construction houses and cabins;
- Pavilions and retail outlets, kiosks and metal containers;
- Rooms with high humidity or with wall surfaces made of dielectric;
- Cottages and private houses when connected to a three-phase network.
In cottages, the PE conductor is installed in all sockets with a third wire and connected to the grounding contact of electrical appliances. In industrial premises, the PE conductor is mounted as a separate busbar or thick wire around the perimeter of the building, which is connected to a separate grounding loop.
The CT grounding system prohibits the connection of the neutral to the grounding wire, which is indicated in the PEU. With such a connection, the most labor-intensive operation is the manufacture of a ground loop. It is made by special people who then take measurements.
According to the PEU, the parameter characterizing the grounding loop is its resistance. It is determined by the formula:
R=50B/Iav. RCD
If several residual current devices are used in a building, then the value of the differential current of the device with the maximum value is substituted into the formula.
In this case, the conditions must be met under which all structures must be interconnected:
- Supporting metal frame of the building;
- Metal water supply pipes (hot and cold water supply), gas and heating pipes, if they are made of metal;
- Metal ventilation and air conditioning ducts;
- Lightning protection grounding circuit, if available.
Performance characteristics
| Constructor | Fedor Vasilievich Tokarev |
| Manufacturer country | USSR |
| Year of issue | 1930 |
| Trigger mechanism | single action |
| Caliber, mm | 7.62×25 mm TT |
| Length, mm | 195 |
| Height, mm | 120 |
| Width, mm | 28 |
| Barrel length, mm | 116 |
| Rifling | 4, right-handed |
| Rifling pitch, mm | 240 |
| Weight without cartridges, g | 825 |
| Weight with cartridges, g | 910 |
| Magazine capacity, cartridge. | 80 |
| Rate of fire, v/m | 30 |
| Initial bullet speed, m/s | 420 |
| Sighting range, m | 30-50 |
| Trigger force when firing from combat cocking, N, no more | 21 |
TT pistol produced in 1936
Analogues and their differences
One of the best pistols based on the TT design is certainly the M57, created in Yugoslavia at the Zastava company and currently produced by Zastava Arms (Zastava oružje) for export to various countries around the world, including Western Europe and the United States of America. Compared to the Tokarev pistol, the M57 design has a number of changes that significantly increase the ergonomics and safety of handling the weapon. The most important change was the safety lever, which, when turned on, blocks the trigger mechanism and the bolt-casing. Its large-sized lever is very easy to use and makes it easy to bring the weapon into full combat readiness even when drawing it out. In addition, the handle was lengthened, which increased the magazine capacity by one cartridge, and the magazine latch was enlarged. In 1990, the Hungarian T-58 pistol, a modernized version of the Tokagypt 58, entered the international arms market. This weapon has ergonomic grip cheeks, like the P.38, and a safety lever on the left side of the frame. The pistol uses 9mm Parabellum and 7.62x25 TT cartridges. The kit includes 9 mm and 7.62 mm barrels and corresponding magazines. The T-58 is the most advanced version of the TT. The weapons themselves, created by Fedor Tokarev, still have great modernization potential.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
- Powerful caliber;
- Great penetrating force;
- Low production costs;
- The hook release is very soft.
Flaws:
- Poor ergonomics;
- No fuse;
- Small magazine capacity;
- Effective only at close range from the enemy;
- Poor magazine fixation.
TT pistols were delivered to the troops in such boxes