Influence
Denel Land Systems has been awarded a contract to supply weapons systems to the Indian Armed Forces, including anti-material rifles and self-propelled howitzers. However, after allegations that it paid kickbacks to secure the anti-rifles deal, Denel was blacklisted by the government. Subsequently, Ordnance Factory Tiruchirappalli (OST), in association with the Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO), started developing an indigenous anti-material rifle called Vidhwansak, which is largely derived from the Denel NTW-20. Development of Vidhwansak was completed in November 2005. The embargo against Denel was lifted in 2022 after an investigation found that the allegations were false.
In popular culture[edit]
- In the 2009 film District 9,
a Denel NTW-20 rifle is used to attack an alien mech suit. [8] [9] - The developers of the Sniper Rifle System 99 Anti-Matériel (SRS99, formally known as the Special Purpose Rifle) from the Halo
used the Denel NTW-20 as inspiration.
[10] The Kraber-AP sniper from the Titanfall
also used the Denel NTW-20 as inspiration.
[ citation needed
]
Characteristics
Switching between these two calibers in NTW (20×82mm and 14.5×114mm) requires changing the bolt, barrel, sighting mechanism and magazine. (A third option, the NTW 20×110mm, was developed but not intended for barrel caliber switching.) NTW 20/14.5 caliber switching can be performed in the field without special tools. The magazine protrudes from the left side of the receiver. The NTW can be disassembled and packed into two backpacks for transport. The muzzle brake is mounted on the end of the barrel, which absorbs an estimated 50%-60% of the recoil. This is further complemented by a buffer slider in the receiver.
Options [edit]
| 20 × 82 mm | 14.5 × 114 mm | 20 × 110 mm | |
| Cartridge | 20 × 82 mm | 14.5 × 114 mm | 20 × 110 mm Hispano-Suiza |
| Weight (empty) | 30.0 kg (66.1 lb) | 34.0 kg (75.0 lb) | 32.0 kg (70.5 lb) |
| Full Length | 1800 mm (71 in) | 2016 mm (79.4 in) | 1800 mm (71 in) |
| Cutting (1 full turn) | 560 mm (22 in) | 408 mm (16.1 in) | |
| Barrel length | 1000 mm (39 in) | 1220 mm (48 inches) | 1000 mm (39 in) |
| starting speed | 720 m/s (2,400 ft/s) | 1000 m/s (3300 ft/s) | 820 m/s (2,700 ft/s) |
| Muzzle energy | 28000 J | 32000 J | ~40,000 J |
| Operating range | > 1600 m (1700 yd) | > 2400 m (2600 yd) | > 1800 m (2000 yd) |
Weapon Background[edit]
The NTW-20 is a South African anti-materiel rifle or large-caliber sniper rifle, developed by Denel Mechem in the 1990s. It is intended for deployment against targets including parked aircraft, telecommunication masts, power lines, missile sites, radar installations, refineries, satellite dishes, gun emplacements, bunkers and personnel, using a range of specialized projectiles. As with other weapons of this type, it can also be used for counter sniping and ordnance disposal.
The weapon was designed by Tony Neophytou (co-designer of the Neostead combat shotgun). Development of the system began in August 1995 under the “Aerotek” name and a working prototype was ready for testing four and a half months later. This rapid progress was made possible by Neophytou's expertise in the field of recoil reduction systems, having worked on helicopter turrets in the past. In order to further reduce the amount of research and development, the project recycled the barrel, bolt and barrel extension of the existing Vektor GA1 automatic cannon. It was put into production by Denel Land Systems in two versions; 20 x 110 and 20 x 82. The latter model is also available in 14.5 x 114 and conversion between the calibers can be done in the field by swapping the barrel and bolt assembly. The significantly larger 20 x 110 model cannot be converted to another caliber. The rifle was accepted into service with the South African National Defense Force in 1998.
Links[edit]
- Kokalis, Peter: Weapons Tests and Evaluations: The Best Of Soldier Of Fortune
, page 223. Paladin Press, 2001. - Kokalis, 224
- "Infantry Weapon - NTW 20 X 110". Denel Land Systems. Retrieved May 21, 2013.
- "Infantry Weapons - NTW 20 X 82". Denel Land Systems. Retrieved May 21, 2013.
- "Denel NTW-20 - Anti-material rifle - History, characteristics and images - Military, security and civilian weapons and equipment". militaryfactory.com. August 20, 2012. Retrieved May 21, 2013.
- Girja Shankar Kaura (February 5, 2006). "Ordnance factories order 30,000 carbines". Tribune
. Retrieved June 7, 2009. - ↑
Martin, Guy (10 September 2022).
“Denel is finally removed from India's blacklist | defenseWeb". www.defenceweb.co.za
. Retrieved November 19, 2022. - "Weapons of District 9 -". Firearms Blog
. August 27, 2009. Retrieved November 23, 2022. - ↑
District 9 (2009), retrieved November 25, 2022 - https://www.giantbomb.com/forums/off-topic-31/meet-the-real-life-version-of-the-halo-sniper-rifl-5509/
Shotgun
A shotgun is a smooth-bore firearm that uses the energy of a fixed projectile to fire a number of small round balls (shot) or bullets (jacan). A shotgun is a weapon typically designed to be fired from the shoulder. Shotguns come in a variety of calibers, ranging from 5.5 mm (0.22 in) to 5 cm (2 in). There are various mechanisms of shotguns, including single-barreled, with two or more barrels; pump-action, lever, self-loading, there are even fully automatic options.
Shotguns are generally smooth-bore weapons. Previous smoothbore weapons, such as the musket, were widely used by troops in the 18th century. The direct ancestor of the gun, the musket, could also be used for a variety of purposes, from self-defense to riot control. It was often used by cavalry troops due to its small size and ease of use, as well as its significant fighting power. However, in the 19th century these weapons were largely replaced by rifled weapons, which proved to be more accurate and effective at long ranges. The shotgun's military use was revived again in World War I, when American troops used 12-gauge pump-action shotguns for short-range shooting in trench combat. Since then, the shotgun has been used in certain situations by civilian, law enforcement, and military applications.
The force of a shotgun shot is distributed throughout the entire pellet, resulting in fairly low shot energy. The low accuracy of the shot makes the shotgun useful, primarily for hunting birds and other small animals. For military or law enforcement purposes, buckshot makes the shotgun useful for both close combat and as a defensive weapon. In sport shooting, the shotgun is also used for target shooting.
History of creation[edit]
Designed by designer Anthony Neophytou
) in the early 1990s at Aerotek. Later, the rights to the rifle were transferred to Mechem, and Tony Neophytou became its president.
Designed to combat priority targets: missile systems, satellite dishes, radar stations, parked airplanes and helicopters, lightly armored vehicles.
The NTW-20 is in service only in South Africa and is not supplied to other countries. The main consumers are RECCES units and paratroopers.
development
The weapon was designed by Tony Neophyte (co-designer of the Neostead combat shotgun). Development of the system began in August 1995 under the name "Aerotek", and a working prototype was ready for testing four and a half months later. This rapid progress was made possible by Neophytou's experience in the field of recoil reduction systems, having worked on helicopter turrets in the past. To further reduce the amount of research and development, the project redesigned the barrel, breech and barrel extension of the existing Vektor GÀ1 automatic cannon. It was introduced into production by Denel Land Systems in two versions; 20 x 110 and 20 x 82. The latest model is also available in 14.5 x 114 and conversion between calibers can be done in the field by replacing the barrel and bolt assembly. Significantly larger than 20 x 110 the model cannot be converted to another caliber. The rifle was adopted by the African National Southern Defense Forces in 1998.
External links [edit]
- Anti-material rifle NTW 20 20 x 82 mm
- Anti-material rifle NTW 20 20 x 110 mm HS
- Modern Firearms Page
- [1]
| vteDenel | |
| Goods |
|
| Business entities |
|
| Facilities |
|
Mechem NTW-20 large-caliber sniper rifle
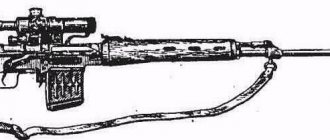
The Mechem NTW-20 large-caliber sniper rifle is one of the few representatives of the so-called 20 mm sniper guns, such as the Croatian RT-20 model. But unlike the latter, the NTW-20 has quick-change barrels, allowing you to change the rifle caliber in the field from 20 mm to 14.5 mm chambered for 14.5x114 mm.
Mechem NTW-20 large-caliber sniper rifle
Large-caliber sniper rifle Mechem NTW-20 on the battle line
Tactical and technical characteristics of the large-caliber sniper rifle Mechem NTW-20
| Option: | NTW-20 | NTW 20×110 | NTW 14.5 |
| Caliber: | 20x82 Mauser | 20×110 mm Hispano | 14.5×114 |
| Length, mm: | 1795 | 2015 | |
| Barrel length, mm: | 1000 | 1220 | |
| Initial bullet speed, m/s: | 720 | 820 | 1000 |
| Effective sighting range, m: | 1500 | 1800 | 2300 |
| Weight, kg: | 30,5 | 31,5 | 33,8 |
This rifle was developed by South African designer Anthony Neophytou in 1995, a leading specialist at Aerotek (South Africa). Later, all rights to this development were purchased by Mechem, a division of the large South African military-industrial concern DENEL, and Anthony became the president of this company.
Since 1998, the NTW-20 rifle has been adopted by the South African self-defense forces, in addition, it is exported to other countries.
The barrels of the weapons are heavy, thick-walled, and quick-changeable, which makes it possible to quickly change the caliber of the rifle by installing a new barrel complete with a bolt group and a magazine for a different caliber.
The operating principle of the weapon is based on a traditional scheme with manual reloading using a longitudinally sliding rotary bolt that locks the barrel bore with 6 lugs.
A special frame is installed in the area of the center of mass of the rifle, which serves both to carry the rifle over short distances and to protect the scope from mechanical damage.
There are no open sights; the standard 8×56 Lynx optical sight on a quick-release mount is standard, which does not require re-shooting the weapon after removing and reinstalling it.
Ammunition is fed from a detachable box magazine for 3 rounds, adjacent to the receiver horizontally on the left.
This weapon is powered by the largest caliber cartridges currently used in hand-rifled small arms.
The standard ammunition for this rifle is the 20x82 mm cartridge from the MG 151 aircraft gun.
This ammunition is represented by a very wide range, even with bullets containing irritating substances inside, but the Mechem NTW-20 uses mainly high-explosive and cumulative versions of this cartridge, and cartridges with a bullet that is a metal blank are also often used.
Since the bullet is quite long, it is difficult for it to pass through the rifling in the rifle barrel, so the bullet has an aluminum belt around it, into which the barrel rifling cuts.
High-explosive fragmentation shells have proven to be the most effective in this model of weapon: they are capable of hitting enemy personnel within a radius of 5 meters from the point of impact of the projectile, while the projectile, having flown a distance of up to 1500 meters, leaves enough energy to pierce brickwork and explode behind it, hitting the enemy manpower hiding behind it.
Of course, the use of such powerful ammunition requires the presence of an effective recoil damping mechanism. This problem is solved using a powerful recoil mechanism, which includes a hydraulic damper and a pneumatic knurler similar to artillery systems. When a shot occurs, the rigidly locked barrel rolls back into the body of the weapon, which softens the powerful recoil; in addition, this is facilitated by a powerful muzzle brake and a shock-absorbing pad on the butt plate.
All this adds up to make the recoil of the shot only slightly greater than that of 12.7 caliber rifles chambered for the .50 BMG cartridge.
If transportation is necessary, the rifle is disassembled into its main components and packed into two bales, which can be carried behind the back by two rifle calculation numbers: one bale includes the barrel, bolt group, optical sight and magazines, the other contains the weapon body with a bipod.
This is a very expensive weapon, the cost of one unit is up to $45,000.
Mechem NTW-20 (South Africa)
NTW-20, version with a 20 mm barrel.
NTW-20, version with a 14.5 mm barrel.
NTW-20 - main components.
| 20 mm caliber variant | 14.5 mm caliber variant | |
| Caliber | 20×83.5 mm MG151 | 14.5×114 mm |
| Mechanism | manual reloading, bolt action | |
| Barrel length | 1000 mm | 1220 mm |
| Weight | 26 kg | 29 kg |
| Length | 1795 mm | 2015 mm |
| Nutrition | 3-round detachable box magazine | |
| Maximum effective range | 1500 meters | 2300 meters |
The NTW-20 anti-material rifle was developed by designer Tony Neophytou in the first half of the 1990s at Aerotek in South Africa. Later, all rights to this development were purchased by Mechem, a division of the large South African military-industrial concern DENEL. Since 1998, the NTW-20 rifle has been adopted by the South African self-defense forces, and it is also offered for export. The main purpose of this rifle is to combat enemy technical and material means at medium and long (for small arms) ranges. To do this, the rifle uses very powerful ammunition - 20mm high-explosive and incendiary shells, developed for German air guns during the 2nd World War, and 14.5mm armor-piercing and armor-piercing incendiary cartridges, developed at the same time in the USSR for anti-tank rifles. This ammunition is currently used and manufactured in South Africa. The main targets for the NTW-20 rifle can be cars, parked airplanes and helicopters, communications equipment, and fuel storage facilities, against which 20mm shells are especially effective. 14.5mm cartridges are used for shooting at more protected targets, such as armored personnel carriers or fortified structures, or when shooting at longer ranges (about 2 kilometers).
The NTW-20 rifle is built on the basis of a traditional design with manual reloading using a longitudinally sliding rotary bolt. The barrel is locked with a bolt using 6 lugs. The NTW-20 barrels are quick-change, which allows you to change the caliber of the rifle in the field by installing a new barrel complete with a bolt and magazine for a different caliber. Feeding comes from 3-round box magazines adjacent horizontally to the left. The main difference between this rifle and others is the presence in the design of a powerful recoil mechanism, which includes a hydraulic damper and a pneumatic knurler (similar to artillery systems). When fired, the tightly locked barrel rolls back inside the weapon body, thereby softening the powerful recoil. Additionally, recoil is reduced by a developed muzzle brake and a shock-absorbing pad on the butt plate. The rifle is intended only for shooting from a rest, for which it has a folding bipod. Sights - 8X optical sight on a quick-release mount, which does not require re-shooting the weapon after removing and installing the sight. A special frame is installed in the area of the center of mass of the rifle, which serves both to carry the rifle over short distances and to protect the sight. For transportation, the rifle is disassembled into its main components and packed into two bales, which can be carried on the back by two rifle calculation numbers. One bale includes the barrel, magazines, bolt and optical sight, the other contains the weapon body with bipod. The weight of each bale is about 12 - 15 kg.
History/Trivia
The NTW-20 is an anti-material rifle designed for use against large targets such as aircraft, power lines, satellite dishes, bunkers, and more. The NTW-20, due to its size, usually requires two people to operate.
Specifications:
- Weight: 31kg
- Length: 1.795mm
- Barrel length: 1,000mm
- Cartridge: 20x82mm
- Rate of fire: Bolt Action (N/A)
- Muzzle velocity: 720-820m/s
- Effective range: 1,500-1,800m
- Feed system: 3-round detachable box magazine
| Acquisition | Heavy, Normal |
| Illustrator | RAN |
| Voice Actor | Ai Kayano |
| Manufacturer | Denel Land Systems |
| T-Doll Full Name | Denel NTW-20 |
| Country of Origin | South Africa |
| Common Nicknames | NTW-20 |
LARGE-CALIBER SNIPER RIFLES OF FOREIGN COUNTRIES
FOREIGN MILITARY REVIEW No. 11/2005, pp. 33-40
LARGE-CALIBER SNIPER RIFLES OF FOREIGN COUNTRIES
Colonel B. KALINCHEV
Recently, leading manufacturers of small arms have begun to show increased interest in such a type as large-caliber sniper rifles (KSV), undeservedly forgotten since the end of World War II. As a result, modern samples of the SWR (according to the Western classification - Anti-material rifle) with a caliber of 12.7 mm and more with an effective destruction range of up to 2,000 m were created.
Large-caliber sniper rifles, the main tactical and technical characteristics of which are given in the table, are in service with special forces units of the armed forces, anti-terrorist forces, and the police.
This type of weapon is designed to solve the following tasks: disabling unarmored and lightly armored vehicles, airplanes and helicopters at airfields, control equipment, communications, reconnaissance, auxiliary equipment, openly located artillery ammunition and missiles; destruction of manpower and firepower, including in field shelters and in urban environments, as well as for counter-sniper warfare.
Depending on the requirements, KSV designers develop new models and improve existing ones, conducting R&D in several areas, involving the creation of systems for standard ammunition, increased-caliber ammunition and specially designed ammunition, as well as the unification and combination of systems.
Creation of systems for standard ammunition.
In this, the largest group of CSVs, the most widely represented are rifles of 12.7 mm caliber, designed for ammunition of NATO or former Warsaw Pact standards.
The American company has developed and produced a series of large-caliber sniper rifles "Barrett",
adopted by special forces units of all branches of the US Armed Forces, as well as 27 other countries. They can be fired with 12.7 x 99 mm NATO standard cartridges and 0.50 BMG, MZZ and API M8 ammunition.
Semi-automatic basic model "Barrett" М82А1
(Fig. 1) is designed as a small weapon with an air-cooled barrel and a short recoil for automatic operation. It has a classic layout and consists of the following main parts: barrel; a receiver made integral with the butt and pistol grip; bolt frame with bolt.
The rifle barrel, made of high-quality steel, is threaded for installing a muzzle brake or silencer. The muzzle brake (double-chamber active-reactive type) is specially designed for this weapon and reduces recoil energy by 60-65 percent. On the upper part of the receiver, which has holes for better cooling, there is a mount for an optical sight and a folding handle for carrying; folding bipods can be installed on the lower part. A shock-absorbing pad is attached to the butt plate, also designed to reduce recoil force.
The weapon is equipped with a standard Swarovski 10×42 optical sight with a rangefinder reticle, allowing firing at a range from 500 to 1
830 m. For shooting in low light conditions (at night), the AN/PVS-4 night sight can be installed on the rifle. The kit also includes a spare box magazine, removable bipod and spare parts.
| Rice. 1. American 12.7 mm sniper rifle “Barrett” M82A1 | Rice. 2. American 12.7 mm Barrett M82A2 sniper rifle |
Rice. 3. American 12.7 mm Barrett M95 sniper rifle
The KSV “Barrett” M82A1 can be carried in the hands or behind the back in a transport case with adjustable straps. For delivery over long distances, it is placed in a sealed case. It has space for the main parts of the rifle and a special valve to equalize pressure during air transport at high altitudes.
Rifle "Barrett" М82А2
(Fig. 2) was created using the bullpup layout. It differs from the base model in its smaller weight and size characteristics and the absence of automatic parts (the weapon is reloaded manually).
In the Barrett M95 model
(Fig. 3),
developed on the basis of the Barrett M90A1 rifle, but not widespread among the troops, the developers used a more effective muzzle brake and butt plate, which made it possible to reduce the recoil force of the system to the level of weapons using 7.62 mm caliber ammunition, and weight - up to 10 kg.
In addition, it is equipped with a larger capacity box magazine. The Barrett M95 rifle is considered by the command of the US Armed Forces as the most acceptable option when re-equipping special forces units with new types of large-caliber small arms. For these purposes, tests are being carried out on a modernized sample of this SSV, designated XM 107. It differs from previous models in a different barrel attachment point, a more resistant anti-corrosion coating and the displacement of the trigger parts forward. In addition, to ensure a more comfortable position for the shooter when firing and to facilitate reloading the weapon, the position of the pistol grip has been optimized, having a more ergonomic shape, and the angle of the window for connecting the magazine has been changed.
The 12.7 mm
Windrunner
sniper rifle (Fig. 4), developed by FDI, provides high fire accuracy with relatively small weight and size characteristics. Its design uses a unique method of connecting the barrel to the chamber, allowing for quick assembly and disassembly of the weapon. The butt is adjustable in length. The optical sight mount is mounted in such a way as to minimize vibration when aiming. It is possible to adjust the force on the trigger in the range from 0.9 to 2.27 kg.
Semi-automatic SSV production, characterized by portability and low weight, is widely represented on the arms market. The smallest of the family of such rifles, the Harris Dezat Rhino, deserves special attention, whose weight is only 6.3 kg, and the effective firing range is almost the same as that of more massive models.
a semi-automatic 12.7-mm sniper rifle
SR
-50 (Fig. 5), the automatic operation of which is based on the principle of removal of powder gases. Ammunition is supplied from a box magazine with a capacity of ten rounds, located horizontally on the receiver on the left. This allows the shooter to take a lower shooting position than the traditional magazine position at the bottom. The trigger is equipped with a two-stage safety, similar to that found on the 5.56 mm AR-15/M16 series automatic rifles.
In the UK, a semi-automatic 12.7 mm sniper rifle
AW
50 (Fig. 6) was developed, equipped with a recoil device whose cylinders are made of aluminum. Other features of this weapon include an adjustable buttplate and cheekpiece, as well as the presence of a universal Picatinny mount on the receiver.
France is represented on the KSV market by the 12.7 mm Heketi-2 rifle
(Fig. 7), adopted by special forces units of the national armed forces. Its characteristic feature is the ability to adjust almost all structural elements taking into account the individual characteristics of the shooter.
The Croatian company RH-ALAN also produces semi-automatic SWRs chambered for the 12.7 mm NATO standard cartridge. The automatic operation of the MACS-M2A and -MZ rifles is based on the use of bolt recoil.
| | |
| Rice. 4. American 12.7 mm Windrunner sniper rifle | Rice. 5. American 12.7 mm sniper rifle SR-50 |
| Rice. 6. British 12.7 mm sniper rifle AW50 | Rice. 7. French 12.7 mm sniper rifle “Heketi-2” |
MACS
- M 3 model (Fig. ) is the use of a bullpup layout in the design, which made it possible to optimize its weight and size characteristics compared to the MACS-M2A.
) is the use of a bullpup layout in the design, which made it possible to optimize its weight and size characteristics compared to the MACS-M2A.
The rifles, which are fired using ammunition of the former Warsaw Pact standard, are represented by a family of large-caliber sniper rifles "Gepard"
(Fig. 9) produced by Hungarian and Landimex. Five models of these SSVs have been adopted, which have proven themselves to be practical and reliable weapon systems that provide high shooting accuracy.
Creation of systems for increased caliber ammunition.
The most typical representatives of this direction at present are the Croatian (RT20) and South African (NTW 20/14.5) large-caliber sniper rifles. Armor-piercing incendiary and high-explosive fragmentation ammunition of 20 mm caliber are used to fire from them.
Rice. 8. Croatian 12.7 mm sniper rifle MACS-M3
Rice. 9. Hungarian large-caliber sniper rifles “Cheetah”: A - model M1, M1A1; B - model M2, M2A1; B - MZ model; G - model M4 SA1
RT
20 rifle (Fig. 10) was developed during the Serbian-Croatian conflict specifically to disable the night branch of the command device of the T-84 tank, which was effectively used by the Serbs for reconnaissance at night and in conditions of limited visibility.
The design of the RT20 is based on the bull-pup layout, which made it possible to reduce the length of the weapon to 1.33 m and assumes a non-standard position for the shooter when firing - on the right. The bolt handle is located on the left. The recoil force is dampened by the action of an active-reactive muzzle brake and the partial removal of powder gases through special tubes to the rear. Currently, work is underway to reduce the weight of the rifle while maintaining the firing range and accuracy. A prototype that meets these requirements has been developed and tested - RT20 Ml.
The design of the South African SWR
NTW 20/14.5
(Fig. 11) uses a classic layout scheme. A design feature of this rifle was the presence of a hydropneumatic recoil brake, which, in combination with a two-chamber active-reactive muzzle brake and a spring damper, reduces the recoil force when firing to the level of conventional small arms.
The rifle is not automatic - reloading is done manually. The barrel bore is locked by a longitudinally sliding rotary bolt with six lugs. Ammunition is fed from a horizontally positioned box magazine with a capacity of three rounds. The magazine socket is located on the receiver on the left, and the window for extracting spent cartridges is on the right. In order to reduce weight and improve air cooling conditions, the rifle barrel has longitudinal grooves. The design of the breech ensures its precise installation and reliable fastening in the seats. A rotary locking coupling with two grooves for the bottom and flanges of cartridge cases of 14.5 and 20 mm calibers, respectively, is tightened by hand. This technical solution allows you to change barrels of various calibers without additional devices and tools in less than 1 minute, while the bolt, magazine and sight are also replaced.
The 8×42 optical sight has a mechanism for introducing corrections and is placed on the Strydom Elevation Drum mount, which ensures its quick installation without additional alignment.
To ensure ease of aiming and stability of the rifle when shooting, a bipod is attached to the lower front part of the receiver. Another stop can be the handle located at the bottom of the butt.
To carry the SWR NTW 20/14.5, two shoulder transport cases on a rigid frame are used. One of them holds the receiver assembly and bipod, and the other holds the barrel, sight, magazines and ammunition. The weight of each of them when equipped is about 15 kg.
American specialists are developing a 25-mm semi-automatic large-caliber sniper rifle, called the Barrett Payload Rifle.
(Fig. 12). It is designed to disable unarmored and lightly armored vehicles, airplanes and helicopters at airfields, control, communications and reconnaissance equipment, auxiliary equipment, as well as openly located manpower, artillery ammunition and fire weapons.
The rifle is unique in
in its class, since it is created for 25 x 59 mm ammunition intended for firing from the promising OCSW automatic mounted grenade launcher. It is assumed that in terms of its combat qualities, thanks to the ability to hit a target with high-explosive fragmentation and cumulative ammunition (warheads are equipped with a mini-fuse), it will significantly exceed other SSVs, including the 20-mm Croatian RT20 and the South African NTW 20/14.5.
A prototype rifle, developed on the basis of the KSV "Barrett" M82AZ,
made using elements of the bullpup layout scheme. Some moving parts of the weapon are located in the butt, which, in combination with a shorter barrel, made it possible to make it more compact (Fig. 13), without reducing its combat qualities. The automatic operation is based on the use of recoil force with a short barrel stroke.
| Rice. 10. Croatian 20 mm sniper rifle RT20 | Rice. 11. South African large-caliber rifle NTW 20/14.5 |
Rice. 12. Prototype of a large-caliber sniper rifle
"Barrett Payload Rifle" in combat position
A special feature of the rifle's design is the presence of two hydraulic recoil brakes and two return springs. A three-chamber active-reactive muzzle brake reduces the recoil force when firing to the level of a 12 klb combat rifle using Magnum ammunition.
| Rice. 13. General view of the prototype of the Barrett Payload Rifle SSV (A) and the Barrett M82AZ SSV (B) | Rice. 14. Czech 12.7 mm sniper rifle “Falcon 96” |
On the top of the receiver there is a universal Picatinny mount, designed for installing optical and optoelectronic sights, as well as a folding handle for carrying weapons. A folding bipod is attached to the lower part in front, providing ease of aiming and greater stability when shooting.
The Barrett Payload Rifle sniper rifle is considered by the US SOF command as one of the most optimal options for re-equipping Special Forces units with new types of large-caliber small arms.
Creation of systems for specially designed ammunition.
The only representative of this direction today is the Austrian 15.2 mm sniper rifle IWS 2000.
For effective destruction of armored targets (armor plate thickness up to 40 mm) at a distance of up to 1,000 m, an armor-piercing sub-caliber cartridge with a feathered bullet with a detachable pan was created. In this case, the initial speed of the bullet is about 1,450 m/s (for more details, see the color insert).
Unification and combination of systems, in
In recent years, several types of SSV have been created, each of which allows the use of a basic model for firing ammunition of various types and calibers, completing it with the spare parts necessary for quick re-equipment, including barrels.
The South African KSV NTW 20/14.5, originally designed for Russian 14.5x114 mm ammunition, can be equipped with parts for retrofitting to fire NATO standard (12.7x99 mm) or Russian (12.7x 107 mm) cartridges. At the customer's request, the system can include 20 mm caliber barrels.
The latest model of the Hungarian Cheetah rifle M4
SA
1 (Fig. 9 D) has a caliber of 12.7 mm. It can fire both NATO-standard cartridges and Russian ammunition, which is fed from a five-round box magazine or from a ten-round spiral magazine. In the promising model of the Gepard M5 rifle, it is planned to increase the barrel length compared to the model mentioned above and, accordingly, the effective firing range to 2,000 m.
The Czech Republic produces the 12.7 mm Falcon sniper rifle
96"
(Fig. 14),
also designed to fire NATO standard cartridges and Russian ammunition of this caliber.
According to foreign military experts, the creation of large-caliber sniper rifles will be further developed. The most promising direction seems to them to be the unification and combination of samples. This will allow the manufacturer, when creating a base model, to provide for the possibility of its prompt re-equipment to customer requirements, and the consumer, who will receive a full set of barrels, spare parts and accessories for re-equipment, will have a universal large-caliber weapon designed using elements of a modular design.
Influence
Denel Land Systems was contracted to supply weapon systems for the Indian Armed Forces, including anti-materiel rifles and self-propelled howitzers. However, following accusations that it had paid kickbacks to secure a deal for anti-materiel rifles, Denel was black-listed by the government. Subsequently, the Ordnance Factory Tiruchirappalli (OFT), in association with the Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO), began developing an indigenous anti-material rifle called Vidhwansak, which borrowed heavily from the Denel NTW-20. The development of Vidhwansak was completed in November 2005. The embargo against Denel was lifted in 2022 after investigations found the suspicion to have been false.
Full Analysis
Due to her extremely niche kit, NTW-20 performs poorly almost all the time.
The first problem is her stats. The main trend in RF stats is that they have high Damage but low RoF, leading to lower DPS compared to ARs due to their shots often hitting harder than necessary yet not hitting fast enough to compensate. NTW-20 is the prime example of this — while she has the highest Damage stat ingame at 165, she also has one of the lowest RoF stats out of RFs, with only 30 RoF at max. Due to such polarizing stats, NTW-20 suffers even more from the problems inherent to her class. In addition, due to the nature of NTW-20's Skill, it's ideal to use Damage-buffing HGs with her instead of RoF-buffing ones, leaving her no way to boost her RoF. Against normal enemies, NTW will have low DPS basically always, further impacting her viability in most areas of the game.
Another problem with NTW-20 is her Skill — the most powerful charge shot in the game, shooting one shot that deals 8 times her Damage stat after a 15 second Initial Cooldown and a 2 second charge. The Skill itself seems solid on paper; with a few Damage-buffing HGs and another doll with charged shot, NTW-20 deals enough damage to easily KO many bosses with her Skill alone. Furthermore, while some bosses have triggers when their health is drained to a certain point NTW-20 can skip these triggers with her Skill and many of the annoying invincibility frames that come with them.This Skill's problem, then, actually lies within its Initial Cooldown of 15 seconds. Since the HG tanks NTW wants to be paired with simply don't have enough HP to tank against bosses for 17 seconds, waiting for her to activate her Skill can have devastating consequences for them. Additionally, despite this Skill being specialized for countering bosses, NTW-20 gets easily outclassed by many other Echelons, including the ubiquitous ARSMG composition. There also exists units that possess a charged shot with a much shorter cooldown, yet they are able to perform just as well as NTW-20. Finally, this Skill simply results in excessive overkill. No boss currently in the game can take the full brunt of NTW's charged shot — and if those exist, then her effectiveness drops dramatically — which raises the question of if she should be used at all when more general-purpose RFs are available.
Stats/Data[edit]
Stats
| Health | Ammo | Ration |
| 47(x1) → 93(x1) / 465(x5) | 15(x1) / 55(x5) | 30(x1) / 90(x5) |
| Damage | 56 | → | 165 |
| → | 29 |
| → | 75 |
| → | 30 |
Equipment
Tiles
Affects handguns Reduce skill cooldown by 18%
| Health | Ammo | Ration |
| 47(x1) → 94(x1) / 470(x5) | 15(x1) / 55(x5) | 30(x1) / 90(x5) |
| Damage | 56 | → | 168 |
| → | 30 |
| → | 80 |
| → | 32 |
Equipment
Tiles
Affects handguns Reduce skill cooldown by 20%
| Health | Ammo | Ration |
| 47(x1) → 95(x1) / 475(x5) | 15(x1) / 55(x5) | 30(x1) / 90(x5) |
| Damage | 56 | → | 169 |
| → | 30 |
| → | 81 |
| → | 32 |
Equipment
Tiles
Affects handguns Reduce skill cooldown by 20%
| Health | Ammo | Ration |
| 47(x1) → 95(x1) / 475(x5) | 15(x1) / 55(x5) | 30(x1) / 90(x5) |
| Damage | 56 | → | 170 |
| → | 31 |
| → | 82 |
| → | 32 |
Equipment
Tiles
Affects handguns Reduce skill cooldown by 20%
Development
The weapon was designed by Tony Neophytou (co-designer of the Neostead combat shotgun). Development of the system began in August 1995 under the “Aerotek” name and a working prototype was ready for testing four and a half months later. This rapid progress was made possible by Neophytou's expertise in the field of recoil reduction systems, having worked on helicopter turrets in the past. To further reduce the amount of research and development, the project recycled the barrel, bolt and barrel extension of the existing Vektor GA1 automatic cannon. It was put into production by Denel Land Systems in two versions; 20 x 110 and 20 x 82. The latter model is also available in 14.5 x 114 and conversion between the calibers can be done in the field by swapping the barrel and bolt assembly. The significantly larger 20 x 110 model cannot be converted to another caliber. The rifle was accepted into service with the South African National Defense Force in 1998.[ citation needed
].
Design description[edit]
The reloading system is manual, with a sliding bolt. A 3-round magazine is attached on the left side.
The kit includes two replacement barrels. The first is designed for firing 20 × 83.5 mm cartridges with the following types of projectiles: OFZ ( HEI
), OFZ-T (
HEI-T
), BR (
SAPHEI
) and Educational (
Practice
).
Projectile mass 0.112 kg, muzzle energy 29.03 kJ. The second barrel of the set is designed to fire 14.5 × 114 mm cartridges with armor-piercing incendiary and armor-piercing incendiary tracer bullets. 20 × 83.5 mm cartridges are produced by PMP/Denel
.
As an alternative, the latest modification of the weapon uses a barrel chambered for a more powerful 20 × 110 mm caliber cartridge ( Hispano-Suiza
), which, however, is not intended to be replaced with another caliber. In this case, the muzzle energy is 37 kJ.
To reduce recoil, a recoil mechanism has been developed, including a shock absorber located inside the butt, which dampens the recoil of the barrel, and a hydraulic damper. In addition, to reduce recoil there is a muzzle brake and a rubber shock absorber on the back of the butt.
The rifle has a two-legged bipod; shooting is carried out only from it.
Sights - 8x optical sight.
For transportation, the rifle is disassembled and packed into two bales weighing 12-15 kg.
Features
Switching between the two calibers of the NTW (20×82mm and 14.5×114mm) requires changing the bolt, barrel, sighting gear and magazine. (A third variant, the NTW 20×110mm has been developed, but is not designed for barrel caliber switching.) Caliber switching the NTW 20/14.5 can be accomplished in the field without specialized tools. The magazine protrudes from the left side of the receiver. The NTW can be disassembled and packed into two backpacks for carriage. A muzzle brake is fitted on the end of the barrel which absorbs an estimated 50%–60% of recoil. This is further supplemented by a buffered slide in the receiver.
uCrazy.ru
- __Fashist__
- October 30, 2007 11:53
- 5322
20 mm caliber variant Caliber
20
×83.5 mm MG151
mechanism
, bolt-action
Barrel length
1000 mm 1
Weight
26 kg
Length
1795 mm
Feeding
detachable box magazine for 3 rounds
Maximum effective range
1500 meters
14.5 mm caliber variant Caliber
14.5
×114 mm
mechanism
, bolt-action Barrel
length
1220 mm
Weight
29 kg
Length
2015 mm
Feeding
detachable box magazine for 3 rounds
Maximum effective range
2300 meters
The NTW-20 anti-material rifle was developed by designer Tony Neophytou in the first half of the 1990s at Aerotek in South Africa. Later, all rights to this development were purchased by Mechem, a division of the large South African military-industrial concern DENEL. Since 1998, the NTW-20 rifle has been adopted by the South African self-defense forces, and it is also offered for export. The main purpose of this rifle is to combat enemy technical and material means at medium and long (for small arms) ranges. To do this, the rifle uses very powerful ammunition - 20mm high-explosive and incendiary shells, developed for German air guns during the 2nd World War, and 14.5mm armor-piercing and armor-piercing incendiary cartridges, developed at the same time in the USSR for anti-tank rifles. This ammunition is currently used and manufactured in South Africa. The main targets for the NTW-20 rifle can be cars, parked airplanes and helicopters, communications equipment, and fuel storage facilities, against which 20mm shells are especially effective. 14.5mm cartridges are used for shooting at more protected targets, such as armored personnel carriers or fortified structures, or when shooting at longer ranges (about 2 kilometers).
The NTW-20 rifle is built on the basis of a traditional design with manual reloading using a longitudinally sliding rotary bolt. The barrel is locked with a bolt using 6 lugs. The NTW-20 barrels are quick-change, which allows you to change the caliber of the rifle in the field by installing a new barrel complete with a bolt and magazine for a different caliber. Feeding comes from 3-round box magazines adjacent horizontally to the left. The main difference between this rifle and others is the presence in the design of a powerful recoil mechanism, which includes a hydraulic damper and a pneumatic knurler (similar to artillery systems). When fired, the tightly locked barrel rolls back inside the weapon body, thereby softening the powerful recoil. Additionally, recoil is reduced by a developed muzzle brake and a shock-absorbing pad on the butt plate. The rifle is intended only for shooting from a rest, for which it has a folding bipod. Sights - 8X optical sight on a quick-release mount, which does not require re-shooting the weapon after removing and installing the sight. A special frame is installed in the area of the center of mass of the rifle, which serves both to carry the rifle over short distances and to protect the sight.
Large-caliber sniper rifle V-94.
The V-94 rifle is a Russian-made self-loading sniper rifle chambered for 12.7x108 mm. Developed in the early 1990s, it had the design code “Volga”. The design of the rifle was carried out by the team of the Instrument Design Bureau (Tula).
The rifle is designed to destroy enemy personnel (also wearing body armor), unarmored and lightly armored vehicles at ranges of up to 1500 meters. The large-caliber 12.7x108 mm cartridge has been used in the Soviet army since 1938; it was created specifically for the DShK machine gun. This cartridge is quite common not only in Russia, but also in the world. The cartridge is used to this day in heavy machine guns DShKM, KORD and NSV “Utes”. To fire from the B-94, you can use armor-piercing tracer, armor-piercing, and incendiary cartridges. The use of armor-piercing cartridges ensures the armor penetration of a 20-mm steel plate at a range of 700-800 meters, which allows penetration of almost all modern lightly armored vehicles. The ability to fire at 1500 (not 2000 meters in other sources) meters ensures the safety of the shooter, since he becomes out of reach of the enemy’s conventional small arms at such a distance. At the same time, the lier will not feel safe, even behind a brick wall or a concrete wall
It is worth noting that the B-94 rifle was the first rifle designed for a large-caliber cartridge 50 years later; the first large-caliber rifles were the PTRD and PTRS anti-tank rifles chambered for 14.5x114 mm cartridges. It is strange why the Soviet army abandoned the use of PTRD and PRTS in the post-war period, since the armies of the world did not abandon lightly armored equipment and were not going to abandon it
NTV-20 (NTW-20)
Large-caliber sniper rifle NTV-20 (NTW-20)
NTV-20 (NTW-20) is a large-caliber sniper rifle, produced in 1993 and is a rifle for destroying enemy material resources.
| Ammo | 20x82 mm | 20x110 mm |
Tactical and technical characteristics of the large-caliber sniper rifle NTV-20 (NTW-20)
Length 1,795 mm Weight without cartridges - 30 kg (20x82 mm) - 32 kg (20x110 mm) Barrel 1,000 mm, 8 grooves (right-handed) magazine , box-type, capacity - 3 cartridges (20x82 mm) - single shot (20x110 mm) Initial bullet speed - 720 m/s (20x82 mm) - 820 m/s (20x110 mm) Effective firing range - 1,500 m (20x82 mm) - 1,800 m (20x110 mm)
Large-caliber sniper rifle NTV-20 (NTW-20), left side
The large-caliber sniper rifle NTV-20 (NTW-20) shoots perhaps one of the most powerful ammunition - 20 mm cartridges, which are currently used in small arms. Heavier cartridges can be found, but they were used in heavier, bulkier weapons. The recoil force of the NTV-20 rifle (NTW-20) is not very high and allows even a soldier of average build to handle it.
The large-caliber sniper rifle NTV-20 (NTW-20) was developed by designer Tony Neophytou in the first half of the 1990s under the name “Aerotek”, and in 1998 it was adopted by the South African National Defense Forces. The NTV-20 sniper rifle (NTW-20) was launched into mass production.
In addition to its size, the model of the large-caliber sniper rifle NTV-20 (NTW-20) has a completely traditional design of a repeating rifle with a long, heavy barrel, an effective muzzle brake and a magazine located on the left side. The barrel bore is locked using a bolt with 6 lugs.
The coupled barrel and bolt move inside the receiver of the NTV-20 rifle (NTW-20). When moving backward during recoil, the bolt mechanism encounters resistance from a hydropneumatic buffer, which resembles the recoil suppression system of artillery guns. The combination of a buffer and a muzzle brake reduces the recoil force of the NTV-20 rifle (NTW-20) to an acceptable level.
The butt of the large-caliber sniper rifle NTV-20 (NTW-20) has such a shape that it can be easily grasped with one hand. The rest of the rifle is supported by the bipod. The NTV-20 rifle (NTW-20) can be disassembled into two parts for easy transportation.