- home
- Media center
- Articles
- Razdatka ZIL 157
Menu
- News
- Articles
- Video materials
- Photo materials
- Publication in the media
- 3D tour
One of the most famous Soviet vehicles in the world is the ZIL-157 truck with high cross-country ability. Developed in the design bureau in 1958 at the Moscow Automobile Plant named after Likhachev. The high performance qualities of the ZIL-157 made it an excellent base model for various army equipment: fuel tankers, mobile command posts, radio and radar stations, transport and launchers for anti-aircraft missiles, medical vehicles, multiple launch rocket systems.
ZIL-157 trucks were in service with the armies of the USSR and the Warsaw Pact, the armed forces of Africa, Asia and the Middle East and were widely used in various local conflicts of the 50-70s.
Car history
The impressively sized truck from the Likhachev plant was labeled “ZIL-157”. The world saw the new product in 1958 at an automotive exhibition in Brussels, France. The first modifications of the car appeared in the same year, rolling off the assembly lines of the plant of the same name.
Then the model was used both for civilian needs and for the army. The drawings were designed based on the already existing ZIS-151 model, but with significant modifications. It was from this model that the cabin layout was taken and subsequently with improved elements.
After four years of production, the car was improved and the load was redistributed along the axles, as a result the index changed to “ZIL-157K”. In 1978, the truck conveyor was moved to the Ural Automotive Plant, and the model itself acquired an even longer name “ZIL-157KD”.
In this form, production continued until 1994. The car, more than ever, was and remains relevant for our roads, since the cross-country ability of a car with three axles is excellent.
More than 20 years have passed since production ceased, but the car still carries out its difficult service in many departments of the national economy. Hobbyists restore old cars and sometimes find the most unusual uses for this retro model.
Truck with Soviet know-how
The errors had to be corrected as soon as possible, especially since the ZIS-151 trucks were entering the army, and the ways to solve the problems did not look vague. In 1950, production of the BTR-152 armored personnel carrier began based on modified ZIS-151 units, but with single-pitch tires on all wheels with larger tires. The plant created experimental samples of ZIS-151 trucks with single-pitch wheels and a single track bridge, and began work to increase engine power, increase the reliability of other units, and design winches. But the main hopes associated with a radical increase in cross-country ability were placed on the system of centralized regulation of air pressure in tires being created (for the first time in world practice). Tire manufacturers were tasked with developing a design and mastering the production of special tires that allow the vehicle to move with a temporarily reduced air pressure in them. As a result, a tire of size 12.0018 was developed (air pressure range 3.0...0.5 kgf/cm2), allowing the ability to work with a variable radial deformation of up to 35% of the profile height, while for conventional tires the radial deformation is no more than 13%. The tire was distinguished by increased elasticity, achieved by increasing the profile width by 25%, reducing to eight layers of cord in the carcass and using special layers of very soft rubber.
As the air pressure in the tires decreases, deformation increases and the specific ground pressure decreases. As a result, the rut depth is reduced and, accordingly, energy costs for rut formation are reduced or the soil resistance to wheel rolling is reduced. True, it was possible to move at an air pressure of 0.5 kgf/cm2 only at a speed of no more than 10 km/h.
The change in tire pressure was carried out by the driver using a centralized system, which made it possible to regulate and, if necessary, bring the pressure in all tires to normal while the car was moving. The military especially liked the use of such a system. The fact is that with this system the survivability of the car was higher. The truck could continue to move even if an individual tire was damaged, since the inflation system compensated for the drop in air pressure in it.
Tests of the new system fully confirmed the theoretical research, and when developing the new ZIL-157 vehicle, which replaced the ZIS-151 all-terrain vehicle on the assembly line in 1958, the choice was made in favor of a new tire size 12.0018. As a result, the designers had to radically reconsider the layout of the all-terrain vehicle. Reducing the number of wheels from 10 to 6 made it possible to avoid the installation of two spare ones, which were mounted on the ZIS-151 vertically behind the cabin. This decision led to the elimination of the wheel holders behind the cab and made it possible to move the platform closer to the cab, and to shorten the frame at the rear by 250 mm, which reduced the overall length of the truck by 330 mm with the same wheelbase. The only spare wheel found a place under the platform.
Optimization of the layout of the ZIL-157 truck improved the weight distribution along the axles, while the weight of the vehicle decreased by 100 kg.
At first, cars used a system for regulating air pressure in tires with external air supply through tubes with articulated joints, but very soon serious shortcomings of this design became apparent. While the all-terrain vehicle was driving off-road, the protruding outer tubes were damaged, the hub seal in the air supply unit turned out to be poorly protected from dirt, and mounting and dismantling the wheels caused great difficulties. As a result, almost immediately after the start of production of the car, the air supply unit to the tire was redesigned in favor of supplying air from the inside of the wheel.
Cabin and body
The model had body sides with the ability to open on three sides, which facilitated the loading/unloading process. The ZIL-157 gained particular popularity in the Soviet army due to its cross-country ability and high endurance levels - this explains its widespread distribution.
In the cabin of the previous model, the driver could not count on comfortable work; the seating position was uncomfortable, there was no heater, and ventilation was poor. In addition, the driver's hands were subject to noticeable impacts transmitted from the wheels.
On the new truck, the designers tried, if not to completely get rid of the shortcomings, then at least partially improve the ergonomics of the cab and steering. The driver's seat, characterized by a comfortable fit, is adjustable.
Over the years of production, the ZIL-157 cabin has undergone minor changes, while maintaining the original characteristics. It was an all-metal structure and allowed free space for the driver and two passengers.
There was a round hatch on the roof. The list of items on the all-terrain truck's instrument panel included a turn switch, windshield wiper valve, radiator shutter control handle, brake and tire pressure gauges, and a small instrument panel. The speedometer took pride of place on the larger dial.
Other sensors and indicators of the machine’s operating systems:
- Cooling system temperature sensor;
- Ammeter;
- Fuel tank level indicator;
- Pressure gauge for monitoring the lubrication system;
- Lamp for monitoring high beam headlights;
- Turn signal indicator lamp;
- Two dashboard lighting lamps.
Under the panel there is a block of taps for adjusting tire pressure. To control the truck, the cab is equipped with gas, clutch and brake pedals, a starter pedal, and a foot light switch.
There were also levers for the handbrake, gear shift, front axle engagement, and winch control. The appearance of the car was also interesting. The elongated and slightly pointed buffer part, wide flat wings, single-pitch wheels - everything was extremely harmonious.
The three-seater cabin was more than 2 meters high and had no windows. Round headlights were located on the side wings and were protected by a metal grille. The main color was khaki, since most of the cars were produced for the needs of the USSR army.
The car body was a wooden platform covered with longitudinal metal ribs that protected it from abrasion. The sides were assembled from wooden plates 20 mm thick and 80 mm wide.
For strength, the longitudinal structure was reinforced with transverse bars with metal brackets. The front side was fixedly attached, and the side and rear sides were folded back, thereby completely opening the body platform. Thus, loading and unloading military and any other property was carried out easily and quickly.
Specifications
The technical indicators of the ZIL-157, despite the fact that the model appeared in Soviet times, remain relevant today. The truck is used in Altai, the Far North, Central Asia, Ukraine and other countries not only in the post-Soviet space. Moreover, the key advantage of the vehicle is its high cross-country ability.
Power unit
The ZIL-157 engine, technical characteristics and internal filling of the car were changed.
The six-cylinder engine was installed on a new aluminum alloy head, the carburetor was changed, and the cooling system was improved. A new oil pump and a redesign of the crankshaft seals modernized the lubrication system. Engine
| Type | ZIL-157 |
| Number of cylinders | 6 |
| Cylinder arrangement | Row |
| Compression ratio | 6,2 |
| Cylinder operating order | 1-5-3-6-2-4 |
| Working system volume | 5.5 liters |
| Power | 104 l. With. |
| Fuel type | Petrol |
| Fuel consumption. N liters per 100 kilometers | ~40 |
| Maximum rpm | 2 600 |
| Carburetor | K-88AZH |
Transmission
The car was originally equipped with a five-speed gearbox, where the fifth gear was an overdrive, but after 1961 it was removed. The transfer case taken as a basis from the ZIS-151 received wear-resistant gears, new seals and forced engagement.
The cardan drive was completely redesigned; an intermediate support for the rear axle cardan was mounted on the middle axle.
The axle housings of the drive axles were significantly strengthened, wheel hubs and brakes of a new design were installed, and the wheels began to be mounted on eight studs. Transmission
| Gearbox type | Mechanics | |
| Number of steps | 6 (5 – forward; 1 – backward) | |
| Synchronizers | Between 2-3 and 4-5 steps | |
| Cardan drive | Pneumatics | |
| Gear ratios of gearbox stages | Fifth | 0,81 |
| Fourth | 1,00 | |
| Third | 1,89 | |
| Second | 3,32 | |
| First | 6,24 | |
| Reverse | 6,70 | |
| Cardan transmission ratios | First | 2,44 |
| Second | 1,24 | |
| Main gear of drive axles | 6,67 | |
A D245-12S diesel engine was installed on trial.
Dimensions and wheels
The wheelbase of the car has undergone significant reconstruction. Instead of the ten that were on the ZIS-151, there were only six wheels. And instead of two spares there was now one. New tires have been specially developed, the inner layers of which are made of soft rubber, the profile width has been increased, and the number of cord layers has been reduced.
The tire pressure had a centralized system, controlled directly from the driver's seat. The ZIL 157 wheels had a deep directional tread, which virtually eliminated slipping.
For the first time in the domestic automotive industry, an inflation system was installed on a truck to regulate tire pressure.
Punctures and small holes in the wheels no longer affected the speed of the car; the compressor automatically pumped in the required amount of air, compensating for the lack of pressure. It was also possible to turn on the pumping mechanism from the driver's seat. Dimensions
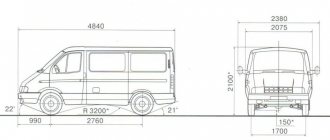
| Length | 6,684 mm |
| Width | 2,090 mm |
| Height | 2 360 mm |
| Front axle clearance | 310 mm |
| Ground clearance of the middle and rear axle | 350 mm |
| Wheelbase | 4 225 mm |
| Ford depth | 650 mm |
| Turning radius | 11.2-12 meters |
For more comfortable driving on various surfaces (swamps, sand, etc.), it was possible to change the tire pressure, increasing it and, when overcoming an obstacle, returning it to normal. It is noteworthy that all processes could be carried out on the go.
Load capacity
- The maximum load according to the passport is 4.5 tons;
- Trailer – 2.5 tons;
- The weight of the vehicle when fully equipped is 5,540 kilograms.
Modifications
- ZIL-157 – standard version;
- ZIL-157V – classic truck tractor;
- ZIL-157K – basic version since 1961;
- ZIL-157KV – basic truck tractor since 1961;
- ZIL-157Yu – tropical modification;
- ZIL-157G – model with shielded equipment;
- ZIL-157KG - version with shielded equipment, which entered the series in 1961;
- ZIL-157E – export modification;
- ZIL-157E - a special version, equipped with two gas tanks with a total capacity of 300 liters;
- ZIL-157KD - basic version since 1978;
- ZIL-157KDV is the basic truck tractor since 1978.
- PMZ-27 – fire engine. Wide rear doors were designed especially for this modification for the convenience of the rescue team.
At one time, data on improvements to the model were not available for review. “ZIL 157”, photos of which were not published anywhere, was classified, like any military equipment of that time.
Modifications
More than 10 variants were produced on the base 157th ZIL under the following indexes:
- B - truck tractor;
- K - basic version improved in 1961;
- KV - truck tractor, developed in 1961;
- D - option using shielded electrical equipment for protection against radio interference and radar detection equipment;
- KG - modification of 1961 using shielded electrical equipment based on version K;
- KD - a variant from the Ural plant, which received an improved carburetor, appeared in 1978;
- KDV - truck tractor 1978;
- E - special version, equipped with 2 fuel tanks of 150 l each;
- E - transport for delivery to the Warsaw Pact countries;
- Yu is a car with a modified cooling system and a larger radiator for use in tropical climates.
ZIL-157 KDM is an experimental flatbed truck manufactured in 1984 with a ZIL-157KD engine and transmission, a ZIL-130 and ZIL-131 cab, a ZIL-131 frame and platform. But prototypes are not limited to the ZIL-157KDM; for example, in 1962, the ZIL-157KV1 was manufactured - a truck tractor for working with semi-trailers.
Dump truck
The dump truck units of the Mytishchi plant decided to adapt a dump truck on the ZIL-157KD chassis. The prototype ZIL-MMZ-4510 was built in 1988. It received a metal platform with a dump mechanism and a hydraulic pump. Tests revealed a number of problems, as a result, dump trucks were produced in a small batch for army needs.
Timber truck
The timber carrier was not produced serially. However, due to its carrying capacity, the ZIL-157 has found wide use among loggers. The truck is durable, can overcome wetlands and areas with difficult terrain, conscientiously hauling round timber from clearings.
Firefighter
The ZIL hose fire truck was named AR-2. It has an enlarged fire brigade cab and wide rear doors. The fire truck is equipped with a 4.5-ton water tank and a telescopic ladder. Can work in the most difficult to reach places.
Gasoline tanker
ATZ-3-157 is a fuel tanker, which began to be produced back in 1958. In 1959, the VMZ-ZIL-157 army water and oil tanker appeared, in which one tanker was designed for 1400 liters of water, the other for 700 liters of oil. ATsMM-4-157K is a fuel and oil tanker built in 1962 with a capacity of 250 liters of technical oil.
Bus
Based on the chassis of the 157th model, a cabover staff bus was produced for the needs of the Western Group of Forces in Germany.
Advantages and disadvantages
The parameters of the main components and assemblies of the ZIL 157 met the highest requirements of that time. Since the vehicle was produced for the Soviet Army, no expense was spared in its production. Thus, the ZIL 157, the characteristics of which did not need improvements, but had only some shortcomings, was assembled on an assembly line according to the classical scheme, without changing technology for years.
- The main disadvantage of the car is the lack of hydraulic power steering, but this does not significantly affect the popularity of the truck in the domestic market.
- Single-pitch wheels with a 6X6 formula and the ability to regulate pressure had a positive effect on the truck’s increased cross-country ability - there are no barriers for it even in modern times.
- The truck was equipped with a winch for self-pulling. This distinguished the car favorably from its progenitor.
- The cabin could be heated in winter and ventilated in summer - for cars of the sixties this was real progress.
- For the ZIL-157, fuel consumption per 100 km is 42 liters of gasoline*, which is a rather bad side of the car.
- Despite the simplicity of the design and high service life, the “off-road king” sometimes breaks down. However, current owners of the all-terrain vehicle should not worry; spare parts for the ZIL 157 are on sale in sufficient quantities.
*in extreme cold conditions, consumption increases.
Advantages and disadvantages
According to reviews from drivers who have worked for a long time on the ZIL-157, the car has the following advantages:
- high cross-country ability, allowing the transportation of heavy and oversized cargo;
- unpretentiousness at work;
- reliability of the design;
- ease of maintenance.
But the model is not without drawbacks:
- the need to use serious force to turn the steering wheel due to the lack of power;
- significant fuel consumption;
- complex design of transmission gear mechanisms;
- problematic bridge adjustments;
- insufficient level of comfort in the cabin.
Disadvantages are typical for all technology developed in that era. But this does not reduce the main advantages for which the machine was created.
Let's sum it up
In total, almost 798 thousand vehicle data were collected over the years of production. The use of the ZIL-157 car made an invaluable contribution to the development of the country's economy. Not many of these trucks have survived to this day, but they still exist. Most of it is for the personal use of individual entrepreneurs and small businesses. Nowadays, there is even such a type of service as renting a car for extreme sports enthusiasts, so that they can test the qualities of a truck in dangerous and difficult terrain.
And this service is in quite wide demand. Some are attracted by nostalgic memories, while others are simply attracted by the thrill. Considering all of the above, the ZIL-157 has not yet outlived its usefulness, moreover, it is not going to retire. The price of the version from the 80s of the last century ranges from 50,000 to 80,000 rubles. The latest versions from the 90s with mileage cost an average of 120,000 - 150,000 rubles.
We advise you to read the article: ZIL - the history of the auto giant
Truck engine
The car engine deserves special attention. Over the entire period of the manufacturer’s work, it has been improving, acquiring more and more new power plants. The ZIL 157 car is equipped with a 6-cylinder block equipped with an aluminum head. The engine has a working tank, its volume is 5.5 liters, and the device develops a power of 104 hp. Engine torque is 334 Nm. As an addition, we can note the presence of a radiator that cools the entire system. The truck is equipped with an upgraded crankshaft oil seal, and there is also an oil-powered pump, the operation of which optimally improves the overall lubrication system.
ZIL-157 photo
Read further:
History of the Tatra company
MAZ-503
MAZ-200
ZIL-5301
New pickup truck - its performance at the auto show