GAZ-63 is a two-axle truck, mass production of which began back in 1948. The model was a variation of the popular national and utility truck GAZ-51. In addition, the GAZ-63 became a full-fledged replacement for the three-axle GAZ-AAA car of pre-war times.
This model was the first in the USSR to have all-wheel drive. Its mass production took place on a fairly large scale.
First of all, the truck was aimed at army needs. Here the technology became one of the best because it was resistant to harsh operating conditions. In addition, the GAZ-63 was used as a standard platform for the BTR-40.
North Korea and China were also involved in the production of this truck. In Korea, the model was called Sungri-61, and in China, as Yuejin NJ230 or NJ230A
Although the GAZ-63 proved to be excellent in the army, it was not entirely suitable for civilian purposes. The engine power was often not enough to complete the assigned tasks. Carrying capacity also introduced its limitations. For example, if a truck was loaded as much as possible, then it lost its high cross-country ability, and this was considered its main advantage.
Story
Designers began designing a new car in 1938. The actively used semi-trucks were already very outdated, both technically and morally. This prompted the Gorky plant to create new machines.
As a result, at the very beginning of the spring of 1938, the design staff of the Gorky Automobile Plant began the development of a new family of trucks with increased cross-country ability and intended for operation in difficult road conditions.
Several debut experimental copies of the GAZ-63 were created between 1939 and 1940 before the Great Patriotic War began. But due to the events that unfolded at that time, production of the models was postponed until 1948. The GAZ-63 was the most popular all-wheel drive truck in service with the Soviet Army, as well as a simple worker in the national economies of the entire Soviet Union from the 1950s to the 1960s.
The first experimental model was built in 1939. He was immediately sent to undergo various tests.
It is worth noting that the main emphasis when developing the new truck was on its all-terrain qualities. Therefore, its appearance is not much different from the trucks produced at that time.
The designers decided to install on the experimental GAZ-63 a cabin from a lorry that was popular at that time. But in all other respects, this truck turned out to be truly original. First of all, this concerns its chassis, which was designed especially for this model almost from scratch. As a result, the GAZ-63 received a 4x4 wheel arrangement and single-pitch tires for the rear wheels.
But the development didn't end there. Simultaneously with work on the off-road GAZ-63, the Gorky Automobile Plant began to design a similar version, but intended to fulfill civilian needs. This model was assigned the factory index GAZ-11-55. The model had high unification with the military 63rd Lawn.
The unification of the two models made it possible to reduce the cost of truck production, simplify operation, and also carry out mass production of these trucks on a common conveyor, which again reduces production costs. It is worth noting that the GAZ-51 and GAZ-63 were equipped with completely new design developments and technical solutions, which were also revolutionary in the mechanical engineering of that time.
All tests in which the GAZ-63 participated were carried out quite successfully. However, the mass production of trucks, planned for the early 1940s, was postponed by the management of the Gorky Automobile Plant. This was due to the beginning of the Great Patriotic War. They returned to the project again in 1943, but then the work was not on production, but on further development.
At that time, the design staff of the Gorky Automobile Plant managed to get acquainted with all-wheel drive trucks produced by American manufacturers. These were models such as Studabeker and Chevrolet. Their appearance is due to the fact that during the war, trucks were produced under Lend-Lease at the facilities of the Gorky Automobile Plant.
Seeing this situation, Gorky engineers did not miss their chance to study foreign technology and borrow some design developments from American manufacturers. But this does not mean that domestic models have repeated their foreign counterparts. The main components were completely designed or improved on the basis of existing components by Gorky engineers.
A new experimental batch of all-wheel drive vehicles, which received a number of improvements, was introduced in 1945. At the same time, various tests were again carried out on the trucks, where the results only got better. In 1948, the Gorky Automobile Plant began serial production of the GAZ-63 off-road trucks.
GAZ-63 photo
Read further:
"Ural" - the history of the automobile plant
History of the Tatra company
KrAZ - the history of the Kremenchug Automobile Plant
New pickup truck - its performance at the auto show
The nuclear war bus or the quirks of Soviet designers
Purpose
The GAZ-63 truck, thanks to its excellent technical and operational characteristics, as well as fairly high cross-country ability, gained great popularity in the Soviet Army. Here the car was mainly used to transport army personnel and any cargo. In addition, the truck towed military guns, and various combat installations could be installed on its platform, which made a special vehicle out of an ordinary truck.
This model was no less popular in the national economy, but here this was largely due to the conditions of the post-war period. At the end of the war, there were very few trucks for public needs, which is why they used what they had, and in this case it was the GAZ-63. The machine was used very actively and working with overload was not uncommon for it.
If the design did not raise even the slightest doubt about its reliability, the truck’s carrying capacity introduced its own limitations. Although the truck could carry fairly heavy loads, it sacrificed its high cross-country ability, which is why the GAZ-63 was developed.
In addition to the deterioration of all-terrain properties, a lot of parts were subject to severe wear during such operation. And carrying out timely maintenance of the truck in rural conditions was very difficult.
Modifications
In addition to the basic model, the Gorky Automobile Plant also produced various modified versions, including:
- Modification of GAZ-63A. Has an elongated frame design. The front version was equipped with a winch with a calculated traction force of 4500 kilograms. The winch operated using a power take-off driven by a driveshaft connected to the truck's transmission. The winch also had a cable 65 meters long;
- Modification of GAZ-63E. Has shielded electrical equipment. Otherwise, it is similar to the basic version of the truck;
- Modification of GAZ-63AE. Has shielded electrical equipment and a winch in the front of the frame. Otherwise, it is similar to the basic version of the truck;
- Modification of GAZ-63U. It is an export version of a standard truck;
- Modification of GAZ-63AU. It is an export version of the GAZ-63A modification;
- Modification of GAZ-63EU. Has shielded electrical equipment and is also an export option;
- Modification of GAZ-63Yu. This modification is intended for use in tropical conditions;
- Modification of GAZ-63EYU. The version has shielded electrical equipment and is also designed for use in tropical conditions;
- Modification of GAZ-63P. It is an all-wheel drive truck tractor. Unlike the base truck, it has smaller wheels. In addition, it can have both single-pitch and double-pitch tires on the rear axle. The modification was produced in limited quantities from 1958 to 1968:
- Modification of GAZ-33. It is an all-wheel drive three-axle truck with a 6x6 wheel arrangement. The maximum load capacity of this version is 3000 kilograms. The GAZ-63 platform was taken as the basis for the GAZ-33. The release of the first experimental models of the 33rd GAZ took place back in 1946. But mass production of such a modification was never realized. The main reason for this was the insufficient power of the power plant, which was borrowed from the GAZ-51.
Simultaneously with the basic modifications, various specialized vehicles were also produced based on the GAZ-63, namely:
- Modification of GAZ-63 ATSU-20. It is a fire truck tank;
- Modification of GAZ-63 PMG-19. It is a fire truck tank;
- Modification of GAZ-63 AR-1.6. Is a hose fire truck;
- Modification of GAZ-63 ASOP-5. Is a fire communication and lighting vehicle;
- Modification AS-3. It is a vehicle for sanitary purposes. Can carry seven stretchers and two seated wounded or sick;
- Modification of BTR-40. This modification is also known as the GAZ-40 and is an armored personnel carrier designed for eight soldiers and two crew members. The GAZ-63 platform was taken as the basis for this model. The power unit used was subjected to modifications, as a result of which its maximum power was increased to 80 horsepower. The development of the model began in 1947, and mass production from 1950 to 1960.
Military equipment based on the vehicle
In October 1943, the Gorky Automobile Plant began to develop a wheeled self-propelled gun with a 76 mm caliber gun. By May 1944, the first copy was released. On both sides of the gun there were seats for the driver and commander-gunner. The ammunition load consisted of fifty-eight shells. This car fought at the end of the Great Patriotic War.
In parallel with the development of a truck model, a light two-axle armored personnel carrier with a monocoque body, called the BTR-40, was developed on its basis in 1947. The armored personnel carrier was designed for eight paratroopers. The wheelbase was reduced by 600 mm, engine power was increased to 81 hp. s., increasing the upper limit of rotation speed and sacrificing durability, which was not of particular importance for military equipment.
The armored personnel carrier was armed with a heavy machine gun of the Goryunov system, the ammunition load of which included 1260 rounds of ammunition. The machine gun could be mounted on the sides on one of four brackets. The same brackets could be used to install the DPM light machine gun, which the paratroopers were armed with. The BTR-40A modification was equipped with twin KVPT heavy machine guns. In 1993, the armored personnel carrier was removed from service.
Since 1950, the BM-14 Katyusha rocket artillery combat vehicle has also been produced on the GAZ-63 chassis.
Specifications
Engine
For the entire period of mass production, GAZ-63 was equipped with only one engine. It was a six-cylinder carburetor power plant with a lower valve arrangement, also installed on such a model as the GAZ-51. With a working volume of 3.5 liters, its maximum output power was 70 horsepower, which was quite enough for that time.
The engine had a liquid cooling system and could accelerate the truck to a maximum speed of 65 kilometers per hour.
Characteristics:
- Working volume – 3.48 l;
- Maximum power – 70 hp. (at 2800 rpm);
- Cylinder diameter – 82 mm;
- Piston stroke – 110 mm;
- The compression ratio in the combustion chamber is 6.2:1;
- The highest torque is 20.5 kgf/m (at 1500-1700 rpm).
Design Features
The GAZ-63 all-terrain vehicle is built on a frame chassis. The layout provides short front and rear overhangs, which has a positive effect on the geometric cross-country ability of the GAZ-63. The design uses tires with the ability to operate at reduced pressure; it is worth noting that this significantly reduced the rubber service life. The wheels were inflated while the engine was running.
To ensure quick start-up, the GAZ-63 radiator had a flame pipe into which a blowtorch was inserted.
The lamp installation location was located in the right front wheel arch. When the lamp was operating, the liquid in the radiator was heated by the flame, and the hot air heated the oil in the engine sump of the all-terrain vehicle.
Brake system
The service brake system is represented by shoe mechanisms with a hydraulic drive. Drum brake mechanisms were also used as a parking brake, but had a mechanical drive in the form of a cable.
It is worth noting that drum mechanisms in the parking brake began to be installed on trucks only in 1955. Previously, the model was equipped with disc brakes.
Chassis
At the front, a dependent suspension is used, consisting of longitudinal semi-elliptical springs and double-acting hydraulic telescopic shock absorbers.
The rear suspension is also dependent and has the same longitudinal semi-elliptic springs, but there are no shock absorbers here.
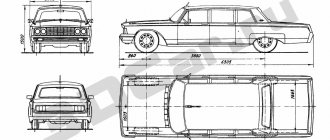
dimensions
- Total length – 5525 mm;
- Full width – 2200 mm;
- Cabin height – 2245 mm;
- Wheelbase length – 3300 mm;
- Front track width – 1590 mm;
- Rear track width -1600 mm;
- Ground clearance – 270 mm;
- The smallest turning radius is 9700 mm.
Peculiarities
The main advantage of the GAZ-63 truck is its truly very high cross-country ability. This is also noted by all those who have ever worked on it.
With a not particularly powerful power unit, this truck coped with quite complex tasks. He could drive almost anywhere and this, again, with low engine power. The design was very reliable and simple. It was on the basis of the GAZ-63 that the legendary domestic all-terrain vehicle GAZ-66 was developed, which almost completely inherited the chassis from its predecessor.
Among other features, the car is unpretentious, simple maintenance and repair, and, of course, phenomenal reliability. Although the GAZ-63 had an all-wheel drive layout, if necessary, the driver could disable the front-wheel drive, which had a positive effect on fuel consumption.
Flaws
The engine used was not perfect. According to drivers, it had a rather short service life, and with intensive use it often did not last its entire service life.
The truck itself was quite slow and clumsy. Despite the presence of all-wheel drive, the transmission was not equipped with differential locks. In the event of any breakdown, it was quite difficult to find spare parts, not to mention nowadays, where if you can find them, the cost for them is usually very high.
Another disadvantage is the poor stability of the machine. This is due to the high center of gravity. Because of this, the car could easily fall on its side while negotiating difficult road sections. Also, such situations often happened due to the inexperience of drivers.
The risk of rollover has only increased if a military KUNG is installed on the truck chassis. It is worth noting that such equipment had a mass of about 1500 kilograms and a very high height. All this had a negative impact on stability, which is why the car required the driver to drive slowly and very carefully when moving through terrain with difficult terrain.
It is worth noting that very sealed, warm and fully shielded KUNGs were offered for the GAZ-63. All this made it possible to significantly reduce interference when using radio stations and wired communication equipment. In addition, the car was equipped with shielded wiring, an ignition coil, a distributor, spark plug caps and high-voltage wires. The model was also equipped with special radio interference filters.
Export to foreign countries
Despite the fact that the GAZ-63 was created primarily for the Soviet Armed Forces, a considerable part of these vehicles were sent abroad. Foreign recipients of this machine were primarily European countries that were part of the “socialist commonwealth”: Yugoslavia, the German Democratic Republic, Czechoslovakia and Poland. In addition, supplies were made to developing countries friendly to the USSR. In particular, the GAZ-63 ended up in Mongolia, Vietnam, North Korea, Laos, as well as in many African states and Cuba.
A number of trucks were sold to Finland. The GAZ-63 also sometimes ended up in other “capital countries”, but these were no longer direct deliveries, but the result of a chain of resales or some kind of accident.
Price
The GAZ-63 truck was discontinued from mass production a long time ago. But even now you can find completely working copies.
Thus, a car in working condition can now be purchased at a minimum price of 80 thousand rubles. However, when buying this option, you should remember that for such a price, equipment in most cases requires painstaking restoration.
Another option, and a very popular one, is to purchase a truck that was taken out of military storage in the 1980s and 1990s. Most often, such machines are equipped with KUNGs and are in excellent technical condition. The cost of this option on average reaches 450 thousand rubles, depending on the equipment.
Body
The military GAZ-63 was equipped with a wooden universal body, which had high lattice side sides and a front wall. Inside there were folding longitudinal benches. The tailgate was also made to open. The side boards had special sockets into which arcs could be installed to tension the awning.
Based on the requirements of the military leadership, the designers increased the capacity of the fuel tanks. A 105-liter tank was added to the main ninety-liter tank, which made it possible to increase the fuel volume to 780 kilometers at full load.